Why is a BOM List Important?
The BOM list is a critical document in the manufacturing process for several reasons:
-
Facilitates material procurement: The BOM list provides a clear and concise list of all materials needed for production, enabling the purchasing department to procure the necessary components in the right quantities and at the right time.
-
Ensures consistency: By adhering to a standardized BOM list, manufacturers can maintain consistency in their products, ensuring that each unit produced is identical in terms of components and quality.
-
Supports Inventory Management: The BOM list helps manufacturers manage their inventory by providing a clear understanding of the materials required for production, allowing them to maintain optimal stock levels and avoid shortages or overstock situations.
-
Enables cost control: By providing a detailed breakdown of all components and their quantities, the BOM list allows manufacturers to accurately calculate the cost of production and make informed decisions regarding pricing and profitability.
-
Facilitates communication: The BOM list serves as a common language between various departments, such as design, engineering, purchasing, and production, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding the product’s composition and requirements.
Types of BOM Lists
There are several types of BOM lists, each serving a specific purpose in the manufacturing process:
1. Engineering BOM (EBOM)
The Engineering BOM, also known as the Design BOM, is created by the product development team and contains all the components and sub-assemblies required to build a product from an engineering perspective. The EBOM focuses on the product’s functional requirements and design specifications.
2. Manufacturing BOM (MBOM)
The Manufacturing BOM, also known as the Production BOM, is derived from the EBOM and is tailored to the specific needs of the manufacturing process. The MBOM takes into account the actual components, materials, and processes required to manufacture the product, including any changes or optimizations made for production efficiency.
3. Sales BOM (SBOM)
The Sales BOM, also known as the Customer BOM, is a simplified version of the BOM list that is provided to customers or sales teams. The SBOM typically includes only the high-level components or sub-assemblies that are relevant to the customer, omitting detailed information about individual parts or proprietary manufacturing processes.
4. Service BOM (SBOM)
The Service BOM, also known as the Maintenance BOM, is a specialized BOM list that focuses on the components and parts required for the maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) of a product. The Service BOM includes spare parts, consumables, and other items needed to keep the product in good working condition throughout its lifecycle.
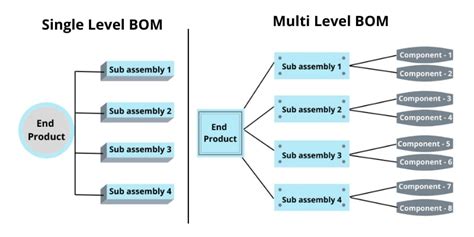
BOM List Structure and Components
A typical BOM list consists of several key components:
-
Level: The level indicates the hierarchical position of a component within the BOM list. Top-level items are assigned level 0, with subsequent levels (1, 2, 3, etc.) representing sub-components or sub-assemblies.
-
Part Number: Each component or sub-assembly in the BOM list is assigned a unique part number for identification and tracking purposes.
-
Part Name: The part name provides a clear and concise description of the component or sub-assembly.
-
Quantity: The quantity specifies the number of units of a particular component or sub-assembly required to produce one unit of the finished product.
-
Unit of Measure: The unit of measure indicates the standard unit in which the quantity is expressed, such as pieces, liters, or kilograms.
-
Reference Designators: Reference designators are alphanumeric codes that identify the specific location or placement of a component within the product or sub-assembly.
Here’s an example of a simple BOM list structure:
| Level | Part Number | Part Name | Quantity | Unit of Measure | Reference Designators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1000 | Bicycle | 1 | EA | |
| 1 | 1100 | Frame | 1 | EA | F1 |
| 1 | 1200 | Wheel Set | 1 | SET | W1, W2 |
| 2 | 1210 | Tire | 2 | EA | T1, T2 |
| 2 | 1220 | Rim | 2 | EA | R1, R2 |
| 2 | 1230 | Spoke | 72 | EA | S1-S72 |
| 1 | 1300 | Handlebar | 1 | EA | H1 |
| 1 | 1400 | Seat | 1 | EA | S1 |

Creating a BOM List
Creating a BOM list involves several steps:
-
Product Design: The product development team designs the product, specifying its features, functions, and components.
-
Component Identification: The team identifies all the components and sub-assemblies required to build the product, assigning each a unique part number and description.
-
Quantity Determination: The team determines the quantity of each component or sub-assembly needed to produce one unit of the finished product.
-
BOM List Structuring: The components and sub-assemblies are organized into a hierarchical structure, with top-level items at level 0 and subsequent levels representing sub-components or sub-assemblies.
-
BOM List Review: The BOM list is reviewed and approved by relevant stakeholders, such as engineering, manufacturing, and purchasing, to ensure accuracy and completeness.
-
BOM List Maintenance: As the product undergoes changes or improvements, the BOM list is updated to reflect any modifications in components, quantities, or structure.
BOM List Management Best Practices
To effectively manage BOM lists, manufacturers should follow these best practices:
-
Standardize Part Numbering: Implement a standardized part numbering system to ensure consistency and avoid confusion or duplication.
-
Use a Centralized Database: Maintain BOM lists in a centralized database or product lifecycle management (PLM) system to ensure data integrity and facilitate collaboration between departments.
-
Establish Change Management Processes: Implement formal change management processes to control and track any modifications to the BOM list, ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of and approve the changes.
-
Conduct Regular Audits: Regularly audit BOM lists to ensure accuracy, completeness, and compliance with design specifications and manufacturing requirements.
-
Integrate with Other Systems: Integrate BOM list management with other key systems, such as ERP, MRP, and SCM, to streamline data flow and ensure consistency across the organization.
Benefits of Using a BOM List
Implementing a well-structured and managed BOM list offers several benefits to manufacturers:
-
Improved Efficiency: By providing a clear and comprehensive list of all components and quantities required for production, BOM lists streamline the manufacturing process, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
-
Enhanced Quality Control: BOM lists ensure that all products are built using the correct components and quantities, maintaining consistency and quality across production runs.
-
Reduced Costs: Accurate BOM lists help manufacturers optimize inventory levels, reduce waste, and avoid production delays, ultimately leading to cost savings.
-
Better Collaboration: BOM lists serve as a common language between departments, fostering collaboration and ensuring that everyone is working towards the same goal.
-
Faster Time-to-Market: By streamlining the manufacturing process and reducing errors, BOM lists help manufacturers bring products to market faster, gaining a competitive edge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between a BOM list and a parts list?
A BOM list is a comprehensive document that includes all the components, sub-assemblies, and quantities required to manufacture a product, organized in a hierarchical structure. A parts list, on the other hand, is a simpler document that typically includes only the individual components or parts, without specifying the quantities or the relationships between them.
2. How often should a BOM list be updated?
A BOM list should be updated whenever there are changes to the product design, components, or manufacturing processes. It is essential to maintain an up-to-date BOM list to ensure that the manufacturing process remains accurate and efficient.
3. Can a BOM list be used for multiple products?
While a BOM list is typically specific to a single product or product variant, manufacturers can create modular or configurable BOM lists that can be used for multiple products with similar components or structures. This approach can help streamline the BOM list management process and reduce duplication of effort.
4. What is the role of BOM list in supply chain management?
The BOM list plays a critical role in supply chain management by providing a clear and comprehensive list of all the materials and components required for production. This information enables manufacturers to plan their procurement activities, manage inventory levels, and ensure that the right components are available at the right time, minimizing production delays and disruptions.
5. How can manufacturers ensure the accuracy of their BOM lists?
To ensure the accuracy of their BOM lists, manufacturers should implement a combination of best practices, including:
- Standardizing part numbering and descriptions
- Maintaining BOM lists in a centralized database or PLM system
- Implementing formal change management processes
- Conducting regular audits and reconciliations
- Integrating BOM list management with other key systems, such as ERP and MRP
By following these best practices, manufacturers can maintain accurate and up-to-date BOM lists, ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of their manufacturing processes.
No responses yet