Introduction to SOLIDWORKS PDM
SOLIDWORKS PDM (Product Data Management) is a powerful tool that integrates with SOLIDWORKS 3D CAD software to provide a comprehensive solution for managing product design data and streamlining workflows. It enables teams to efficiently collaborate, control revisions, and automate processes across the product development lifecycle.
Key Features of SOLIDWORKS PDM
- Centralized data management
- Version control and revision history
- Secure data access and permissions
- Automated workflows and notifications
- Integration with SOLIDWORKS CAD
By leveraging SOLIDWORKS PDM, organizations can improve productivity, reduce errors, and accelerate time-to-market for their products.
Benefits of Using SOLIDWORKS PDM with SOLIDWORKS MCAD
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
SOLIDWORKS PDM provides a centralized repository for storing and managing SOLIDWORKS CAD files and related design data. This enables team members to easily access, share, and collaborate on projects in real-time, regardless of their location.
Some key collaboration features include:
- Check-in/check-out functionality to prevent conflicts
- Version control to track changes and revisions
- Secure access control based on user roles and permissions
- Integration with Microsoft Office for sharing documents
Streamlined Workflows and Processes
With SOLIDWORKS PDM, you can automate and standardize workflows to reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and ensure consistency across projects. Some examples of workflows include:
- Design review and approval processes
- Engineering change orders (ECOs)
- Bill of Materials (BOM) management
- Release to manufacturing
Automated notifications and reminders keep team members informed of task assignments and deadlines.
Improved Data Security and Compliance
SOLIDWORKS PDM provides robust security features to protect sensitive design data and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. These include:
- Granular access control based on user roles and permissions
- Data encryption and secure file transfer
- Audit trails to track user actions and file history
- Automated backup and disaster recovery
By implementing SOLIDWORKS PDM, organizations can mitigate risk, safeguard intellectual property, and meet regulatory requirements.
Implementing SOLIDWORKS PDM
System Requirements and Setup
To run SOLIDWORKS PDM, you’ll need a Windows-based server and client machines that meet the minimum system requirements:
| Component | Minimum Requirement |
|---|---|
| Processor | Intel or AMD processor, 3.3 GHz or higher |
| RAM | 16 GB |
| Hard Drive | 250 GB or more |
| Graphics Card | Certified graphics card for SOLIDWORKS |
| Operating System | Windows 10 64-bit |
The setup process involves installing the SOLIDWORKS PDM server and client components, configuring the database, and setting up user accounts and permissions.
Configuring Vaults and Folders
In SOLIDWORKS PDM, design data is organized into vaults and folders. A vault is a centralized repository that stores all the files and metadata related to a project or product line. Within each vault, you can create a hierarchical folder structure to organize files based on your specific needs.
Some best practices for configuring vaults and folders include:
- Creating separate vaults for different projects or product lines
- Organizing folders based on product structure or lifecycle stages
- Applying naming conventions for folders and files
- Setting up appropriate access controls and permissions for each folder
Migrating Existing Data
If you have existing SOLIDWORKS files and design data, you’ll need to migrate them into SOLIDWORKS PDM. This process involves:
- Planning the data migration strategy
- Cleaning up and organizing the existing data
- Exporting files from their current location
- Importing files into SOLIDWORKS PDM vaults and folders
- Verifying the migrated data and fixing any issues
It’s important to plan and test the migration process carefully to avoid data loss or corruption.

Working with SOLIDWORKS PDM
Checking Files In and Out
To work on a SOLIDWORKS file in PDM, you need to check it out from the vault. This locks the file so that other users cannot make changes simultaneously, preventing version conflicts. Once you’ve made your changes, you check the file back into the vault, creating a new version.
Here’s an example workflow:
- Open SOLIDWORKS and connect to the PDM vault
- Browse to the folder containing the file you want to edit
- Right-click the file and select “Check Out”
- Make your changes to the file in SOLIDWORKS
- Save the file and close SOLIDWORKS
- In the PDM vault view, right-click the checked-out file and select “Check In”
- Enter a comment describing your changes and click “OK”
The new version of the file is now available for other users to access.
Managing Revisions and Versions
SOLIDWORKS PDM automatically tracks revisions and versions of files as they are checked in and out of the vault. This provides a complete history of changes made to each file over time.
Some key features for managing revisions and versions include:
- Automatic version numbering
- User-defined revision numbering schemes
- Ability to view and compare different versions of a file
- Option to promote a version to a new revision
- Ability to restore previous versions if needed
By effectively managing revisions and versions, teams can collaborate efficiently, track changes, and maintain a clear audit trail.
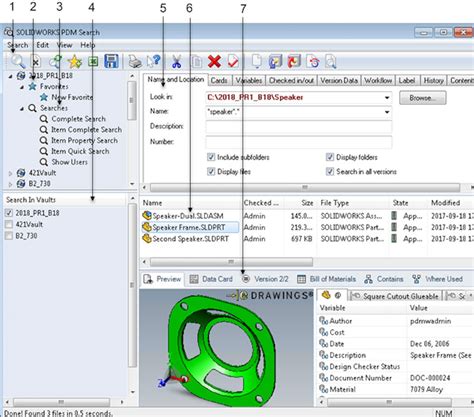
Searching and Retrieving Data
SOLIDWORKS PDM provides powerful search capabilities to help users quickly find and retrieve the data they need. You can search for files based on various criteria, such as:
- File name or type
- Metadata properties (e.g., title, description, custom properties)
- Workflow state
- Check-in/check-out status
- Date range
Search results can be further filtered, sorted, and exported as needed. SOLIDWORKS PDM also supports saved searches and search templates to streamline frequently used queries.
Advanced SOLIDWORKS PDM Features
Automated Workflows
SOLIDWORKS PDM allows you to automate complex workflows, such as design reviews, approvals, and release processes. Workflows are defined using a graphical interface where you can specify tasks, transitions, and conditional routing.
Some examples of automated workflows include:
- Engineering Change Request (ECR) process
- Design review and approval process
- Release to manufacturing process
Automated workflows ensure that tasks are assigned to the right people at the right time, reducing manual effort and errors.
Integration with Other Systems
SOLIDWORKS PDM integrates with various other systems and tools to provide a seamless product development ecosystem. Some examples include:
- ERP systems for sharing BOMs and product data
- PLM systems for managing product lifecycles
- CAE tools for simulation and analysis
- Manufacturing systems for production planning and execution
Integration with other systems enables data to flow seamlessly across the organization, reducing duplication and errors.
Customization and Extensibility
SOLIDWORKS PDM provides APIs and customization options to tailor the system to your specific needs. You can:
- Create custom metadata fields and forms
- Develop custom add-ins using the SOLIDWORKS PDM API
- Integrate with custom applications using web services
- Customize reports and dashboards
Customization and extensibility options allow you to adapt SOLIDWORKS PDM to your unique processes and requirements.
Conclusion
SOLIDWORKS PDM is a powerful tool for managing SOLIDWORKS MCAD data and streamlining product development processes. By providing centralized data management, version control, automated workflows, and secure access control, SOLIDWORKS PDM enables teams to collaborate efficiently, reduce errors, and accelerate time-to-market.
Implementing SOLIDWORKS PDM involves careful planning, system setup, data migration, and user training. Once in place, users can effectively manage files, revisions, and workflows within the system.
Advanced features such as automated workflows, integration with other systems, and customization options further enhance the capabilities of SOLIDWORKS PDM, making it a comprehensive solution for product data management.
FAQ
What is the difference between SOLIDWORKS PDM Standard and Professional?
SOLIDWORKS PDM Standard is an entry-level solution for small teams and simple workflows, while SOLIDWORKS PDM Professional provides advanced features such as automated workflows, advanced search, and integrations with other systems. PDM Professional is suitable for larger teams and more complex processes.
Can SOLIDWORKS PDM be used with non-SOLIDWORKS CAD files?
Yes, SOLIDWORKS PDM can manage various file types, including non-SOLIDWORKS CAD files. However, some features, such as preview and revision tracking, may be limited for non-native file formats.
How does SOLIDWORKS PDM handle multi-site collaboration?
SOLIDWORKS PDM supports multi-site collaboration through replication and synchronization of vaults across different locations. This allows teams to work together seamlessly while minimizing network latency and ensuring data consistency.
What is the best way to train users on SOLIDWORKS PDM?
SOLIDWORKS offers various training options for PDM, including instructor-led courses, online tutorials, and certifications. It’s recommended to start with basic training for all users, followed by role-specific advanced training. Ongoing support and mentoring can help users become proficient with the system.
How does SOLIDWORKS PDM ensure data security and compliance?
SOLIDWORKS PDM provides granular access control, data encryption, audit trails, and automated backup and recovery features to ensure data security and compliance. It also supports various industry standards and regulations, such as ISO, ITAR, and GDPR. Regular security audits and updates can help maintain a secure and compliant environment.

No responses yet