Introduction to PCB thermal management
In the world of electronic devices, printed circuit boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in connecting and supporting various components. As technology advances and devices become more compact and powerful, effective thermal management has become a critical aspect of PCB design. Thermal management in PCBs refers to the process of controlling and dissipating heat generated by electronic components to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity of the device.
Importance of Thermal Management in PCBs
Proper thermal management is essential for several reasons:
- Component reliability: Excessive heat can cause components to degrade or fail prematurely, leading to device malfunctions and shortened lifespan.
- Performance optimization: High temperatures can negatively impact the performance of electronic components, resulting in reduced efficiency and potential system failures.
- User safety: Inadequate thermal management can lead to overheating, posing safety risks to users and potentially causing damage to the device or surrounding objects.
Factors Affecting PCB Thermal Management
Several factors influence the thermal management of PCBs, including:
Component Power Dissipation
The power dissipation of individual components on a PCB directly contributes to the overall heat generation. High-power components, such as processors, graphics cards, and power regulators, require special attention in terms of thermal management.
PCB Layout and Design
The layout and design of a PCB can significantly impact its thermal performance. Factors such as component placement, trace routing, and layer stack-up play a crucial role in heat distribution and dissipation.
Ambient Temperature and Airflow
The operating environment of a PCB, including ambient temperature and airflow, affects its thermal management. Higher ambient temperatures and limited airflow can exacerbate heating issues, requiring more robust thermal management solutions.
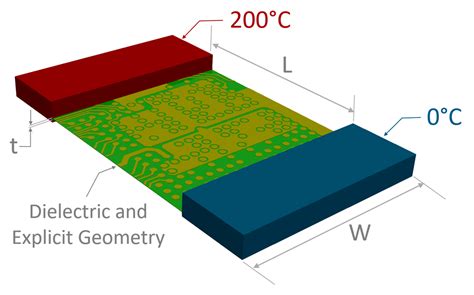
Thermal Management Techniques for PCBs
To address the challenges of thermal management in PCBs, various techniques and strategies are employed:
Heatsinks and Thermal Interface Materials
Heatsinks are commonly used to dissipate heat from high-power components. They work by increasing the surface area for heat dissipation and facilitating heat transfer to the surrounding air. Thermal interface materials (TIMs), such as thermal paste or thermal pads, are used to enhance the thermal coupling between components and heatsinks.
Thermal Vias and Copper Pours
Thermal vias are strategically placed in PCBs to provide a low-resistance path for heat to transfer from components to other layers or to heatsinks. Copper pours, which are large areas of copper on the PCB, help spread heat and improve overall thermal conductivity.
Component Placement and Spacing
Proper component placement and spacing are crucial for effective thermal management. Components that generate significant heat should be placed away from temperature-sensitive components and positioned to maximize airflow. Adequate spacing between components allows for better heat dissipation and prevents thermal coupling.
Thermal Simulation and Analysis
Thermal simulation tools and analysis techniques are used to predict and optimize the thermal performance of PCBs during the design phase. These tools help identify potential hot spots, evaluate the effectiveness of thermal management solutions, and guide design decisions.

Advanced Thermal Management Solutions
As PCBs become more complex and power-dense, advanced thermal management solutions are being developed to address the increasing thermal challenges:
Active Cooling Systems
Active cooling systems, such as fans or liquid cooling, are used in high-performance applications to provide enhanced heat dissipation. Fans create forced airflow over the PCB and heatsinks, while liquid cooling systems use coolants to transfer heat away from components.
Phase-Change Materials (PCMs)
Phase-change materials are substances that absorb heat by changing their phase from solid to liquid. When incorporated into PCBs, PCMs can help regulate temperature by absorbing excess heat during peak periods and releasing it during cooler periods, providing a form of passive thermal management.
Advanced Substrate Materials
Emerging substrate materials, such as ceramic or metal-core PCBs, offer improved thermal conductivity compared to traditional FR-4 substrates. These materials help dissipate heat more efficiently, making them suitable for high-power applications.

PCB Thermal Management Design Considerations
When designing PCBs with thermal management in mind, several key considerations should be taken into account:
Thermal Design Guidelines
Following established thermal design guidelines is essential for achieving effective thermal management. These guidelines cover aspects such as component placement, copper pours, thermal vias, and heatsink selection. Adhering to these guidelines helps ensure that the PCB can dissipate heat efficiently and maintain reliable operation.
Thermal Modeling and Simulation
Incorporating thermal modeling and simulation into the PCB design process allows for the identification and resolution of potential thermal issues early on. Thermal simulation tools can predict the temperature distribution across the PCB, identify hot spots, and evaluate the effectiveness of various thermal management strategies.
Collaboration with Thermal Experts
Collaborating with thermal management experts can greatly benefit the PCB design process. Thermal experts can provide valuable insights, recommend appropriate thermal management solutions, and assist in optimizing the PCB layout for optimal thermal performance.
Environmental Considerations in PCB Thermal Management
In addition to the technical aspects of thermal management, environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important in PCB design:
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Designing PCBs with energy efficiency and sustainability in mind is gaining traction. This involves selecting components with lower power consumption, optimizing PCB layouts to minimize power losses, and implementing power management techniques to reduce overall energy consumption.
Eco-Friendly Materials and Manufacturing Processes
The use of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes is becoming more prevalent in PCB production. This includes the adoption of halogen-free and lead-free materials, as well as implementing green manufacturing practices to minimize environmental impact.
Future Trends in PCB Thermal Management
As technology continues to evolve, new trends and innovations are emerging in the field of PCB thermal management:
Advanced Cooling Technologies
Researchers are exploring advanced cooling technologies, such as microfluidic cooling and thermoelectric cooling, to address the thermal challenges of high-performance PCBs. These technologies aim to provide more efficient and compact cooling solutions.
Integration of Thermal Management into PCB Design Automation
There is a growing trend towards integrating thermal management considerations into PCB design automation tools. This allows designers to analyze and optimize thermal performance simultaneously with other design aspects, streamlining the overall design process.
Collaboration with AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning techniques are being applied to PCB thermal management. These technologies can assist in predicting thermal behavior, optimizing component placement, and identifying potential thermal issues, leading to more efficient and reliable PCB designs.
Conclusion
Thermal management in PCBs is a critical aspect of electronic device design. As technology advances and devices become more compact and powerful, effective thermal management strategies are essential to ensure reliability, performance, and user safety. By understanding the factors affecting PCB thermal management, employing appropriate techniques, and considering advanced solutions and future trends, designers can create PCBs that can effectively dissipate heat and operate reliably in various environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is thermal management in PCBs?
Thermal management in PCBs refers to the process of controlling and dissipating heat generated by electronic components to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity of the device. -
Why is thermal management important in PCBs?
Proper thermal management is essential for several reasons, including ensuring component reliability, optimizing performance, and maintaining user safety. Excessive heat can cause components to degrade or fail prematurely, negatively impact performance, and pose safety risks. -
What are some common thermal management techniques used in PCBs?
Common thermal management techniques used in PCBs include the use of heatsinks and thermal interface materials, thermal vias and copper pours, strategic component placement and spacing, and thermal simulation and analysis. -
What are some advanced thermal management solutions for PCBs?
Advanced thermal management solutions for PCBs include active cooling systems (fans or liquid cooling), phase-change materials (PCMs), and the use of advanced substrate materials with improved thermal conductivity. -
What are some future trends in PCB thermal management?
Future trends in PCB thermal management include the development of advanced cooling technologies, the integration of thermal management into PCB design automation tools, and the application of AI and machine learning techniques to predict and optimize thermal performance.
| Thermal Management Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Heatsinks and TIMs | Heatsinks increase surface area for heat dissipation, while thermal interface materials enhance thermal coupling. |
| Thermal Vias and Copper Pours | Thermal vias provide low-resistance heat transfer paths, and copper pours help spread heat and improve conductivity. |
| Component Placement and Spacing | Proper component placement and spacing maximize airflow and prevent thermal coupling. |
| Thermal Simulation and Analysis | Simulation tools predict and optimize thermal performance during the design phase, identifying potential hot spots. |
| Advanced Thermal Management Solution | Description |
|---|---|
| Active Cooling Systems | Fans or liquid cooling provide enhanced heat dissipation in high-performance applications. |
| Phase-Change Materials (PCMs) | PCMs absorb heat by changing phase from solid to liquid, helping regulate temperature. |
| Advanced Substrate Materials | Ceramic or metal-core PCBs offer improved thermal conductivity compared to traditional FR-4 substrates. |
By implementing effective thermal management techniques, considering advanced solutions, and staying informed about future trends, PCB designers can ensure that their designs can effectively handle the thermal challenges of modern electronic devices.
No responses yet