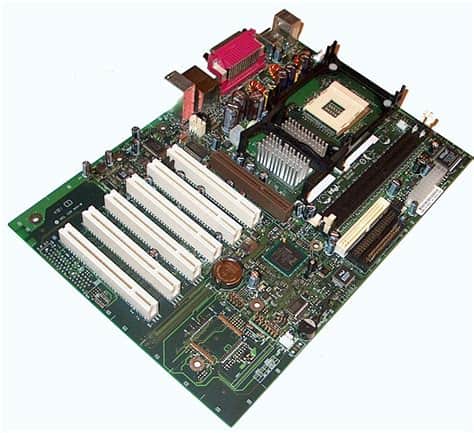
Motherboard Features
1. CPU Socket
The CPU socket is one of the most critical components of a motherboard. It determines the type of processor that can be installed on the board. Modern motherboards support a variety of CPU sockets, including:
- Intel LGA (Land Grid Array) sockets: LGA 1151, LGA 1200, LGA 2066
- AMD AM4 and TR4 sockets
It is essential to choose a motherboard with a socket that is compatible with your desired processor to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
2. Chipset
The chipset is a set of electronic components that manage the data flow between the processor, memory, and other peripherals. It plays a crucial role in determining the features and capabilities of a motherboard. Some popular chipsets include:
- Intel: Z490, B460, H410
- AMD: X570, B550, A520
The choice of chipset depends on the processor and the desired features, such as overclocking support, PCIe lanes, and USB ports.
3. Memory Slots
Modern motherboards come with multiple memory slots, allowing users to install RAM modules for improved multitasking and performance. The number of memory slots varies depending on the motherboard form factor and chipset. Most modern boards support DDR4 memory, with speeds ranging from 2133 MHz to 5000 MHz or higher.
| Form Factor | Number of Memory Slots |
|---|---|
| ATX | 4 |
| Micro-ATX | 2 – 4 |
| Mini-ITX | 2 |
4. Expansion Slots
Expansion slots allow users to add various components to their system, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network adapters. The most common types of expansion slots on modern motherboards include:
- PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots: PCIe 4.0 and PCIe 3.0
- M.2 slots for high-speed solid-state drives (SSDs)
The number and type of expansion slots vary based on the motherboard form factor and chipset.
5. Storage Connectors
Modern motherboards provide multiple storage connectors to accommodate various types of storage devices. These include:
- SATA (Serial ATA) ports for hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs)
- M.2 slots for high-speed NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs
- U.2 connectors for enterprise-grade SSDs
The number of storage connectors depends on the motherboard form factor and chipset.
6. USB Ports
USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports are essential for connecting various peripherals, such as keyboards, mice, external storage devices, and printers. Modern motherboards offer a mix of USB port types, including:
- USB 3.2 Gen 2 (10 Gbps)
- USB 3.2 Gen 1 (5 Gbps)
- USB 2.0 (480 Mbps)
Some high-end motherboards also feature USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 ports, which offer speeds up to 20 Gbps.
7. Network Connectivity
Modern motherboards come with built-in network connectivity options, enabling users to connect their systems to the internet or local networks. The most common network features include:
- Gigabit Ethernet (10/100/1000 Mbps)
- Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) or Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac)
- Bluetooth 5.0 or higher
Some motherboards also offer dual Ethernet ports or 2.5G/5G/10G Ethernet for faster network speeds.
8. Audio
Motherboards have integrated audio codecs that provide high-quality sound output. Some popular audio codecs include:
- Realtek ALC1200
- Realtek ALC1220
- Creative Sound Blaster
High-end motherboards may also feature dedicated audio capacitors, shielding, and amplifiers for improved sound quality.
9. BIOS and UEFI
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is the firmware that initializes hardware components and boots the operating system. Modern motherboards come with user-friendly BIOS/UEFI interfaces that allow users to configure various settings, such as:
- Boot order
- CPU and memory overclocking
- Fan control
- Power management
Many motherboards also support BIOS/UEFI updates to improve stability, compatibility, and security.
10. Form Factor
Motherboards come in various form factors to accommodate different case sizes and system requirements. The most common form factors include:
- ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended): The most popular form factor for desktop systems, measuring 305 x 244 mm.
- Micro-ATX: A smaller form factor, measuring 244 x 244 mm, suitable for compact systems.
- Mini-ITX: The smallest form factor, measuring 170 x 170 mm, ideal for small form factor (SFF) systems.
The choice of form factor depends on the case size, expansion requirements, and portability needs.
FAQ
-
Q: What should I consider when choosing a motherboard?
A: When choosing a motherboard, consider factors such as the CPU socket, chipset, memory support, expansion slots, storage connectors, network connectivity, and form factor. Ensure that the motherboard is compatible with your desired processor and offers the features and capabilities you need for your specific use case. -
Q: Can I mix different brands of RAM on a motherboard?
A: While mixing different brands of RAM is possible, it is recommended to use the same brand, model, and speed for optimal compatibility and performance. Mixing different RAM modules may lead to stability issues or reduced performance. -
Q: What is the difference between SATA and NVMe storage?
A: SATA (Serial ATA) is an older interface for connecting storage devices, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a newer and faster interface designed specifically for SSDs, offering lower latency and higher throughput compared to SATA. -
Q: Do I need to update my motherboard BIOS?
A: Updating your motherboard BIOS can improve stability, compatibility, and security. It may also be necessary when upgrading to a newer processor or fixing specific issues. However, updating the BIOS carries a small risk of rendering the motherboard non-functional if the process is interrupted or the wrong BIOS version is used. Always consult your motherboard manual and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully when updating the BIOS. -
Q: What is the difference between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 5?
A: Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) is the latest wireless networking standard, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and improved efficiency compared to Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac). Wi-Fi 6 is designed to handle more connected devices and provide better performance in congested environments. If you have a compatible router and wireless devices, Wi-Fi 6 can offer a superior wireless experience.

Conclusion
Modern motherboards include a wide range of features that cater to various computing needs, from basic home and office use to high-performance gaming and content creation. When choosing a motherboard, it is essential to consider factors such as the CPU socket, chipset, memory support, expansion slots, storage connectors, network connectivity, and form factor. By understanding the key features and capabilities of modern motherboards, you can make an informed decision and select the best board for your specific requirements and budget.
No responses yet