Introduction to BOM (Bill of Materials)
In the world of printed circuit board (PCB) design, the BOM, or Bill of Materials, is an essential document that lists all the components required to manufacture a PCB assembly. It serves as a comprehensive guide for the procurement, assembly, and testing processes, ensuring that the right components are used in the correct quantities and specifications. A well-organized and accurate BOM is crucial for the success of any PCB project, as it can help avoid delays, reduce costs, and improve overall product quality.
What is a BOM?
A BOM is a structured list of all the parts, components, and materials needed to produce a PCB assembly. It typically includes information such as:
- Part numbers
- Descriptions
- Quantities
- Manufacturers
- Reference designators
- Supplier information
The BOM is usually created by the PCB designer or engineer responsible for the project and is shared with the procurement team, manufacturers, and other stakeholders involved in the production process.
Why is a BOM important?
Having a comprehensive and accurate BOM is essential for several reasons:
-
Procurement: The BOM helps the procurement team source the correct components from reliable suppliers, ensuring that the parts meet the required specifications and are available when needed.
-
Assembly: Manufacturing teams rely on the BOM to guide them through the assembly process, ensuring that the right components are placed in the correct locations on the PCB.
-
Quality control: A well-maintained BOM helps to minimize the risk of using incorrect or outdated components, which can lead to product failures or reliability issues.
-
Cost management: By providing a clear list of required components, a BOM enables better cost estimation and helps identify opportunities for cost reduction through alternative sourcing or bulk purchasing.
-
Revision control: As a PCB design undergoes changes and updates, the BOM serves as a record of the components used in each revision, making it easier to track and manage product variations.
Types of BOMs
There are several types of BOMs used in PCB design, each serving a specific purpose and audience. The most common types include:
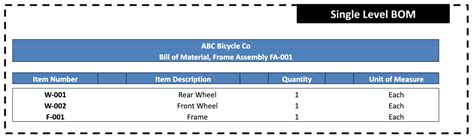
1. Engineering BOM (EBOM)
The Engineering BOM, also known as the Design BOM, is created by the PCB designer or engineer during the design phase. It contains a complete list of all the components required for the PCB assembly, along with their specifications, quantities, and reference designators. The EBOM is typically used for prototyping and initial production runs.
2. Manufacturing BOM (MBOM)
The Manufacturing BOM is derived from the EBOM and is tailored for use by the manufacturing team. It may include additional information such as component packaging details, assembly instructions, and any special handling requirements. The MBOM is often optimized for efficient procurement and assembly processes.
3. Production BOM (PBOM)
The Production BOM is a refined version of the MBOM, used for large-scale production runs. It incorporates any changes or optimizations made during the initial production phases and includes finalized component sourcing information, lead times, and cost data.
4. Configurable BOM (CBOM)
A Configurable BOM is used for products that have multiple variations or customization options. It consists of a master BOM that lists all the possible components and sub-assemblies, along with rules or guidelines for selecting the appropriate parts based on the desired configuration.
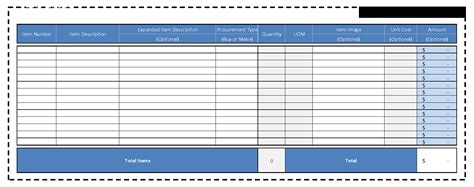
Creating a BOM
Creating an accurate and comprehensive BOM is a critical step in the PCB design process. Here are some best practices for creating a BOM:
1. Use a consistent format
Establish a standard format for your BOM, including the order of columns, units of measurement, and terminology used. This consistency helps to avoid confusion and ensures that all stakeholders can easily interpret the information.
2. Include all necessary information
A complete BOM should include the following information for each component:
- Part number
- Description
- Quantity
- Manufacturer
- Manufacturer part number
- Reference designator
- Footprint
- Value (if applicable)
- Tolerance (if applicable)
- Supplier information
- Notes or comments
3. Use automated tools
Many PCB design software packages include tools for generating BOMs automatically from the schematic and layout data. These tools can save time and reduce the risk of manual errors. However, it’s essential to review and validate the generated BOM to ensure accuracy.
4. Collaborate with stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders, such as procurement, manufacturing, and quality control teams, in the BOM creation process. Their input can help identify potential issues early on and ensure that the BOM meets their specific requirements.
5. Maintain version control
As the PCB design evolves, keep track of changes to the BOM by using version numbers or revision dates. This practice helps to avoid confusion and ensures that all stakeholders are working with the most up-to-date information.

BOM Management
Effective BOM management is essential for ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and accessibility of the BOM throughout the PCB design and production process. Some key aspects of BOM management include:
1. Centralized storage
Store your BOMs in a centralized location, such as a shared database or PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) system. This approach ensures that all stakeholders have access to the most current version of the BOM and helps to avoid version control issues.
2. Change management
Establish a clear process for managing changes to the BOM, including a system for requesting, reviewing, and approving modifications. This process should involve all relevant stakeholders and ensure that changes are communicated effectively.
3. Supplier management
Regularly review and update supplier information in the BOM, including lead times, minimum order quantities, and pricing. This practice helps to ensure that the procurement team has accurate data for sourcing components and managing costs.
4. Integration with other systems
Consider integrating your BOM management system with other tools used in the PCB design and production process, such as EDA (Electronic Design Automation) software, MRP (Material Requirements Planning) systems, and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) platforms. This integration can help streamline data flow and reduce the risk of errors.
Common BOM Challenges and Solutions
Creating and maintaining an accurate BOM can be challenging, particularly for complex PCB designs. Some common issues and their solutions include:
1. Incomplete or inaccurate data
Problem: BOMs with missing or incorrect information can lead to procurement delays, assembly errors, and product failures.
Solution: Implement a rigorous review and validation process for BOMs, involving multiple stakeholders. Use automated tools to help identify and correct errors, and establish clear guidelines for data entry and formatting.
2. Obsolete or end-of-life components
Problem: Components that are no longer available or are nearing end-of-life can cause supply chain disruptions and require costly redesigns.
Solution: Regularly review component availability and lifecycle status, and proactively identify potential obsolescence risks. Work with suppliers to find suitable alternatives, and consider designing for flexibility to accommodate future component changes.
3. Inconsistent or duplicate part numbers
Problem: Inconsistencies in part numbering or the presence of duplicate part numbers can lead to confusion and procurement errors.
Solution: Establish a standardized part numbering system and maintain a master parts list or database. Use automated tools to identify and resolve inconsistencies or duplicates, and regularly audit the BOM for accuracy.
4. Lack of collaboration
Problem: Siloed BOM management can result in communication breakdowns and inconsistencies between different teams or departments.
Solution: Foster a culture of collaboration and communication, and establish clear roles and responsibilities for BOM management. Use centralized storage and version control to ensure that all stakeholders have access to the most current and accurate BOM data.
Best Practices for BOM Management
To ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of your BOM management process, consider the following best practices:
-
Standardize your BOM format: Establish a consistent format for your BOMs, including the order of columns, units of measurement, and terminology used. This standardization helps to avoid confusion and ensures that all stakeholders can easily interpret the information.
-
Use automated tools: Leverage automated BOM generation and management tools to save time, reduce the risk of manual errors, and ensure consistency across projects.
-
Collaborate with stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders, such as procurement, manufacturing, and quality control teams, in the BOM management process. Their input can help identify potential issues early on and ensure that the BOM meets their specific requirements.
-
Maintain version control: Keep track of changes to the BOM by using version numbers or revision dates, and establish a clear process for managing and communicating updates.
-
Regularly audit and update the BOM: Conduct periodic audits of your BOMs to ensure accuracy, identify obsolescence risks, and resolve any inconsistencies or discrepancies. Update the BOM as needed to reflect changes in component availability, pricing, or specifications.
-
Integrate with other systems: Consider integrating your BOM management system with other tools used in the PCB design and production process, such as EDA software, MRP systems, and ERP platforms. This integration can help streamline data flow and reduce the risk of errors.
-
Train your team: Provide training and resources to help your team understand the importance of accurate BOM management and how to use the tools and processes effectively.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your BOMs are accurate, up-to-date, and easily accessible to all stakeholders, ultimately contributing to the success of your PCB projects.
FAQs
-
What is the difference between an EBOM and an MBOM?
An Engineering BOM (EBOM) is created by the PCB designer or engineer during the design phase and contains a complete list of all the components required for the PCB assembly. A Manufacturing BOM (MBOM) is derived from the EBOM and is tailored for use by the manufacturing team, including additional information such as component packaging details and assembly instructions. -
How often should I update my BOM?
BOMs should be updated whenever there are changes to the PCB design, component availability, or sourcing information. It’s also a good practice to regularly audit your BOMs to ensure accuracy and identify any potential issues or risks. -
Can I use the same BOM for multiple PCB projects?
While some components may be common across different PCB projects, it’s generally recommended to create a unique BOM for each project to ensure accuracy and avoid confusion. However, you can use a master parts list or database to standardize component information and streamline the BOM creation process. -
How can I ensure that my team is using the most up-to-date BOM?
Establish a centralized storage location for your BOMs, such as a shared database or PLM system, and implement version control to track changes and revisions. Communicate updates to all relevant stakeholders and ensure that they are using the most current version of the BOM. -
What should I do if a component in my BOM becomes obsolete or unavailable?
If a component becomes obsolete or unavailable, work with your suppliers to identify suitable alternatives that meet the required specifications and performance criteria. Update the BOM to reflect the new component information and communicate the change to all relevant stakeholders. In some cases, a redesign may be necessary to accommodate the new component.
Conclusion
A well-managed and accurate BOM is a critical component of successful PCB design and manufacturing. By understanding the different types of BOMs, following best practices for BOM creation and management, and addressing common challenges, you can ensure that your PCB projects run smoothly and deliver high-quality products.
Remember to involve all relevant stakeholders in the BOM management process, use automated tools to streamline workflows, and maintain version control to avoid confusion and errors. By continually refining and improving your BOM management practices, you can optimize your PCB design and production processes, reduce costs, and enhance overall product quality.
| BOM Type | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Engineering BOM (EBOM) | Used during the design phase by PCB designers and engineers | Contains a complete list of all components required for the PCB assembly, along with specifications, quantities, and reference designators |
| Manufacturing BOM (MBOM) | Tailored for use by the manufacturing team | Includes additional information such as component packaging details, assembly instructions, and special handling requirements |
| Production BOM (PBOM) | Used for large-scale production runs | Incorporates changes and optimizations made during initial production, includes finalized sourcing information, lead times, and cost data |
| Configurable BOM (CBOM) | Used for products with multiple variations or customization options | Consists of a master BOM with all possible components and sub-assemblies, along with rules for selecting appropriate parts based on the desired configuration |
No responses yet