Introduction to Solder Mask
Solder mask, also known as solder resist or solder stop, is a thin layer of polymer applied to the copper traces of a printed circuit board (PCB) to protect them from oxidation, prevent Solder Bridges, and provide electrical insulation. This essential component of PCB Manufacturing plays a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and functionality of electronic devices.
What is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB)?
A printed circuit board is a flat board made of insulating materials, such as fiberglass or plastic, with conductive pathways etched onto its surface. These pathways, called traces, connect various electronic components mounted on the board, allowing for the flow of electrical signals. PCBs are the foundation of modern electronics and can be found in virtually every electronic device, from smartphones and computers to medical equipment and aerospace systems.
The Role of Solder Mask in PCB Manufacturing
Solder mask serves several important functions in the PCB manufacturing process:
-
Protection from oxidation: Copper traces on a PCB are susceptible to oxidation when exposed to air, which can lead to decreased conductivity and potential failures. Solder mask acts as a barrier, preventing oxygen from reaching the copper and preserving its conductive properties.
-
Prevention of solder bridges: During the soldering process, molten solder can inadvertently flow between adjacent traces, creating unwanted connections called solder bridges. These bridges can cause short circuits and lead to device malfunction. Solder mask covers the areas between traces, preventing solder from spreading and forming bridges.
-
Electrical insulation: Solder mask provides electrical insulation between traces, ensuring that electrical signals flow only along the intended pathways. This insulation helps to prevent short circuits and Crosstalk between different signals on the board.
-
Improved aesthetics: Solder mask is available in various colors, with green being the most common. The uniform color of the solder mask enhances the visual appearance of the PCB and makes it easier to identify components and traces.
Types of Solder Mask
There are two main types of solder mask used in PCB manufacturing: liquid photoimageable solder mask (LPSM) and dry film solder mask (DFSM).
Liquid Photoimageable Solder Mask (LPSM)
LPSM is the most widely used type of solder mask in the PCB industry. It is applied to the PCB as a liquid polymer and then exposed to UV light through a photomask, which hardens the exposed areas. The unexposed areas are then removed using a developer solution, leaving the desired solder mask pattern on the board.
Advantages of LPSM:
– High resolution and accuracy
– Excellent adhesion to the PCB surface
– Flexibility in design changes
– Suitable for both small and large production runs
Disadvantages of LPSM:
– Requires specialized equipment for application and development
– Longer processing time compared to DFSM
– Higher cost for small production runs
Dry Film Solder Mask (DFSM)
DFSM is a solid film that is laminated onto the PCB surface using heat and pressure. Like LPSM, it is exposed to UV light through a photomask and then developed to remove the unexposed areas.
Advantages of DFSM:
– Faster processing time compared to LPSM
– Lower cost for small production runs
– Easier to handle and apply
Disadvantages of DFSM:
– Lower resolution and accuracy compared to LPSM
– Less flexibility in design changes
– Not suitable for large production runs
Solder Mask Application Process
The application of solder mask involves several steps, regardless of the type of solder mask used.
-
Surface preparation: The PCB surface is cleaned and roughened to ensure good adhesion of the solder mask.
-
Solder mask application: The solder mask is applied to the PCB surface, either as a liquid (LPSM) or a dry film (DFSM).
-
Exposure: The solder mask is exposed to UV light through a photomask, which hardens the exposed areas.
-
Development: The unexposed areas of the solder mask are removed using a developer solution, leaving the desired solder mask pattern on the board.
-
Curing: The solder mask is cured using heat to fully harden and improve its adhesion to the PCB surface.
-
Inspection: The PCB is inspected for any defects or irregularities in the solder mask coverage.

Solder Mask Colors and Finishes
Solder mask is available in various colors, with green being the most common. Other popular colors include red, blue, yellow, black, and white. The choice of color is often based on aesthetic preferences, but it can also serve functional purposes, such as improving the contrast between components and traces for easier assembly and inspection.
In addition to color, solder mask can have different finishes, which affect its appearance and performance.
Glossy Finish
A glossy finish provides a smooth, shiny surface that enhances the visual appeal of the PCB. It also offers better protection against moisture and chemical contamination. However, glossy finishes can create glare, making it more difficult to inspect the board for defects.
Matte Finish
A matte finish has a non-reflective, textured surface that reduces glare and improves the readability of component markings. It also provides a better surface for applying conformal coatings or adhesives. However, matte finishes may be more susceptible to moisture and chemical contamination compared to glossy finishes.
Comparison of Solder Mask Colors and Finishes
| Color | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Green | – Most common and readily available – Good contrast with copper traces – Suitable for most applications |
– May not be visually appealing for some designs – Can cause eye strain during prolonged inspection |
| Red | – High visibility for easy inspection – Aesthetically pleasing for certain designs |
– May be more expensive than green – Can be difficult to match with other components |
| Blue | – Visually appealing for certain designs – Good contrast with copper traces |
– May be more expensive than green – Can be difficult to match with other components |
| Yellow | – High visibility for easy inspection – Suitable for certain industrial applications |
– May not be visually appealing for some designs – Can cause eye strain during prolonged inspection |
| Black | – Aesthetically pleasing for certain designs – Good contrast with white silkscreen |
– Can make inspection more difficult – May be more expensive than green |
| White | – Aesthetically pleasing for certain designs – Good contrast with black silkscreen |
– Can make inspection more difficult – May be more expensive than green |
| Finish | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Glossy | – Enhances visual appeal – Better protection against moisture and contamination |
– Can create glare, making inspection more difficult |
| Matte | – Reduces glare for easier inspection – Better surface for conformal coatings and adhesives |
– May be more susceptible to moisture and contamination |
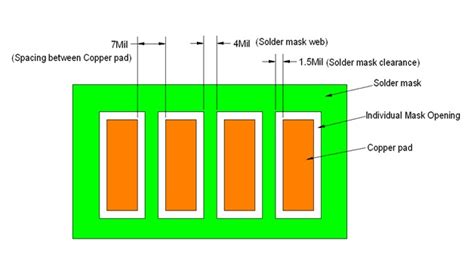
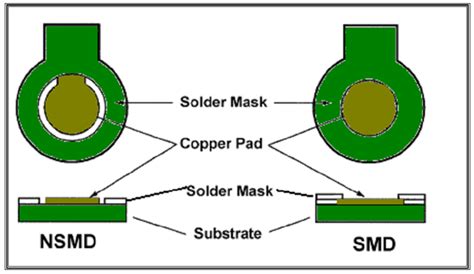
Solder Mask Design Considerations
When designing a PCB, several factors must be considered to ensure proper solder mask application and performance.
Solder Mask Clearance
Solder mask clearance refers to the distance between the edge of a copper pad or trace and the solder mask opening. Adequate clearance is necessary to ensure proper soldering and prevent solder mask from encroaching on the pad or trace. The recommended solder mask clearance varies depending on the pcb manufacturer and the specific design requirements, but a typical value is 0.05-0.1 mm (2-4 mils).
Solder Mask Expansion
During the curing process, solder mask can expand slightly, which can cause it to encroach on adjacent pads or traces if not accounted for in the design. To prevent this, designers should include solder mask expansion in their calculations and ensure that there is sufficient space between features.
Solder Mask Sliver
A solder mask sliver is a thin strip of solder mask between two adjacent pads or traces. If the sliver is too thin, it may break off during processing or use, leading to potential short circuits. To avoid this, designers should ensure that the minimum solder mask sliver width is maintained, typically around 0.1-0.15 mm (4-6 mils).
Solder Mask Registration
Solder mask registration refers to the alignment of the solder mask layer with the underlying copper features. Poor registration can result in solder mask encroaching on pads or traces, or leaving them exposed. To ensure proper registration, designers should work closely with their PCB manufacturer and provide accurate artwork files.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the purpose of solder mask on a PCB?
A: Solder mask serves several purposes, including protecting copper traces from oxidation, preventing solder bridges, providing electrical insulation, and improving the aesthetic appearance of the PCB. -
Q: What are the main types of solder mask?
A: The two main types of solder mask are liquid photoimageable solder mask (LPSM) and dry film solder mask (DFSM). LPSM is applied as a liquid and is more common, while DFSM is a solid film that is laminated onto the PCB surface. -
Q: What is the most common color for solder mask?
A: The most common color for solder mask is green, but other colors such as red, blue, yellow, black, and white are also available. -
Q: What is solder mask clearance, and why is it important?
A: Solder mask clearance is the distance between the edge of a copper pad or trace and the solder mask opening. It is important to ensure proper soldering and prevent solder mask from encroaching on the pad or trace. -
Q: How can I ensure proper solder mask registration on my PCB?
A: To ensure proper solder mask registration, work closely with your PCB manufacturer and provide accurate artwork files. Your manufacturer can advise you on the best practices for solder mask design and registration.
Conclusion
Solder mask is a critical component of PCB manufacturing that provides protection, insulation, and improved aesthetics. Understanding the types of solder mask, application processes, colors, finishes, and design considerations is essential for creating reliable and high-quality PCBs.
By working closely with PCB manufacturers and following best practices for solder mask design, engineers and designers can ensure that their PCBs meet the required specifications and perform optimally in their intended applications. As technology continues to advance, the role of solder mask in PCB manufacturing will remain crucial in enabling the development of increasingly complex and sophisticated electronic devices.
No responses yet