Introduction to Requirements Management and QFD
Requirements management is a critical process in product development that involves identifying, documenting, analyzing, prioritizing, and tracking requirements throughout the product lifecycle. It ensures that the final product meets the needs and expectations of stakeholders, including customers, users, and regulatory bodies. Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is a powerful tool that complements requirements management by translating customer requirements into technical specifications and prioritizing them based on their importance to the customer.
What is Requirements Management?
Requirements management is the process of managing the requirements of a product, system, or service throughout its lifecycle. It involves the following activities:
- Eliciting requirements from stakeholders
- Documenting requirements in a clear and concise manner
- Analyzing requirements for completeness, consistency, and feasibility
- Prioritizing requirements based on their importance and urgency
- Tracking requirements throughout the product development process
- Validating requirements against the final product
Effective requirements management ensures that the product meets the needs of stakeholders and reduces the risk of project failure due to incomplete or incorrect requirements.
What is Quality Function Deployment (QFD)?
Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is a structured approach to translating customer requirements into technical specifications for a product or service. It involves the following steps:
- Identifying customer requirements (Voice of the Customer)
- Prioritizing customer requirements based on their importance
- Translating customer requirements into technical specifications
- Identifying relationships between customer requirements and technical specifications
- Prioritizing technical specifications based on their importance to the customer
QFD helps to ensure that the product design is driven by customer needs and that the most important requirements are given the highest priority.
The Requirements Management Process
The requirements management process consists of the following steps:
1. Requirements Elicitation
Requirements elicitation involves gathering requirements from stakeholders, including customers, users, and regulatory bodies. This can be done through various techniques such as interviews, surveys, focus groups, and observation. The goal is to identify the needs and expectations of stakeholders and to document them in a clear and concise manner.
2. Requirements Documentation
Requirements documentation involves creating a written record of the requirements gathered during the elicitation phase. This document should be clear, concise, and unambiguous, and should include the following information:
- A unique identifier for each requirement
- A description of the requirement
- The priority of the requirement
- The source of the requirement
- Any dependencies or constraints associated with the requirement
3. Requirements Analysis
Requirements analysis involves reviewing the documented requirements for completeness, consistency, and feasibility. This involves identifying any missing or conflicting requirements, as well as assessing the technical and financial feasibility of implementing the requirements.
4. Requirements Prioritization
Requirements prioritization involves ranking the requirements based on their importance and urgency. This can be done using various techniques such as the MoSCoW method (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won’t have) or the Kano model (Basic, Performance, Excitement). The goal is to ensure that the most important requirements are given the highest priority and are implemented first.
5. Requirements Tracking
Requirements tracking involves monitoring the progress of requirements throughout the product development process. This involves ensuring that requirements are being implemented as planned and that any changes to requirements are documented and communicated to stakeholders.
6. Requirements Validation
Requirements validation involves testing the final product against the documented requirements to ensure that it meets the needs and expectations of stakeholders. This can be done through various techniques such as acceptance testing, user testing, and beta testing.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD)
Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is a structured approach to translating customer requirements into technical specifications for a product or service. It involves the following steps:
1. Identifying Customer Requirements (Voice of the Customer)
The first step in QFD is to identify the requirements of the customer, also known as the Voice of the Customer (VOC). This can be done through various techniques such as interviews, surveys, and focus groups. The goal is to understand the needs and expectations of the customer and to document them in a clear and concise manner.
2. Prioritizing Customer Requirements
Once the customer requirements have been identified, the next step is to prioritize them based on their importance to the customer. This can be done using various techniques such as the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) or the Pairwise Comparison method. The goal is to ensure that the most important requirements are given the highest priority.
3. Translating Customer Requirements into Technical Specifications
The next step in QFD is to translate the customer requirements into technical specifications for the product or service. This involves identifying the technical characteristics that are necessary to meet the customer requirements and defining them in measurable terms.
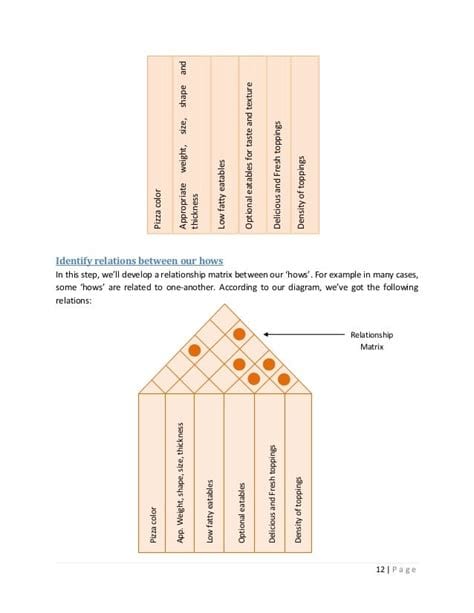
4. Identifying Relationships between Customer Requirements and Technical Specifications
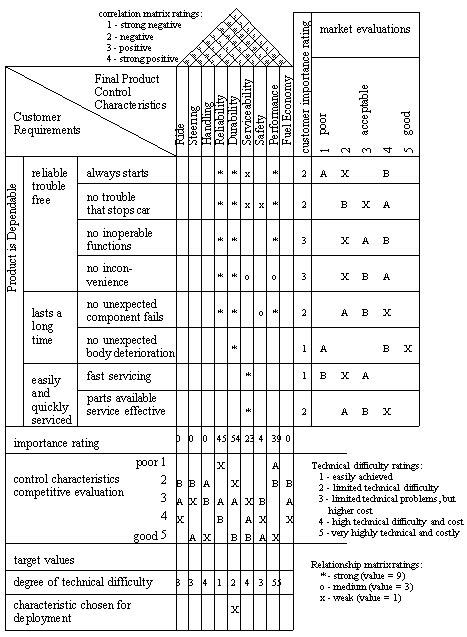
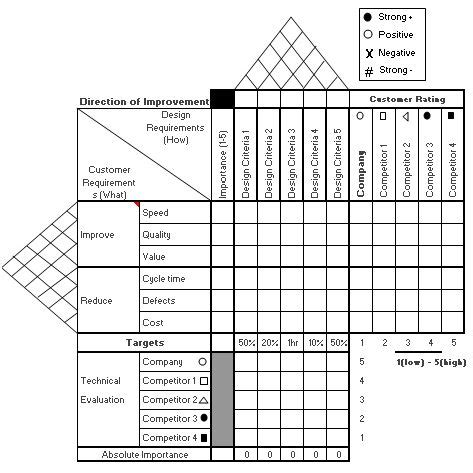
Once the customer requirements and technical specifications have been identified, the next step is to identify the relationships between them. This involves creating a matrix, known as the House of Quality, which shows how each customer requirement is related to each technical specification.
5. Prioritizing Technical Specifications
The final step in QFD is to prioritize the technical specifications based on their importance to the customer. This involves using the relationships identified in the House of Quality to determine which technical specifications are most important for meeting the customer requirements.

Benefits of Requirements Management and QFD
Effective requirements management and QFD offer several benefits to organizations, including:
-
Improved customer satisfaction: By ensuring that the product meets the needs and expectations of customers, organizations can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-
Reduced development time and cost: By identifying and prioritizing requirements early in the development process, organizations can reduce the time and cost associated with rework and changes later in the process.
-
Improved product quality: By ensuring that the product meets the specified requirements, organizations can improve the overall quality of the product.
-
Better communication and collaboration: By involving stakeholders throughout the requirements management and QFD processes, organizations can improve communication and collaboration between teams and departments.
-
Reduced risk: By identifying and mitigating risks associated with requirements early in the development process, organizations can reduce the overall risk of project failure.
Challenges of Requirements Management and QFD
While requirements management and QFD offer many benefits, there are also several challenges associated with these processes, including:
-
Complexity: Requirements management and QFD can be complex and time-consuming processes, particularly for large and complex projects.
-
Stakeholder involvement: Ensuring that all stakeholders are involved in the requirements management and QFD processes can be challenging, particularly when stakeholders have conflicting needs and priorities.
-
Changing requirements: Requirements can change throughout the product development process, which can be challenging to manage and can impact the overall project timeline and budget.
-
Limited resources: Organizations may have limited resources available for requirements management and QFD activities, which can impact the effectiveness of these processes.
-
Lack of expertise: Requirements management and QFD require specialized skills and knowledge, which may not be available within the organization.
Best Practices for Requirements Management and QFD
To overcome the challenges associated with requirements management and QFD and to ensure the success of these processes, organizations should follow these best practices:
-
Involve stakeholders early and often: Ensure that all stakeholders are involved in the requirements management and QFD processes from the beginning and throughout the product development lifecycle.
-
Use a structured approach: Use a structured approach, such as the Requirements Management Process and the QFD process, to ensure that requirements are identified, documented, analyzed, prioritized, and tracked effectively.
-
Prioritize requirements: Prioritize requirements based on their importance and urgency to ensure that the most important requirements are given the highest priority and are implemented first.
-
Communicate effectively: Ensure that requirements are communicated effectively to all stakeholders, including development teams, testing teams, and management.
-
Manage change: Establish a change management process to ensure that changes to requirements are documented, communicated, and managed effectively.
-
Measure and monitor: Establish metrics to measure the effectiveness of the requirements management and QFD processes and to monitor progress throughout the product development lifecycle.
-
Provide training and support: Provide training and support to team members involved in requirements management and QFD activities to ensure that they have the necessary skills and knowledge to perform these activities effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between requirements management and requirements engineering?
Requirements management is the process of managing requirements throughout the product development lifecycle, while requirements engineering is the process of eliciting, analyzing, and documenting requirements. Requirements engineering is a subset of requirements management.
2. What is the House of Quality in QFD?
The House of Quality is a matrix used in QFD to identify the relationships between customer requirements and technical specifications. It helps to prioritize technical specifications based on their importance to the customer.
3. What are some common techniques for requirements elicitation?
Common techniques for requirements elicitation include interviews, surveys, focus groups, observation, and document analysis.
4. What is the MoSCoW method for requirements prioritization?
The MoSCoW method is a technique for prioritizing requirements based on their importance and urgency. Requirements are categorized as Must have, Should have, Could have, or Won’t have.
5. What is the role of requirements traceability in requirements management?
Requirements traceability is the ability to trace requirements throughout the product development lifecycle, from elicitation to validation. It helps to ensure that requirements are being implemented as planned and that any changes to requirements are documented and communicated to stakeholders.
Conclusion
Requirements management and Quality Function Deployment (QFD) are critical processes in product development that help to ensure that the final product meets the needs and expectations of stakeholders. Effective requirements management involves eliciting, documenting, analyzing, prioritizing, tracking, and validating requirements throughout the product lifecycle. QFD is a powerful tool that complements requirements management by translating customer requirements into technical specifications and prioritizing them based on their importance to the customer.
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Requirements Elicitation | Gathering requirements from stakeholders |
| Requirements Documentation | Creating a written record of requirements |
| Requirements Analysis | Reviewing requirements for completeness, consistency, and feasibility |
| Requirements Prioritization | Ranking requirements based on importance and urgency |
| Requirements Tracking | Monitoring progress of requirements throughout product development |
| Requirements Validation | Testing final product against documented requirements |
To overcome the challenges associated with requirements management and QFD and to ensure the success of these processes, organizations should follow best practices such as involving stakeholders early and often, using a structured approach, prioritizing requirements, communicating effectively, managing change, measuring and monitoring progress, and providing training and support to team members.
By effectively managing requirements and using QFD to prioritize customer needs, organizations can improve customer satisfaction, reduce development time and cost, improve product quality, and reduce the risk of project failure.
No responses yet