Introduction to GaN and SiC FETs
Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) Field Effect Transistors (FETs) are two of the most advanced semiconductor technologies in the power electronics industry. These devices offer superior performance compared to traditional silicon-based FETs, making them ideal for high-power, high-frequency, and high-temperature applications.
GaN and SiC FETs are widely used in various industries, including:
– Automotive (electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles)
– Renewable energy (solar inverters and wind turbines)
– Consumer electronics (fast chargers and power adapters)
– Aerospace and defense (radar systems and satellite communications)
In this article, we will dive deep into the world of GaN and SiC FETs, exploring their properties, advantages, applications, and future prospects.
Properties of GaN and SiC FETs
GaN FETs
GaN is a wide bandgap semiconductor material with a bandgap of 3.4 eV. This property enables GaN FETs to operate at higher voltages, frequencies, and temperatures compared to silicon FETs. Some key properties of GaN FETs include:
- High breakdown voltage: GaN FETs can withstand voltages up to 1200 V, making them suitable for high-power applications.
- Low on-resistance: GaN FETs have lower on-resistance than silicon FETs, resulting in lower conduction losses and higher efficiency.
- High electron mobility: GaN has a higher electron mobility than silicon, allowing GaN FETs to switch at higher frequencies.
- High thermal conductivity: GaN has a higher thermal conductivity than silicon, enabling better heat dissipation and higher power density.
SiC FETs
SiC is another wide bandgap semiconductor material with a bandgap of 3.3 eV. SiC FETs share many of the advantages of GaN FETs, but with some unique properties:
- Higher breakdown voltage: SiC FETs can withstand voltages up to 1700 V, making them suitable for even higher-power applications than GaN FETs.
- Higher thermal conductivity: SiC has a higher thermal conductivity than GaN, allowing for better heat dissipation and higher power density.
- Higher critical electric field: SiC has a higher critical electric field than GaN, enabling thinner drift layers and lower on-resistance.
- Higher radiation hardness: SiC is more resistant to radiation damage than GaN, making it suitable for aerospace and defense applications.
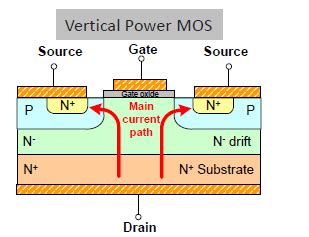
Advantages of GaN and SiC FETs over Silicon FETs
GaN and SiC FETs offer several advantages over traditional silicon FETs:
- Higher efficiency: GaN and SiC FETs have lower conduction and switching losses, resulting in higher overall efficiency.
- Higher power density: GaN and SiC FETs can handle higher power levels in smaller packages, enabling more compact and lightweight designs.
- Higher operating temperature: GaN and SiC FETs can operate at higher junction temperatures, reducing the need for bulky cooling systems.
- Faster switching: GaN and SiC FETs can switch at higher frequencies, enabling faster and more responsive power conversion.
- Longer lifetime: GaN and SiC FETs have higher reliability and longer lifetimes than silicon FETs, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.

Applications of GaN and SiC FETs
Automotive
GaN and SiC FETs are increasingly used in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) for various applications:
- Traction inverters: GaN and SiC FETs enable more efficient and compact traction inverters, increasing the driving range and reducing the weight of EVs.
- On-board chargers: GaN and SiC FETs enable faster and more efficient on-board charging, reducing charging time and improving user experience.
- DC-DC converters: GaN and SiC FETs enable more efficient and compact DC-DC converters, optimizing power distribution and management in EVs.
Renewable Energy
GaN and SiC FETs are also widely used in renewable energy applications:
- Solar inverters: GaN and SiC FETs enable more efficient and reliable solar inverters, increasing the energy yield and reducing the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE).
- Wind turbines: GaN and SiC FETs enable more efficient and compact power converters for wind turbines, reducing the weight and size of the nacelle and improving the overall efficiency.
- Energy storage systems: GaN and SiC FETs enable more efficient and compact bidirectional power converters for energy storage systems, facilitating the integration of renewable energy into the grid.
Consumer Electronics
GaN and SiC FETs are used in various consumer electronics applications:
- Fast chargers: GaN FETs enable ultra-fast charging for smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices, reducing charging time and improving user experience.
- Power adapters: GaN FETs enable more compact and efficient power adapters for consumer electronics, reducing the size and weight of the devices.
- Home appliances: GaN and SiC FETs enable more efficient and reliable power conversion in home appliances, such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines.
Aerospace and Defense
GaN and SiC FETs are used in various aerospace and defense applications:
- Radar systems: GaN FETs enable high-power and high-frequency radar systems, improving the range and resolution of the radar.
- Satellite communications: GaN FETs enable more efficient and compact power amplifiers for satellite communications, reducing the size and weight of the satellites.
- Directed energy weapons: GaN and SiC FETs enable high-power and high-frequency directed energy weapons, such as lasers and microwaves.

Future Prospects of GaN and SiC FETs
GaN and SiC FETs are expected to continue their growth in the power electronics industry, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance and energy-efficient solutions. Some of the future prospects of GaN and SiC FETs include:
- Wider adoption in electric vehicles: As the demand for EVs continues to grow, GaN and SiC FETs are expected to play a crucial role in improving the efficiency, range, and charging speed of EVs.
- Expansion in renewable energy: With the global push towards renewable energy, GaN and SiC FETs are expected to be widely used in solar inverters, wind turbines, and energy storage systems, enabling more efficient and reliable power conversion.
- Development of integrated solutions: GaN and SiC FETs are expected to be integrated with other components, such as drivers, protections, and sensors, to create more compact and efficient power modules and systems.
- Advancement in packaging technologies: New packaging technologies, such as 3D packaging and wafer-level packaging, are expected to further improve the performance and reliability of GaN and SiC FETs.
- Expansion in new applications: GaN and SiC FETs are expected to find new applications in emerging fields, such as solid-state circuit breakers, wireless power transfer, and high-frequency power conversion.
Comparison of GaN and SiC FETs
| Parameter | GaN FETs | SiC FETs |
|---|---|---|
| Bandgap | 3.4 eV | 3.3 eV |
| Breakdown Voltage | Up to 1200 V | Up to 1700 V |
| On-Resistance | Lower than Si FETs | Lower than Si FETs |
| Electron Mobility | Higher than Si FETs | Lower than GaN FETs |
| Thermal Conductivity | Higher than Si FETs | Higher than GaN FETs |
| Critical Electric Field | Lower than SiC FETs | Higher than GaN FETs |
| Radiation Hardness | Lower than SiC FETs | Higher than GaN FETs |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the main differences between GaN and SiC FETs?
GaN and SiC FETs are both wide bandgap semiconductor devices, but they have some differences in their properties. GaN FETs have a higher electron mobility and lower on-resistance than SiC FETs, but SiC FETs have a higher breakdown voltage, thermal conductivity, critical electric field, and radiation hardness than GaN FETs.
2. Can GaN and SiC FETs replace silicon FETs in all applications?
While GaN and SiC FETs offer superior performance compared to silicon FETs in many applications, they may not be suitable for all applications. Silicon FETs still have advantages in terms of cost, availability, and ease of use in low-power and low-frequency applications.
3. What are the main challenges in adopting GaN and SiC FETs?
Some of the main challenges in adopting GaN and SiC FETs include higher cost compared to silicon FETs, limited availability and supply chain, lack of standardization and interoperability, and the need for new design and manufacturing processes.
4. How do GaN and SiC FETs contribute to energy efficiency?
GaN and SiC FETs contribute to energy efficiency by reducing the conduction and switching losses in power conversion systems. This leads to higher overall efficiency, lower heat generation, and smaller cooling requirements, enabling more compact and lightweight designs.
5. What are the future growth opportunities for GaN and SiC FETs?
The future growth opportunities for GaN and SiC FETs include wider adoption in electric vehicles and renewable energy applications, expansion in new applications such as solid-state circuit breakers and wireless power transfer, development of integrated solutions and advanced packaging technologies, and continuous improvement in performance and cost.
Conclusion
GaN and SiC FETs are transforming the power electronics industry with their superior performance and energy efficiency compared to traditional silicon FETs. These devices are enabling more compact, lightweight, and reliable solutions in various applications, from electric vehicles and renewable energy to consumer electronics and aerospace and defense.
As the demand for high-performance and energy-efficient power electronics continues to grow, GaN and SiC FETs are expected to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of the industry. With continuous advancements in material growth, device fabrication, packaging, and system integration, GaN and SiC FETs are poised to unlock new possibilities and opportunities in the ever-evolving landscape of power electronics.
No responses yet