Introduction to PCB Autorouting
PCB autorouting, also known as automatic routing or autorouter, is a feature found in many PCB design software packages that automatically routes the connections between components on a printed circuit board (PCB). This powerful tool can significantly reduce the time and effort required to design complex PCBs, allowing engineers and designers to focus on other critical aspects of the design process.
In this article, we will explore the top reasons why PCB design software auto routing can save you time and improve your overall design workflow.
What is PCB Autorouting?
PCB autorouting is an automated process that uses algorithms to determine the optimal paths for connecting components on a PCB. The autorouter takes into account various design constraints, such as component placement, signal integrity, and manufacturing guidelines, to create efficient and reliable Routing Solutions.
Autorouting algorithms can be classified into two main categories:
-
Grid-based autorouting: This method uses a predefined grid to route connections, with traces following the grid lines. Grid-based autorouting is faster but less flexible than other methods.
-
Topological autorouting: This more advanced method uses a mathematical model to represent the PCB and its connections, allowing for more complex routing patterns and better optimization of trace paths.
Benefits of PCB Autorouting
1. Faster Design Time
One of the most significant advantages of using PCB autorouting is the considerable reduction in design time. Manual routing can be a time-consuming and tedious process, especially for complex designs with a high number of components and connections. Autorouting algorithms can complete the routing process in a fraction of the time it would take a human designer, allowing you to iterate and refine your designs more quickly.
2. Improved Consistency and Reliability
Autorouting ensures a consistent and reliable approach to routing, minimizing the risk of human error. By adhering to predefined design rules and constraints, the autorouter creates routing solutions that are optimized for signal integrity and manufacturability. This consistency helps to reduce the likelihood of design errors and manufacturing issues, ultimately saving time and money in the long run.
3. Enhanced Design Optimization
PCB autorouting algorithms are designed to optimize the routing process, taking into account factors such as trace length, signal integrity, and manufacturability. By automatically finding the most efficient paths for connections, the autorouter can help to minimize signal reflections, crosstalk, and other issues that can impact the performance of the final product. This optimization can lead to improved product quality and reliability, reducing the need for time-consuming design revisions.
4. Easier Design Revisions
When changes need to be made to a PCB design, manually rerouting can be a daunting task. With PCB autorouting, design revisions become much more manageable. The autorouter can quickly adapt to changes in component placement or design constraints, regenerating the routing solution in a matter of minutes. This flexibility allows you to explore different design options and make necessary changes without investing significant time in manual rerouting.
5. Increased Productivity
By automating the routing process, PCB autorouting frees up valuable time for engineers and designers to focus on other critical aspects of the design, such as component selection, schematic capture, and design verification. This increased productivity can lead to faster time-to-market and a more efficient use of resources within your organization.

Best Practices for Using PCB Autorouting
While PCB autorouting can provide numerous benefits, it’s essential to follow best practices to ensure optimal results. Some key considerations include:
-
Proper setup of design constraints: Before running the autorouter, ensure that all design constraints, such as trace width, clearance, and via settings, are properly defined. This will help the autorouter create a routing solution that meets your specific requirements.
-
Review and refine the autorouted design: While the autorouter can generate an efficient routing solution, it’s essential to review the results and make any necessary manual adjustments. This may include optimizing critical signal paths, adding shielding, or adjusting trace widths for improved signal integrity.
-
Verify the design: Always perform a thorough design verification after autorouting, including running design rule checks (DRC) and ensuring that all connections are properly routed. This will help to catch any potential issues before moving on to the manufacturing stage.
-
Collaborate with your manufacturer: Work closely with your PCB manufacturer to ensure that the autorouted design meets their specific manufacturing guidelines and capabilities. This collaboration can help to minimize the risk of manufacturing issues and delays.
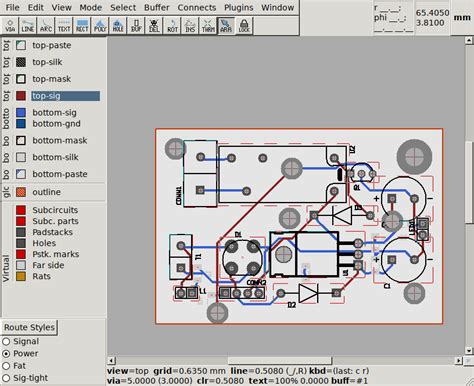
PCB Autorouting vs. Manual Routing
While PCB autorouting offers numerous advantages, there are still situations where manual routing may be preferred. The following table compares PCB autorouting and manual routing:
| Aspect | PCB Autorouting | Manual Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast, can route complex designs quickly | Slower, time-consuming for complex designs |
| Consistency | High, follows predefined rules and constraints | Depends on the skill and consistency of the designer |
| Flexibility | Limited by predefined rules and algorithms | High, allows for custom routing solutions |
| Optimization | Automatically optimizes for signal integrity and manufacturability | Requires manual optimization by the designer |
| Critical Signals | May require manual adjustments for critical signals | Allows for precise control over critical signal routing |
In practice, a combination of PCB autorouting and manual routing is often used to achieve the best results. Autorouting can be used to quickly generate an initial routing solution, which can then be refined and optimized manually as needed.
FAQ
-
Is PCB autorouting suitable for all designs?
While PCB autorouting can be used for a wide range of designs, it may not be the best choice for every situation. Designs with very high-speed signals, strict impedance control requirements, or complex routing constraints may benefit from manual routing or a combination of autorouting and manual routing. -
Can PCB autorouting completely replace manual routing?
In most cases, PCB autorouting is used in combination with manual routing. Autorouting can quickly generate an initial routing solution, which can then be refined and optimized manually as needed. Some critical signals or complex routing areas may require manual intervention to ensure optimal performance. -
How do I choose the right PCB design software with autorouting capabilities?
When selecting PCB design software with autorouting capabilities, consider factors such as the complexity of your designs, the autorouting algorithms supported (grid-based or topological), and the ease of use and learning curve of the software. It’s also essential to ensure that the software is compatible with your existing design workflow and can generate output files suitable for your PCB manufacturer. -
What are the limitations of PCB autorouting?
PCB autorouting is limited by the predefined rules and constraints set up in the design software. It may not always find the optimal solution for every design, particularly for complex or high-speed designs. Autorouting may also struggle with certain design features, such as differential pairs or high-density interconnect (HDI) structures. -
How can I ensure the best results when using PCB autorouting?
To achieve the best results with PCB autorouting, follow best practices such as properly setting up design constraints, reviewing and refining the autorouted design, verifying the design with design rule checks, and collaborating closely with your PCB manufacturer. It’s also essential to have a good understanding of the autorouting algorithms and settings available in your design software to make informed decisions during the routing process.
Conclusion
PCB autorouting is a powerful tool that can significantly reduce design time, improve consistency and reliability, and enhance design optimization. By automating the routing process, engineers and designers can focus on other critical aspects of the design, leading to increased productivity and faster time-to-market.
However, it’s essential to use PCB autorouting in combination with manual routing and to follow best practices to ensure optimal results. By properly setting up design constraints, reviewing and refining the autorouted design, and collaborating with your PCB manufacturer, you can harness the full potential of PCB autorouting and create high-quality, reliable PCB designs in a fraction of the time.

No responses yet