The Importance of PCB-PLM Integration for Electronics Design and Manufacturing
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) solutions have become increasingly important for managing the complex process of designing, manufacturing, and supporting electronic products. One critical aspect of PLM for electronics companies is integrating printed circuit board (PCB) design data and processes into the overall product development workflow. PCB-PLM integration enables seamless collaboration, data continuity, and traceability across the product lifecycle.
Benefits of PCB-PLM Integration
Integrating PCB design tools and data with a PLM system offers several key benefits:
- Improved collaboration: PCB-PLM integration allows electrical engineers, mechanical engineers, and other stakeholders to work together more effectively by providing a single source of truth for product data.
- Reduced errors and rework: By ensuring that everyone is working with the most up-to-date design data, PCB-PLM integration helps minimize errors and the need for costly rework.
- Faster time-to-market: Streamlined data management and collaboration enabled by PCB-PLM integration can significantly reduce design cycle times and accelerate product launches.
- Better traceability and compliance: Integrating PCB data into PLM provides a complete history of design changes and approvals, making it easier to meet regulatory requirements and conduct failure analysis.
Key Considerations for PCB-PLM Integration
When planning to integrate PCB design into a PLM environment, there are several important factors to consider:
Data Management and Synchronization
One of the primary challenges in PCB-PLM integration is ensuring that design data is consistently synchronized between the PCB design tools and the PLM system. This requires careful planning and the use of appropriate data exchange formats and APIs.
Some key data management considerations include:
- Defining a clear data model and schema for PCB design data in the PLM system
- Establishing rules and processes for data synchronization and version control
- Implementing automated data transfer and validation mechanisms to minimize manual effort and errors
BOM Management
The bill of materials (BOM) is a critical output of the PCB design process and must be effectively managed within the PLM system. PCB-PLM integration should enable:
- Automatic generation and synchronization of BOMs between PCB design tools and PLM
- Association of BOM items with other product data, such as mechanical CAD models and documentation
- Management of BOM revisions and change history
- Integration with ERP and supply chain management systems for procurement and manufacturing
Design Collaboration and Review
PCB-PLM integration should facilitate collaboration and design review processes among electrical engineers, mechanical engineers, and other stakeholders. This may involve:
- Providing web-based viewer and markup tools for PCB designs within the PLM interface
- Enabling cross-discipline collaboration through the association of PCB and mechanical CAD data
- Establishing formal design review and approval workflows within the PLM system
- Capturing and tracking design issues, comments, and decisions within the context of the PLM data model
Library and Component Management
Effective PCB-PLM integration requires a robust approach to managing component libraries and ensuring consistency between the PCB design environment and the PLM system. This includes:
- Establishing a central, controlled library of approved components and their attributes within PLM
- Synchronizing component data between PLM and PCB design tools
- Managing component lifecycles, including obsolescence and alternative parts
- Integrating with external component data sources and distributors for real-time availability and pricing information
Implementation Approaches
There are several approaches to implementing PCB-PLM integration, depending on the specific tools and systems involved:
Direct CAD-PLM Integration
Some PLM systems offer direct integrations with popular PCB design tools, such as Cadence OrCAD and Allegro or Mentor Graphics PADS and Xpedition. These integrations typically provide built-in functionality for data synchronization, BOM management, and design collaboration.
| PCB Design Tool | PLM System | Integration Features |
|---|---|---|
| Cadence OrCAD | PTC Windchill | – Automated BOM synchronization – Component library management – Design review and markup |
| Mentor PADS | Siemens Teamcenter | – Real-time design data synchronization – Integrated component management – Change management and traceability |
| Altium Designer | Dassault Systèmes 3DX | – Bi-directional BOM synchronization – Component data management – Collaborative design review |
Middleware and PLM Connectors
In cases where direct CAD-PLM integrations are not available or sufficient, companies may use middleware solutions or develop custom PLM connectors to enable data exchange between PCB design tools and PLM systems. These approaches often involve:
- Extracting design data from PCB tools using APIs or export formats
- Transforming and mapping data to the PLM schema using middleware or custom scripts
- Loading data into the PLM system using web services or other integration mechanisms
- Implementing bi-directional synchronization and change management processes
| Middleware / Connector | Description |
|---|---|
| Omnify Empower | A middleware solution that enables bidirectional data exchange between PCB design tools and PLM systems |
| XPLM PCB Connector | A connector that allows direct integration between PCB design tools and PLM systems, supporting data synchronization and collaboration |
| Custom PLM Connector | A custom-developed solution that extracts PCB design data, transforms it, and loads it into a PLM system using APIs or web services |
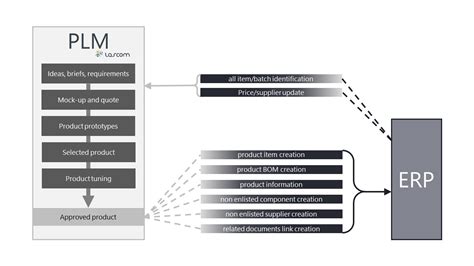
PLM-ERP Integration
To fully realize the benefits of PCB-PLM integration, it is often necessary to also integrate the PLM system with an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system. This enables seamless flow of BOM and component data from design to manufacturing and supply chain processes.
PLM-ERP integration typically involves:
- Establishing a master data management (MDM) strategy to ensure consistency between PLM and ERP data models
- Implementing data synchronization processes to transfer BOMs, item masters, and other data between systems
- Defining business rules and workflows to manage change propagation and approval processes across PLM and ERP
- Enabling real-time visibility and traceability of design, manufacturing, and supply chain data across the enterprise

Best Practices for Successful PCB-PLM Integration
To ensure a successful PCB-PLM integration, consider the following best practices:
- Clearly define requirements and objectives: Engage all stakeholders to identify the specific needs and goals for PCB-PLM integration, considering both current and future business requirements.
- Establish a robust data model and governance: Define a comprehensive and scalable data model for PCB design data in the PLM system, and establish clear policies and procedures for data management and access control.
- Invest in training and change management: Provide adequate training to PCB designers, engineers, and other users on the new integrated workflows and tools, and manage the organizational change process to ensure adoption and success.
- Start small and iterate: Begin with a pilot project or focused integration effort, and then continuously improve and expand the integration based on lessons learned and user feedback.
- Monitor and measure performance: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the effectiveness of PCB-PLM integration, such as design cycle time, BOM accuracy, and collaboration efficiency, and use this data to drive continuous improvement.
Conclusion
PCB-PLM integration is a critical capability for electronics companies looking to streamline product development, improve collaboration, and accelerate time-to-market. By understanding the key considerations, implementation approaches, and best practices outlined in this article, PCB designers and their organizations can successfully integrate PCB design into a comprehensive PLM environment, unlocking significant benefits across the product lifecycle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the main benefits of PCB-PLM integration for PCB designers?
PCB-PLM integration offers several key benefits for PCB designers, including:
- Improved collaboration with mechanical engineers and other stakeholders
- Reduced errors and rework due to consistent, up-to-date design data
- Faster design cycles and time-to-market
- Better traceability and change management throughout the design process
2. What are some common challenges in implementing PCB-PLM integration?
Some common challenges in PCB-PLM integration include:
- Ensuring consistent data synchronization between PCB design tools and PLM systems
- Managing complex BOM structures and relationships
- Integrating with existing component libraries and data sources
- Change management and user adoption of new workflows and processes
3. What are the different approaches to integrate PCB design tools with PLM systems?
There are three main approaches to PCB-PLM integration:
- Direct CAD-PLM integrations provided by PLM vendors
- Middleware solutions or custom PLM connectors for data exchange
- PLM-ERP integration to extend the benefits of integration across the enterprise
4. How can I ensure the success of a PCB-PLM integration project?
To ensure the success of a PCB-PLM integration project:
- Clearly define requirements and objectives with input from all stakeholders
- Establish a robust data model and governance framework
- Invest in user training and change management
- Start small with a pilot project and iterate based on feedback
- Monitor and measure performance using established KPIs
5. What role does ERP integration play in the context of PCB-PLM integration?
ERP integration extends the benefits of PCB-PLM integration by enabling seamless data flow from design to manufacturing and supply chain processes. This includes synchronizing BOM and component data, managing change propagation, and providing real-time visibility and traceability across the enterprise.
No responses yet