What is PCB Thermal Management?
PCB thermal management refers to the process of designing and implementing methods to effectively dissipate heat generated by electronic components on a PCB. It involves the use of various techniques and materials to ensure that the temperature of the PCB and its components remains within acceptable limits, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Why is PCB Thermal Management Important?
Effective PCB thermal management is essential for several reasons:
-
Component Longevity: Overheating can significantly reduce the lifespan of electronic components. By maintaining proper operating temperatures, thermal management helps extend the life of components and the overall PCB.
-
Performance Optimization: Excessive heat can adversely affect the performance of electronic components, leading to reduced efficiency and potential malfunctions. Proper thermal management ensures that components operate at their optimal levels.
-
Reliability: Overheating can cause component failures, short circuits, and other reliability issues. Effective thermal management minimizes the risk of such problems, resulting in a more reliable electronic device.
-
Safety: In extreme cases, overheating can pose safety hazards, such as fire or burns to users. Thermal management techniques help prevent such risks by keeping temperatures within safe limits.
Techniques for PCB Thermal Management
Several techniques can be employed to achieve effective PCB thermal management. These include:
1. Component Placement and Layout
Strategic component placement and layout play a crucial role in thermal management. By placing heat-generating components away from each other and in areas with good airflow, the overall temperature of the PCB can be reduced. Additionally, placing temperature-sensitive components away from heat sources helps maintain their optimal performance.
2. Thermal Vias and Planes
Thermal vias are conductive paths that transfer heat from the component to the other layers of the PCB, ultimately dissipating it into the environment. By strategically placing thermal vias near heat-generating components, heat can be effectively conducted away from the source.
Thermal planes, on the other hand, are large copper areas on the PCB that act as heat spreaders. These planes help distribute heat evenly across the PCB, reducing hot spots and improving overall thermal performance.
3. Heat Sinks and Cooling Solutions
Heat sinks are passive cooling devices that are attached to heat-generating components to increase their surface area and facilitate better heat dissipation. They are commonly used on high-power components such as processors, power regulators, and transistors.
In addition to heat sinks, other cooling solutions such as fans, liquid cooling systems, and thermoelectric coolers can be employed for more demanding thermal management requirements.
4. Materials and Coatings
The choice of materials used in PCB fabrication can significantly impact thermal management. Using high thermal conductivity materials, such as copper or aluminum, for the PCB substrate and traces helps dissipate heat more efficiently.
Moreover, applying thermal interface materials (TIMs) between components and heat sinks can improve heat transfer by filling air gaps and reducing thermal resistance.
Conformal coatings, which are thin layers of insulating material applied to the PCB surface, can also provide additional thermal insulation and protection against environmental factors.
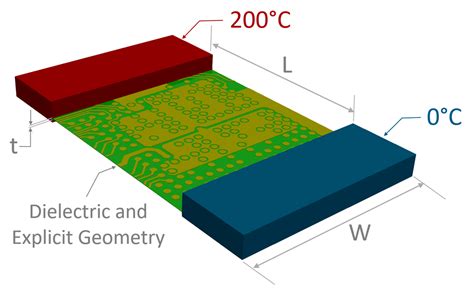
Best Practices for PCB Thermal Management
To achieve optimal thermal management in PCB design, consider the following best practices:
-
Conduct Thermal Analysis: Perform thermal simulations and analysis during the design phase to identify potential hot spots and optimize component placement and layout accordingly.
-
Use Adequate Copper Thickness: Ensure that the copper thickness of the PCB traces is sufficient to handle the expected current flow without excessive heating.
-
Implement Thermal Reliefs: Use thermal reliefs, which are small copper spokes that connect components to thermal planes, to prevent solder joint failures due to thermal stress.
-
Consider Airflow: When designing the enclosure or housing for the PCB, consider the airflow paths and ensure adequate ventilation to facilitate heat dissipation.
-
Test and Validate: Conduct thorough testing and validation of the PCB’s thermal performance under various operating conditions to ensure that it meets the required specifications.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the difference between passive and active cooling in PCB thermal management?
Passive cooling relies on natural heat transfer mechanisms, such as conduction and convection, without the use of external power. Examples include heat sinks and thermal planes. Active cooling, on the other hand, involves the use of powered devices, such as fans or thermoelectric coolers, to actively remove heat from the system. -
How do I select the appropriate heat sink for my PCB components?
When selecting a heat sink, consider factors such as the component’s power dissipation, the available space on the PCB, and the desired thermal performance. Heat sink manufacturers often provide thermal resistance data and selection guides to help choose the most suitable heat sink for a given application. -
Can I use thermal simulation software to analyze my PCB’s thermal performance?
Yes, thermal simulation software tools are widely available and can be used to analyze the thermal performance of a PCB design. These tools allow designers to simulate heat flow, identify hot spots, and optimize the placement of components and cooling solutions before physical prototyping. -
What is the role of thermal interface materials (TIMs) in PCB thermal management?
Thermal interface materials, such as thermal greases, pads, or adhesives, are used to fill the air gaps between components and heat sinks, improving heat transfer efficiency. TIMs help reduce thermal resistance and ensure better contact between the heat-generating component and the cooling solution. -
How do I ensure proper thermal management in high-density PCB designs?
In high-density PCB designs, thermal management becomes more challenging due to the close proximity of components. To ensure proper thermal management, consider techniques such as strategic component placement, the use of thermal vias and planes, and the implementation of advanced cooling solutions like micro-channel heat sinks or liquid cooling systems.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Component Placement | Strategic placement of components to optimize heat dissipation |
| Thermal Vias | Conductive paths that transfer heat from components to other layers |
| Thermal Planes | Large copper areas that spread heat evenly across the PCB |
| Heat Sinks | Passive cooling devices attached to components to increase surface area |
| Cooling Solutions | Fans, liquid cooling systems, or thermoelectric coolers for active cooling |
| Materials and Coatings | High thermal conductivity materials and coatings for efficient heat transfer |

Conclusion
Effective thermal management is a critical aspect of PCB design in today’s electronics industry. By understanding the principles and techniques of PCB thermal management, designers can create robust and reliable electronic devices that perform optimally and maintain longevity. From strategic component placement and the use of thermal vias and planes to the implementation of advanced cooling solutions and materials, a holistic approach to thermal management is essential.
As electronic devices continue to push the boundaries of performance and miniaturization, the importance of thermal management will only continue to grow. By staying informed about the latest advancements and best practices in PCB thermal management, designers can stay ahead of the curve and create innovative solutions that meet the ever-increasing demands of the industry.
No responses yet