Introduction to PCB Data Management
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) data management refers to the process of organizing, storing, and sharing all the data and files related to designing and manufacturing PCCs. Effective PCB data management is crucial for electronics companies to streamline their workflows, collaborate efficiently, and deliver high-quality products on time and within budget.
In today’s fast-paced and competitive electronics industry, PCB designs are becoming increasingly complex. A single PCB project can involve multiple design iterations, numerous files in various formats, and input from different teams such as design, engineering, manufacturing, and quality control. Without a robust data management system in place, it’s easy for important data to get lost, overwritten, or misinterpreted, leading to costly mistakes and delays.
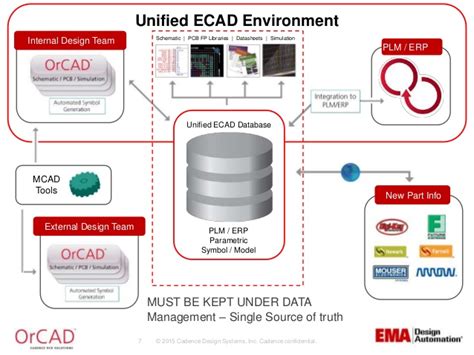
PCB data management aims to address these challenges by providing a centralized platform for managing all PCB-RElated data throughout the product lifecycle. This includes schematic diagrams, bill of materials (BOM), Gerber files, NC drill files, design rules, simulation results, and documentation. By keeping all this data organized and easily accessible, PCB data management enables teams to work more efficiently, reduces the risk of errors, and helps ensure that everyone is working with the most up-to-date information.
Key Benefits of PCB Data Management
Implementing a PCB data management system offers several key benefits for electronics companies:
-
Improved collaboration: A centralized data management platform makes it easy for different teams to access and share PCB data, regardless of their location. This enables better collaboration and communication between design, engineering, manufacturing, and other stakeholders.
-
Increased efficiency: With all PCB data organized and easily searchable, teams can quickly find the information they need without wasting time hunting through multiple sources. This streamlines workflows and reduces the time required to complete projects.
-
Reduced errors: PCB data management helps ensure that everyone is working with the most up-to-date and accurate data, reducing the risk of errors caused by using outdated or incorrect information. Version control features also make it easy to track changes and revert to previous versions if needed.
-
Better traceability: A PCB data management system provides a complete history of all changes made to PCB data, making it easy to trace issues back to their source and identify areas for improvement in the design and manufacturing process.
-
Faster time-to-market: By streamlining workflows and reducing errors, PCB data management helps electronics companies bring their products to market faster, giving them a competitive edge.
PCB Data Management Challenges
Despite the many benefits of PCB data management, implementing an effective system can be challenging. Some of the key challenges include:
Data Volume and Complexity
Modern PCB designs can generate vast amounts of data, including schematic diagrams, layout files, bill of materials, manufacturing files, and documentation. Managing this data effectively requires a system that can handle large file sizes and complex data structures.
Data Formats and Compatibility
PCB data comes in a wide variety of file formats, each with its own properties and limitations. Common formats include:
| File Format | Description |
|---|---|
| Gerber | Industry-standard format for PCB manufacturing data |
| ODB++ | Comprehensive PCB manufacturing data format |
| IPC-2581 | Generic data format for PCB design and manufacturing |
| STEP | 3D CAD data format for mechanical design |
| IDX | PCB design data format used by Mentor Graphics PADS |
Ensuring compatibility between these different formats and the tools used to create and edit them can be a significant challenge.
Version Control and Change Management
PCB designs often go through multiple iterations and revisions before they are finalized. Keeping track of these changes and ensuring that everyone is working with the most up-to-date version of the data is crucial for avoiding errors and delays. A PCB data management system must provide robust version control and change management features to address this challenge.
Data Security and Access Control
PCB data often includes sensitive information such as intellectual property, proprietary designs, and customer data. Protecting this data from unauthorized access or theft is essential for maintaining competitiveness and customer trust. A PCB data management system must provide secure data storage and granular access controls to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
Integration with Other Systems
PCB design and manufacturing workflows often involve multiple software tools and systems, such as EDA tools, PLM systems, and ERP systems. Integrating a PCB data management system with these other tools can be challenging, but it is essential for achieving end-to-end traceability and efficiency.

PCB Data Management Best Practices
To address these challenges and ensure the success of a PCB data management implementation, electronics companies should follow these best practices:
1. Standardize Data Formats and Naming Conventions
Establishing standard data formats and naming conventions helps ensure consistency and compatibility across different teams and tools. It also makes it easier to search for and locate specific data when needed. Some key considerations include:
- Use industry-standard file formats whenever possible (e.g., Gerber, ODB++, IPC-2581)
- Define clear and consistent naming conventions for files, folders, and other data elements
- Use metadata to provide additional context and make data more searchable
2. Implement Version Control and Change Management
A robust version control system is essential for managing changes to PCB data over time. Key features to look for include:
- Automatic versioning of files and data elements
- Ability to compare different versions and highlight changes
- Ability to revert to previous versions if needed
- Integration with change management workflows for approvals and notifications
3. Ensure Data Security and Access Control
Protecting sensitive PCB data requires a multi-layered approach to security, including:
- Secure data storage with encryption and backup
- Granular access controls based on user roles and permissions
- Audit trails to track data access and changes
- Regular security assessments and penetration testing
4. Integrate with Other Systems
To achieve end-to-end traceability and efficiency, a PCB data management system should integrate with other key systems and tools used in the design and manufacturing process, such as:
- EDA tools for schematic capture and layout
- PLM systems for product lifecycle management
- ERP systems for supply chain and production management
- Manufacturing execution systems (MES) for factory floor control
5. Provide Training and Support
Implementing a PCB data management system is not just a technical challenge, but also a cultural one. Providing adequate training and support is essential for ensuring user adoption and success. Key elements include:
- User training on system features and workflows
- Clear documentation and user guides
- Responsive technical support for troubleshooting and issue resolution
- Regular user feedback and system updates to address emerging needs

PCB Data Management Tools and Solutions
There are a variety of tools and solutions available for implementing PCB data management, ranging from simple file-sharing platforms to comprehensive product lifecycle management (PLM) systems. Some popular options include:
1. PLM Systems
PLM systems provide a holistic approach to managing product data throughout the entire lifecycle, from concept to retirement. They offer a wide range of features for PCB data management, including:
- Version control and change management
- BOM management and supply chain integration
- Design collaboration and review workflows
- Manufacturing process management
Examples of PLM systems with PCB data management capabilities include:
- Siemens Teamcenter
- PTC Windchill
- Dassault Systèmes Enovia
- Oracle Agile PLM
2. PCB Design Data Management (PDDM) Systems
PDDM systems are specialized solutions focused specifically on managing PCB design data. They offer features tailored to the unique needs of PCB design workflows, such as:
- Integration with popular EDA tools
- Schematic and layout file management
- Design rule checking and validation
- Manufacturing data generation and distribution
Examples of PDDM systems include:
- Altium Concord Pro
- Cadence PCB Design Data Management
- Mentor Graphics Xpedition Enterprise
3. Cloud-Based Collaboration Platforms
Cloud-based collaboration platforms provide a simple and accessible way to share and manage PCB data across distributed teams. They typically offer features such as:
- File sharing and versioning
- Commenting and markup tools
- Access controls and user management
- Integration with popular CAD and office tools
Examples of cloud-based collaboration platforms suitable for PCB data management include:
- Dropbox
- Google Drive
- Microsoft OneDrive
- Autodesk Fusion 360 Manage
4. Git-Based Version Control Systems
Git is a popular version control system used widely in software development, but it can also be adapted for managing PCB design data. Git-based solutions offer powerful version control and branching capabilities, as well as integration with various EDA tools. Examples include:
- Altium Designer with Git integration
- Cadence OrCAD with Git integration
- KiCad with Git integration
FAQ
What is the difference between PLM and PDDM systems for PCB data management?
PLM systems provide a comprehensive solution for managing product data throughout the entire lifecycle, including PCB data. They offer a wide range of features beyond just PCB design data management, such as BOM management, supply chain integration, and manufacturing process management.
PDDM systems, on the other hand, are specialized solutions focused specifically on managing PCB design data. They offer features tailored to the unique needs of PCB design workflows, such as integration with EDA tools, design rule checking, and manufacturing data generation.
Can I use a cloud-based collaboration platform like Dropbox for PCB data management?
Yes, cloud-based collaboration platforms like Dropbox can be used for basic PCB data management tasks such as file sharing and versioning. However, they may lack some of the more advanced features offered by specialized PLM or PDDM systems, such as EDA tool integration, design rule checking, and manufacturing data management.
How do I choose the right PCB data management solution for my company?
Choosing the right PCB data management solution depends on several factors, including your company size, design complexity, budget, and existing tools and workflows. Here are some key considerations:
- Identify your specific data management needs and pain points
- Evaluate different solutions based on their features, ease of use, and integration capabilities
- Consider the scalability and flexibility of the solution to accommodate future growth and changes
- Look for solutions with strong security and access control features to protect your sensitive data
- Consider the total cost of ownership, including licensing, implementation, and training costs
It’s also a good idea to involve key stakeholders from different departments in the evaluation and selection process to ensure that the chosen solution meets the needs of all users.
How much does a PCB data management system cost?
The cost of a PCB data management system can vary widely depending on the specific solution and deployment model. Some factors that can impact the cost include:
- Licensing model (perpetual vs. subscription)
- Number of users and data volume
- Deployment model (on-premise vs. cloud-based)
- Implementation and customization requirements
- Training and support needs
PLM and PDDM systems tend to be more expensive due to their comprehensive feature sets and customization options. Cloud-based collaboration platforms and Git-based solutions are often more affordable, especially for smaller teams.
It’s important to consider the total cost of ownership when evaluating different solutions, including not just the initial licensing costs but also ongoing maintenance, support, and training expenses.
How long does it take to implement a PCB data management system?
The implementation time for a PCB data management system can vary depending on the complexity of the solution and the size and needs of your organization. A simple cloud-based collaboration platform may only take a few days to set up, while a comprehensive PLM system may take several months to fully implement and customize.
Here are some factors that can impact the implementation timeline:
- Data migration and conversion requirements
- Integration with existing tools and workflows
- Customization and configuration needs
- User training and adoption
To ensure a successful implementation, it’s important to work closely with your chosen solution provider and have a clear plan in place for data migration, integration, and user training. It’s also a good idea to start with a pilot project or phased rollout to identify and address any issues early on before expanding to the full organization.
Conclusion
PCB data management is a critical component of modern electronics design and manufacturing workflows. By providing a centralized platform for organizing, sharing, and tracking PCB data throughout the product lifecycle, PCB data management systems help electronics companies streamline their processes, reduce errors and delays, and bring products to market faster.
However, implementing a PCB data management system can be challenging due to the complexity and volume of PCB data, the need for compatibility between different tools and formats, and the importance of data security and access control. To ensure success, electronics companies should follow best practices such as standardizing data formats and naming conventions, implementing version control and change management, integrating with other key systems, and providing adequate training and support for users.
There are a variety of tools and solutions available for PCB data management, ranging from comprehensive PLM systems to specialized PDDM solutions to cloud-based collaboration platforms and Git-based version control systems. The right solution for a given company will depend on factors such as company size, design complexity, budget, and existing tools and workflows.
By carefully evaluating their needs and options and following best practices for implementation and adoption, electronics companies can realize the many benefits of PCB data management and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving industry.
No responses yet