Introduction to OSP PCB Finish
Organic Solderability Preservative (OSP) is a type of surface finish commonly used on printed circuit boards (PCBs). It is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to other finishes such as Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL), Immersion Silver, and Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG). OSP finish provides excellent solderability, protects the copper pads from oxidation, and enhances the shelf life of PCBs.
What is OSP?
OSP is a water-based organic compound that is applied to the exposed copper surfaces of a PCB after the etching process. The organic compound forms a thin, transparent layer on the copper, protecting it from oxidation and contamination. This layer is typically between 0.2 to 0.5 microns thick and does not affect the electrical or mechanical properties of the PCB.
How is OSP Applied?
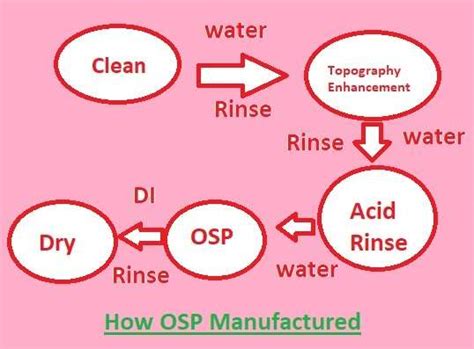
The OSP application process involves the following steps:
- Cleaning: The PCB is thoroughly cleaned to remove any dirt, grease, or residues from the copper surface.
- Microetching: The copper surface is slightly etched to improve the adhesion of the OSP coating.
- OSP Application: The PCB is immersed in the OSP solution, allowing the organic compound to form a protective layer on the copper surface.
- Drying: The PCB is then dried using hot air to remove any excess moisture and ensure a uniform coating.
Advantages of OSP PCB Finish
Cost-effectiveness
One of the primary advantages of OSP finish is its cost-effectiveness compared to other surface finishes. The application process is simple and does not require expensive equipment or materials, making it an attractive option for Low-Cost PCB manufacturing.
Environmental Friendliness
OSP is an environmentally friendly surface finish as it does not contain any hazardous substances such as lead or other heavy metals. The organic compounds used in OSP are biodegradable and do not pose a threat to the environment.
Good Solderability
OSP finish provides excellent solderability, ensuring strong and reliable solder joints. The organic layer protects the copper from oxidation, allowing for easy solder wetting during the assembly process.
Flat Surface
Unlike HASL, which can result in uneven surfaces due to the hot air leveling process, OSP finish provides a flat and uniform surface. This makes it suitable for fine-pitch components and high-density PCB designs.
Improved Shelf Life
OSP finish can extend the shelf life of PCBs by protecting the copper from oxidation and contamination. PCBs with OSP finish can be stored for up to 12 months without significant degradation in solderability.
Disadvantages of OSP PCB Finish
Limited Shelf Life
Although OSP finish can extend the shelf life of PCBs, it is still limited compared to other surface finishes such as ENIG or Immersion Silver. The organic layer can degrade over time, especially when exposed to high temperatures or humidity, leading to reduced solderability.
Susceptibility to Contamination
OSP finish is more susceptible to contamination compared to other surface finishes. Contaminants such as dirt, grease, or fingerprints can easily adhere to the organic layer, affecting the solderability and reliability of the PCB.
Incompatibility with Some Cleaning Processes
Some cleaning processes, such as plasma cleaning or ultrasonic cleaning, can damage the OSP layer, leading to reduced protection against oxidation and contamination.
Difficulty in Inspection
The transparent nature of the OSP layer makes it difficult to visually inspect the PCB for any defects or irregularities. This can lead to potential quality issues during the assembly process.

Comparison of OSP with Other PCB Finishes
| Finish | Cost | Shelf Life | Solderability | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSP | Low | Moderate | Good | Low |
| HASL | Low | Long | Good | High (lead-based) |
| ENIG | High | Long | Excellent | Moderate |
| Immersion Silver | Moderate | Long | Excellent | Low |
| Immersion Tin | Moderate | Moderate | Good | Low |
Applications of OSP PCB Finish
OSP finish is suitable for a wide range of PCB Applications, including:
- Consumer electronics
- Automotive electronics
- Industrial control systems
- Medical devices
- Telecommunications equipment
However, OSP may not be the best choice for applications that require long storage times or exposure to harsh environments. In such cases, other surface finishes like ENIG or Immersion Silver may be more appropriate.
Proper Handling and Storage of OSP PCBs
To maintain the solderability and reliability of OSP PCBs, proper handling and storage practices should be followed:
- Wear gloves when handling OSP PCBs to prevent contamination from skin oils and dirt.
- Store OSP PCBs in a cool, dry place with a relative humidity of 30-50% and a temperature between 20-30°C.
- Use moisture barrier bags with desiccants to protect OSP PCBs during storage and transportation.
- Avoid exposing OSP PCBs to direct sunlight or UV light, as this can degrade the organic layer.
- Assemble OSP PCBs within the recommended shelf life to ensure optimal solderability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is OSP finish suitable for lead-free soldering?
Yes, OSP finish is compatible with lead-free soldering processes. The organic layer provides good solderability and allows for the formation of reliable lead-free solder joints.
2. Can OSP PCBs be reworked?
Yes, OSP PCBs can be reworked, but the process requires careful handling to avoid damaging the organic layer. It is recommended to use low-temperature soldering techniques and avoid excessive heat exposure.
3. How does OSP finish compare to HASL in terms of cost?
OSP finish is generally more cost-effective than HASL, as it does not require the use of expensive equipment or materials. However, the total cost of ownership may depend on factors such as PCB complexity, production volume, and specific manufacturing processes.
4. Is OSP finish RoHS compliant?
Yes, OSP finish is RoHS compliant as it does not contain any restricted hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, or cadmium.
5. Can OSP PCBs be used in high-temperature applications?
OSP finish is not recommended for high-temperature applications, as the organic layer can degrade when exposed to temperatures above 150°C. In such cases, other surface finishes like ENIG or Immersion Silver may be more suitable.
Conclusion
OSP finish is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly surface finish option for PCBs. It provides good solderability, protects the copper from oxidation, and enhances the shelf life of PCBs. However, it also has some limitations, such as susceptibility to contamination and a limited shelf life compared to other finishes.
When choosing a surface finish for your PCB, consider factors such as the application requirements, storage conditions, assembly processes, and cost. OSP finish is suitable for many applications but may not be the best choice for every situation.
By understanding the pros and cons of OSP finish and following proper handling and storage practices, you can ensure the reliability and performance of your OSP PCBs.
No responses yet