Introduction to Solder Mask and Solder Paste
When it comes to the world of electronics manufacturing, two terms that often come up are solder mask and solder paste. While they may sound similar, they serve very different purposes in the printed circuit board (PCB) assembly process. Understanding the difference between solder mask and solder paste is crucial for anyone involved in electronics design or manufacturing.
What is Solder Mask?
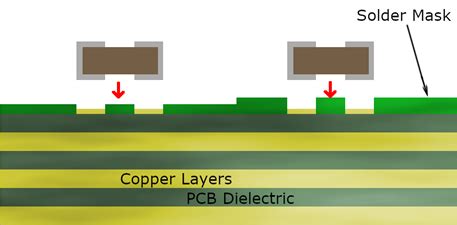
Solder mask, also known as solder resist or solder stop, is a thin layer of polymer that is applied to the surface of a PCB. Its primary purpose is to protect the copper traces and pads from oxidation and prevent solder bridges from forming between adjacent pads during the soldering process. Solder mask also provides electrical insulation and helps to improve the overall durability of the PCB.
Types of Solder Mask
There are two main types of solder mask:
- Liquid Photoimageable Solder Mask (LPSM)
- Applied as a liquid and then exposed to UV light to cure
- Offers high resolution and accuracy
- Commonly used in high-density PCB Designs
- Dry Film Solder Mask (DFSM)
- Applied as a pre-manufactured film and laminated onto the PCB surface
- More cost-effective for large-scale production
- Provides good coverage and protection
Solder Mask Application Process
The solder mask application process typically involves the following steps:
- Cleaning the PCB surface to remove any contaminants
- Applying the solder mask material (liquid or film)
- Exposing the solder mask to UV light through a photomask
- Developing the solder mask to remove unexposed areas
- Curing the solder mask to achieve its final properties
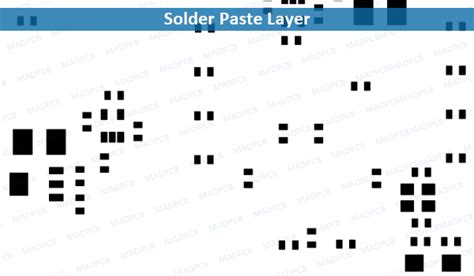
What is Solder Paste?
Solder paste, on the other hand, is a mixture of tiny solder particles suspended in a flux medium. It is used to form the electrical and mechanical connection between electronic components and the PCB during the surface mount technology (SMT) assembly process. Solder paste is applied to the PCB pads using a stencil or screen printing method before the components are placed.
Composition of Solder Paste
Solder paste consists of two main components:
- Solder Alloy Particles
- Typically made of tin, lead, and/or silver
- Available in various particle sizes and alloy compositions
- Melt during the Reflow Soldering process to form the solder joint
- Flux Medium
- Helps to remove oxidation and improve wetting of the solder
- Activates at specific temperatures during the reflow process
- Can be water-soluble, no-clean, or rosin-based
Solder Paste Application Process
The solder paste application process involves the following steps:
- Printing the solder paste onto the PCB pads using a stencil or screen
- Inspecting the solder paste deposits for consistency and accuracy
- Placing the electronic components onto the solder paste deposits
- Reflowing the PCB in a controlled temperature profile to melt the solder and form the solder joints
Differences Between Solder Mask and Solder Paste
Now that we have a basic understanding of solder mask and solder paste, let’s explore the key differences between them:
Function
- Solder Mask: Protects and insulates the PCB surface, preventing solder bridges and oxidation.
- Solder Paste: Forms the electrical and mechanical connection between components and the PCB.
Composition
- Solder Mask: A polymer material that is applied as a liquid or film and cured.
- Solder Paste: A mixture of solder alloy particles suspended in a flux medium.
Application Method
- Solder Mask: Applied to the entire PCB surface and selectively removed to expose pads and traces.
- Solder Paste: Applied only to the PCB pads where components will be placed, using a stencil or screen printing method.
Stage in the Assembly Process
- Solder Mask: Applied during the PCB fabrication process, before components are assembled.
- Solder Paste: Used during the SMT assembly process, after the PCB has been fabricated and before components are placed.
Visual Appearance
- Solder Mask: Typically green in color, but can also be found in other colors such as red, blue, or black.
- Solder Paste: Gray in color and has a paste-like consistency.
Solder Mask and Solder Paste Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Solder Mask | Solder Paste |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Protects and insulates the PCB surface | Forms electrical and mechanical connection |
| Composition | Polymer material (liquid or film) | Solder alloy particles suspended in flux medium |
| Application Method | Applied to entire PCB surface and selectively removed | Applied only to PCB pads using stencil or screen printing |
| Assembly Stage | During PCB fabrication, before component assembly | During SMT assembly, after PCB fabrication |
| Visual Appearance | Typically green, but available in other colors | Gray, paste-like consistency |

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can solder mask be used instead of solder paste?
No, solder mask and solder paste serve different purposes and cannot be used interchangeably. Solder mask is used to protect the PCB surface, while solder paste is used to form the solder joints between components and the PCB.
2. What happens if solder paste is applied over the solder mask?
Applying solder paste over the solder mask is not recommended, as it can lead to poor solder joint formation and reduced reliability. Solder paste should only be applied to exposed PCB pads where components will be placed.
3. Can solder mask be removed after it has been applied?
While it is possible to remove solder mask using abrasive methods or chemical strippers, it is not a common practice. Removing solder mask can damage the underlying copper traces and compromise the integrity of the PCB.
4. How does the choice of solder mask color affect the PCB?
The choice of solder mask color is primarily aesthetic and does not significantly impact the functionality of the PCB. However, some colors may offer better contrast for inspection purposes or be preferred for certain applications (e.g., white solder mask for LED lighting).
5. What factors influence the selection of solder paste?
The selection of solder paste depends on several factors, including the type of components being assembled, the reflow temperature profile, the desired solder joint properties, and the manufacturing process requirements. Considerations such as particle size, alloy composition, and flux type should be carefully evaluated.
Conclusion
In summary, solder mask and solder paste are two essential materials used in the electronics manufacturing process, but they serve distinct purposes. Solder mask is a protective and insulating layer applied to the PCB surface, while solder paste is a conductive material used to form solder joints between components and the PCB. Understanding the differences between solder mask and solder paste is crucial for designing and manufacturing reliable electronic devices.
As electronics continue to advance and become more complex, the importance of selecting the appropriate solder mask and solder paste materials will only grow. By staying informed about the latest developments in these materials and their application techniques, electronics professionals can ensure the highest quality and performance of their products.
No responses yet