Introduction to ULN2003 IC
The ULN2003 is a high-voltage, high-current Darlington transistor array IC. It is commonly used as a relay driver, Stepper Motor driver, and for driving other high-current loads. The ULN2003 contains seven Darlington pair transistors, each capable of driving up to 500mA of current and withstanding up to 50V.
Key Features of ULN2003
- Seven Darlington pair transistors in a single package
- High-voltage capability (up to 50V)
- High-current capacity (up to 500mA per channel)
- Integrated suppression diodes for inductive load driving
- Inputs compatible with TTL and CMOS logic levels
- Output clamp diodes for transient suppression
- Thermal shutdown protection
ULN2003 Pinout and Pin Description
The ULN2003 comes in a 16-pin DIP (Dual Inline Package) or a 16-pin SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) package. The pinout for both packages is identical.
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1B | Input 1 |
| 2 | 1C | Output 1 (Collector) |
| 3 | 2B | Input 2 |
| 4 | 2C | Output 2 (Collector) |
| 5 | 3B | Input 3 |
| 6 | 3C | Output 3 (Collector) |
| 7 | 4B | Input 4 |
| 8 | 4C | Output 4 (Collector) |
| 9 | 5B | Input 5 |
| 10 | 5C | Output 5 (Collector) |
| 11 | 6B | Input 6 |
| 12 | 6C | Output 6 (Collector) |
| 13 | 7B | Input 7 |
| 14 | 7C | Output 7 (Collector) |
| 15 | COM | Common Emitter (Ground) |
| 16 | +Vcc | Supply Voltage (Up to 50V) |
Input Pins (1B, 2B, 3B, 4B, 5B, 6B, 7B)
The input pins are used to control the state of the corresponding output pins. When an input pin is driven high (logic “1”), the corresponding output pin is turned on (pulled low). When an input pin is driven low (logic “0”), the corresponding output pin is turned off (pulled high through an external pull-up resistor).
Output Pins (1C, 2C, 3C, 4C, 5C, 6C, 7C)
The output pins are the collectors of the Darlington pair transistors. When an output pin is turned on, it is pulled low (close to ground). When an output pin is turned off, it is pulled high through an external pull-up resistor connected to the supply voltage.
Common Emitter (COM)
The common emitter pin is the ground reference for the ULN2003. All emitters of the Darlington pair transistors are connected to this pin internally.
Supply Voltage (+Vcc)
The supply voltage pin is used to provide power to the ULN2003. The maximum supply voltage is 50V, but it is typically used with lower voltages such as 5V, 12V, or 24V, depending on the application.
ULN2003 Internal Structure and Operation
The ULN2003 consists of seven Darlington pair transistors, each with a corresponding input and output pin. A Darlington pair is a configuration of two bipolar transistors that provides high current gain and high voltage capability.
Each Darlington pair in the ULN2003 has the following structure:
- The input pin is connected to the base of the first transistor (Q1) through a resistor (R1).
- The emitter of Q1 is connected to the base of the second transistor (Q2) through another resistor (R2).
- The collector of Q2 is connected to the corresponding output pin.
- The emitter of Q2 is connected to the common emitter pin (ground).
- A suppression diode is connected between the collector and emitter of Q2 to protect against transient voltages caused by inductive loads.
When an input pin is driven high, Q1 turns on, which in turn causes Q2 to turn on. This pulls the corresponding output pin low (close to ground). When an input pin is driven low, both Q1 and Q2 turn off, and the output pin is pulled high through an external pull-up resistor.

ULN2003 Applications
The ULN2003 is widely used in various applications that require driving high-current loads or interfacing with high-voltage devices. Some common applications include:
Relay Driving
The ULN2003 can be used to drive relays, allowing low-voltage, low-current control signals to switch high-voltage, high-current loads. Each output of the ULN2003 can drive a relay coil, with the suppression diode protecting against the back-EMF generated when the relay is switched off.
Stepper Motor Driving
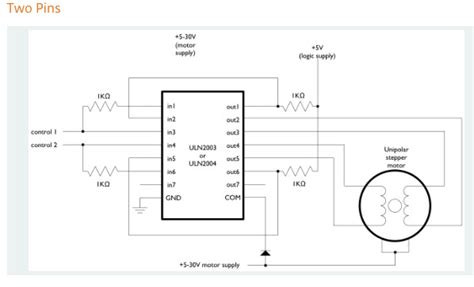
Stepper motors require precise control of multiple coils to achieve accurate positioning. The ULN2003 can be used to drive the coils of a unipolar stepper motor, with each output controlling a single coil. By sequencing the inputs in the appropriate pattern, the stepper motor can be made to rotate in either direction with precise step angles.
LED Driving
The ULN2003 can be used to drive high-current LED arrays or segments in LED displays. Each output can control a single LED or a series of LEDs, with the current limiting resistors sized appropriately for the desired brightness.
Solenoid Driving
Solenoids, such as those used in valves or actuators, can be driven by the ULN2003. The high-current capability of the ULN2003 allows it to provide the necessary driving current for the solenoid coil, while the suppression diode protects against the back-EMF generated when the solenoid is switched off.
ULN2003 IC Datasheet
The ULN2003 IC datasheet provides detailed information about the device’s electrical characteristics, absolute maximum ratings, and operating conditions. Some key specifications from the datasheet include:
Absolute Maximum Ratings
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 50V |
| Input Voltage | 30V |
| Output Voltage | 50V |
| Output Current (per channel) | 500mA |
| Total Package Power Dissipation | 2.25W |
Electrical Characteristics
| Parameter | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Low Voltage | – | – | 0.8 | V |
| Input High Voltage | 2.4 | – | – | V |
| Output Low Voltage (I_out = 350mA) | – | 1.2 | 1.6 | V |
| Output High Voltage (I_out = 100µA) | Vcc-1.7 | – | – | V |
| Supply Current (all inputs low) | – | 4 | 8 | mA |
| Supply Current (all inputs high) | – | 80 | 100 | mA |
For more detailed information, refer to the complete ULN2003 IC datasheet provided by the manufacturer.
ULN2003 Connection and Interfacing
When using the ULN2003 in a circuit, proper connection and interfacing are essential for reliable operation. Here are some guidelines to follow:
Power Supply
Connect the supply voltage (Vcc) to the ULN2003’s Vcc pin (pin 16). The supply voltage should not exceed the absolute maximum rating of 50V. Typically, the ULN2003 is used with supply voltages such as 5V, 12V, or 24V, depending on the application.
Ground
Connect the common emitter pin (COM, pin 15) to the ground of the circuit. This provides a reference for the input and output signals.
Input Signals
Connect the input signals to the corresponding input pins (1B, 2B, 3B, 4B, 5B, 6B, 7B). The input signals should be compatible with the ULN2003’s input voltage levels (0.8V max for low, 2.4V min for high). If the input signals are from a microcontroller or other logic device, ensure that the voltage levels are compatible.
Output Loads
Connect the output loads (relays, motors, LEDs, etc.) between the corresponding output pins (1C, 2C, 3C, 4C, 5C, 6C, 7C) and the positive supply voltage. Include appropriate current limiting resistors for LEDs and other sensitive loads.
Pull-up Resistors
If the output loads require a pull-up resistor, connect a resistor between each output pin and the positive supply voltage. The value of the pull-up resistor depends on the load current and the desired output voltage.
Suppression Diodes
The ULN2003 has built-in suppression diodes between the collector and emitter of each Darlington pair. These diodes protect the device from transient voltages caused by inductive loads (relays, motors, solenoids). When using inductive loads, no additional external suppression diodes are required.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the maximum supply voltage for the ULN2003?
The maximum supply voltage (Vcc) for the ULN2003 is 50V, as specified in the absolute maximum ratings. However, in most applications, lower voltages such as 5V, 12V, or 24V are used.
2. How much current can each output of the ULN2003 sink?
Each output of the ULN2003 can sink up to 500mA of current, as specified in the absolute maximum ratings. However, the total package power dissipation should not exceed 2.25W.
3. Can the ULN2003 be used to drive a bipolar stepper motor?
No, the ULN2003 is designed for driving unipolar stepper motors. Bipolar stepper motors require a different type of driver, such as an H-bridge circuit.
4. Is it necessary to use external suppression diodes when driving inductive loads with the ULN2003?
No, the ULN2003 has built-in suppression diodes between the collector and emitter of each Darlington pair. These diodes protect the device from transient voltages caused by inductive loads, so no additional external suppression diodes are required.
5. Can the ULN2003 be directly interfaced with a 3.3V microcontroller?
Yes, the ULN2003 can be directly interfaced with a 3.3V microcontroller, as long as the input voltage levels are compatible. The ULN2003 requires a minimum input high voltage of 2.4V, which is compatible with 3.3V logic levels.
Conclusion
The ULN2003 is a versatile and widely used Darlington transistor array IC that simplifies the process of driving high-current loads and interfacing with high-voltage devices. By understanding the ULN2003 pinout, internal structure, and application guidelines, designers can effectively incorporate this device into their projects.
When using the ULN2003, it is essential to adhere to the absolute maximum ratings and electrical characteristics specified in the datasheet to ensure reliable operation and prevent damage to the device or connected components.
With its high-voltage and high-current capabilities, integrated suppression diodes, and compatibility with various logic levels, the ULN2003 is an excellent choice for a wide range of applications, including relay driving, stepper motor control, LED driving, and solenoid control.
No responses yet