What is the TIP31C?
The TIP31C is a high-power NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) designed for general-purpose amplification and switching applications. It belongs to the TIP series of transistors, which are known for their robust performance and reliability. The TIP31C is capable of handling high currents and voltages, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic projects.
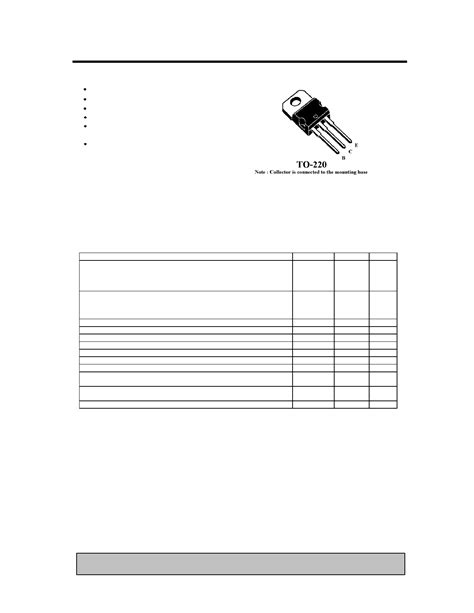
TIP31C Pinout
To effectively use the TIP31C transistor, it is crucial to understand its pinout. The TIP31C has three pins: the emitter (E), base (B), and collector (C). Here’s a detailed look at each pin:
| Pin | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | E | Emitter |
| 2 | B | Base |
| 3 | C | Collector |
Emitter (E)
The emitter is the pin through which current flows out of the transistor when it is operating in the forward active region. In a common emitter configuration, the emitter is usually connected to the ground or the negative supply voltage.
Base (B)
The base is the control pin of the transistor. A small current flowing into the base allows a much larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter. The base current determines the amount of collector current that can flow through the transistor.
Collector (C)
The collector is the pin through which current flows into the transistor when it is operating in the forward active region. The collector is typically connected to the positive supply voltage through a load resistor.
Electrical Characteristics
To effectively design circuits using the TIP31C, it is essential to understand its electrical characteristics. Here are some key specifications of the TIP31C:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO) | 100V |
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | 60V |
| Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO) | 5V |
| Maximum Collector Current (IC) | 3A |
| Maximum Power Dissipation (PD) | 40W |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 100-300 |
| Transition Frequency (fT) | 3 MHz |
These specifications provide insight into the operating limits and performance of the TIP31C transistor. It is important to ensure that the transistor operates within these limits to prevent damage and ensure reliable operation.

TIP31C Applications
The TIP31C transistor finds applications in various electronic circuits. Some common applications include:
-
Power Amplifiers: The TIP31C can be used in audio power amplifiers to drive speakers and deliver high-power output.
-
Motor Drivers: TIP31C transistors are commonly used in motor driver circuits to control the speed and direction of DC motors.
-
Switching Circuits: The TIP31C can be used as a switch to control the flow of current in circuits, such as relay drivers and power supply switching.
-
Voltage Regulators: TIP31C transistors can be employed in voltage regulator circuits to maintain a stable output voltage.
-
LED Drivers: The TIP31C can be used to drive high-power LEDs, providing sufficient current for bright illumination.
TIP31C Circuit Examples
To better understand how the TIP31C is used in practice, let’s explore a few circuit examples.
Simple LED Driver Circuit
In this circuit, the TIP31C is used to control the current flowing through an LED. The base of the transistor is connected to a resistor, which limits the base current. The collector is connected to the LED and a resistor in series, while the emitter is connected to ground.
+12V
|
+-+
| |
| | R1
| | 1k
+-+
|
|
|B|
+---| |---+
| |C| |
| | | |
| / \ |
| / \ |
| / \ |
| / \ |
| / \ |
| / \ |
| / \ |
|/ \|
+ +
| |
| |
| |
| R2 |
| 220 |
| |
+-+ +---+
| |
+-----|>|-----+
LED
When a sufficient voltage is applied to the base of the TIP31C, it turns on, allowing current to flow through the LED and the resistor R2. The brightness of the LED can be controlled by adjusting the base current using resistor R1.
Motor Speed Control Circuit
The TIP31C can be used to control the speed of a DC motor by varying the voltage applied to the motor. In this circuit, a potentiometer is used to adjust the base current of the TIP31C, which in turn controls the voltage applied to the motor.
+12V
|
+-+
| |
| | R1
| | 10k
+-+
|
|
|B|
+---| |---+
| |C| |
| | | |
| / \ |
| / \ |
| / \ |
| / \ |
| / \ |
| / \ |
| / \ |
|/ \|
+ +
| |
| |
| M |
| - |
| | | |
| +V- |
| |
+-+ +---+
| |
+-------------+
By adjusting the potentiometer R1, the base current of the TIP31C is varied, which controls the voltage applied to the motor. This allows for smooth speed control of the motor.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the maximum voltage that can be applied to the collector of the TIP31C?
The maximum collector-emitter voltage (VCEO) of the TIP31C is 60V. It is important to ensure that the applied voltage does not exceed this value to prevent damage to the transistor. -
How much current can the TIP31C handle?
The TIP31C can handle a maximum collector current (IC) of 3A. However, it is essential to consider the power dissipation limit of the transistor and ensure proper heat sinking when operating at high currents. -
What is the purpose of the base resistor in a TIP31C circuit?
The base resistor is used to limit the base current flowing into the transistor. It is important to select an appropriate value for the base resistor to ensure that the transistor operates in the desired region (saturation or active) and to prevent excessive base current that can damage the transistor. -
Can the TIP31C be used as a switch?
Yes, the TIP31C can be used as a switch in various applications. When a sufficient base current is applied, the Transistor Switches on, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter. When the base current is removed, the transistor turns off, blocking the current flow. -
How can I determine the heat sink requirements for the TIP31C?
The heat sink requirements for the TIP31C depend on the power dissipation and the maximum allowable junction temperature. To determine the appropriate heat sink, you need to calculate the power dissipation of the transistor based on the collector current and voltage. Then, consider the thermal resistance of the transistor and the ambient temperature to select a heat sink that can effectively dissipate the generated heat.
Conclusion
The TIP31C is a versatile NPN transistor that finds widespread use in various electronic circuits. Understanding its pinout, electrical characteristics, and applications is crucial for designing and troubleshooting circuits effectively. By utilizing the TIP31C within its specified limits and with proper circuit design techniques, you can harness its capabilities for amplification, switching, and power control in your electronic projects.
Remember to consider factors such as maximum voltage and current ratings, power dissipation, and heat sinking requirements when working with the TIP31C. Additionally, always refer to the transistor’s datasheet for detailed specifications and application guidelines.
With the knowledge gained from this article, you are now equipped to utilize the TIP31C transistor in your electronic designs and explore its potential in various applications. Happy designing!
No responses yet