Introduction to Sawtooth Wave Generators
A sawtooth wave generator is an electronic circuit that produces a specific type of waveform known as a sawtooth wave. This waveform is characterized by a linear rise in voltage followed by a rapid drop, resembling the teeth of a saw blade. Sawtooth waves are commonly used in various applications, including audio synthesis, test equipment, and control systems.
What is a Sawtooth Wave?
A sawtooth wave is a type of periodic waveform that consists of a linear ramp followed by a sharp drop. The ramp can be either ascending (rising) or descending (falling), depending on the specific application. The period of a sawtooth wave is the time it takes for one complete cycle, which includes both the ramp and the drop.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Amplitude | The peak-to-peak voltage of the sawtooth wave |
| Frequency | The number of complete cycles per second (measured in Hz) |
| Slope | The rate of change of the voltage during the ramp portion |
Applications of Sawtooth Waves
Sawtooth waves find applications in various fields, including:
- Audio synthesis
- Generating rich harmonics for synthesized sounds
- Creating unique timbres in electronic music
- Test equipment
- Generating sweep signals for frequency response measurements
- Testing the linearity of amplifiers and filters
- Control systems
- Generating ramp signals for motor control
- Producing timing signals for synchronization
Types of Sawtooth Wave Generators
There are several types of sawtooth wave generators, each with its own characteristics and circuit implementation. Some common types include:
Integrator-Based Sawtooth Generator
An integrator-based sawtooth generator uses an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured as an integrator to generate the sawtooth waveform. The circuit works by charging a capacitor at a constant rate, producing a linear ramp. When the voltage reaches a predetermined threshold, a comparator triggers a switch that discharges the capacitor rapidly, resulting in the sharp drop of the sawtooth wave.
Circuit Diagram
+Vcc
|
|
R1
|
Input >---|
|
|
|-|
| |
| \/| Op-Amp
| |
|-|
|
|
C1
|
___
___ GND
Current Mirror-Based Sawtooth Generator
A current mirror-based sawtooth generator utilizes the properties of current mirrors to produce the sawtooth waveform. In this circuit, a constant current source charges a capacitor, generating the linear ramp. A transistor acts as a switch to discharge the capacitor when the voltage reaches a certain level, creating the sharp drop.
Circuit Diagram
+Vcc
|
|
R1
|
Input >---|
|
|
|B |C
| |
| | NPN
| |
|E |
|
|
C1
|
___
___ GND
Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) Based Sawtooth Generator
A DAC-based sawtooth generator uses a digital-to-analog converter to generate the sawtooth waveform. The DAC receives a digital input that represents the desired sawtooth wave, and it converts this digital signal into an analog voltage. The resolution of the DAC determines the smoothness of the generated sawtooth wave.
Block Diagram
Digital Input
|
|
-------
| DAC |
-------
|
|
Sawtooth Output
Designing a Sawtooth Wave Generator
When designing a sawtooth wave generator, several factors need to be considered to achieve the desired performance. These include:
Frequency Range
The frequency range of the sawtooth wave generator determines the range of frequencies over which the circuit can operate. The frequency is controlled by the rate at which the capacitor charges and discharges. The frequency can be adjusted by changing the values of the resistors and capacitors in the circuit.
Amplitude Control
The amplitude of the sawtooth wave can be controlled by adjusting the reference voltage or the gain of the output stage. In some designs, a variable resistor or a voltage divider can be used to provide amplitude control.
Linearity
The linearity of the sawtooth wave refers to how closely the ramp portion of the waveform follows a straight line. Factors such as the accuracy of the current source, the stability of the capacitor, and the performance of the op-amp can affect the linearity of the generated sawtooth wave.
Output Impedance
The output impedance of the sawtooth wave generator should be considered when interfacing with other circuits or loads. A low output impedance ensures that the generator can drive the load without distortion or loss of signal integrity.

Building a Sawtooth Wave Generator
Building a sawtooth wave generator involves selecting the appropriate components and constructing the circuit according to the chosen design. Here are some steps to follow:
- Choose the type of sawtooth wave generator based on the application requirements.
- Select the op-amp, transistors, resistors, and capacitors based on the desired specifications.
- Assemble the components on a breadboard or design a printed circuit board (PCB) for a more permanent solution.
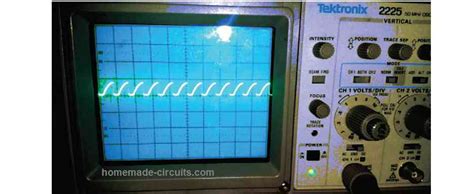
- Test the circuit using an oscilloscope to verify the generated sawtooth waveform.
- Make any necessary adjustments to the component values to fine-tune the performance.
Troubleshooting Sawtooth Wave Generators
If the sawtooth wave generator is not functioning as expected, here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Check the power supply voltage and ensure it is within the specified range for the components used.
- Verify that the components are connected correctly according to the circuit diagram.
- Use an oscilloscope to observe the waveform at different points in the circuit to identify where the problem may be occurring.
- Check for any damaged or faulty components and replace them if necessary.
- Ensure that the frequency and amplitude controls are adjusted correctly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the difference between a rising sawtooth wave and a falling sawtooth wave?
A: A rising sawtooth wave has a linear ramp that increases in voltage over time, while a falling sawtooth wave has a linear ramp that decreases in voltage over time. -
Q: Can a sawtooth wave generator be used for audio applications?
A: Yes, sawtooth waves are commonly used in audio synthesis to create rich harmonics and unique timbres in electronic music. -
Q: How can I change the frequency of a sawtooth wave generator?
A: The frequency of a sawtooth wave generator can be changed by adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors in the circuit that control the charging and discharging rates. -
Q: What is the purpose of the sharp drop in a sawtooth wave?
A: The sharp drop in a sawtooth wave serves to reset the waveform quickly to its starting point, allowing the next cycle to begin. This rapid transition is essential for maintaining the periodic nature of the sawtooth wave. -
Q: Can a sawtooth wave generator be implemented using digital techniques?
A: Yes, a sawtooth wave generator can be implemented using digital techniques such as a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). The DAC receives a digital input representing the desired sawtooth wave and converts it into an analog voltage.
Conclusion
Sawtooth wave generators are versatile circuits that produce a specific type of waveform with a linear ramp followed by a sharp drop. They find applications in various fields, including audio synthesis, test equipment, and control systems. Understanding the different types of sawtooth wave generators, their design considerations, and troubleshooting techniques is essential for effectively utilizing these circuits in practical applications.
By exploring the concepts and principles behind sawtooth wave generators, designers and engineers can harness their capabilities to create innovative solutions in electronics and signal processing. As technology continues to advance, the importance of sawtooth wave generators in shaping the future of electronic systems remains significant.
No responses yet