Introduction to PCB Manufacturing
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics. They are used in almost every electronic device, from smartphones and computers to medical equipment and aerospace systems. PCB manufacturing is a complex process that involves multiple steps, including design, fabrication, assembly, and testing. In this article, we will explore the world of PCB manufacturing in the United States, focusing on the key aspects of the industry, its trends, and challenges.
What is a PCB?
A PCB is a flat board made of insulating materials, such as fiberglass or plastic, with conductive pathways etched on its surface. These pathways, also known as traces, connect various electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits (ICs), to form a functional electronic circuit. PCBs come in various types, including:
- Single-sided PCBs: These have conductive traces on only one side of the board.
- Double-sided PCBs: These have conductive traces on both sides of the board, with through-hole connections linking the two sides.
- Multi-layer PCBs: These consist of multiple layers of conductive traces separated by insulating layers, allowing for more complex circuit designs and higher component density.
The PCB Manufacturing Process
The PCB manufacturing process typically involves the following steps:
-
Design: The PCB design is created using specialized software, such as Altium Designer or Eagle. The design includes the placement of components, routing of traces, and creation of solder masks and silkscreen layers.
-
Fabrication: The PCB fabrication process begins with the creation of a photomask, which is used to transfer the circuit pattern onto the copper-clad board. The board is then coated with a photoresist layer, exposed to UV light through the photomask, and developed to remove the unexposed areas. The exposed copper is etched away, leaving only the desired circuit pattern. This process is repeated for each layer of the PCB.
-
Drilling: Holes are drilled into the PCB to accommodate through-hole components and to create vias, which are used to connect traces on different layers.
-
Plating: The drilled holes are plated with copper to ensure electrical connectivity between layers.
-
Solder Mask and Silkscreen: A solder mask is applied to the PCB to protect the copper traces from oxidation and to prevent solder bridges during the assembly process. A silkscreen layer is added to provide labels and markings for components and test points.
-
Surface Finishing: The exposed copper areas, such as pads and plated through-holes, are coated with a protective finish, such as HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), or OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative), to improve solderability and prevent oxidation.
-
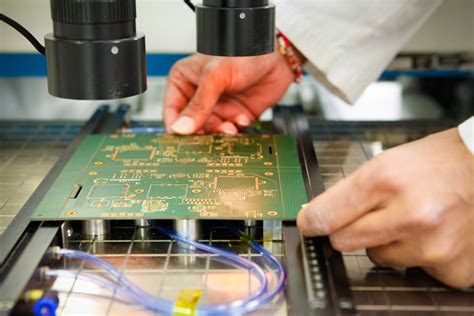
Assembly: The electronic components are placed on the PCB and soldered into place using either through-hole or Surface-Mount Technology (SMT).
-
Testing: The assembled PCB undergoes various tests, such as in-circuit testing (ICT), functional testing, and boundary scan testing, to ensure proper functionality and reliability.
The US PCB Manufacturing Industry
The United States has a long history of PCB manufacturing, dating back to the 1950s. However, in recent decades, the industry has faced significant challenges due to globalization and the rise of low-cost manufacturing in countries like China and Taiwan. Despite these challenges, the US PCB manufacturing industry remains a significant player in the global market, with a focus on high-quality, high-reliability, and quick-turn production.
Market Size and Trends
According to a report by Grand View Research, the global PCB market size was valued at USD 60.2 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2021 to 2028. The US PCB market is a significant contributor to this growth, driven by factors such as the increasing demand for high-end electronics, the growing automotive and aerospace industries, and the resurgence of domestic manufacturing.
| Year | Global PCB Market Size (USD Billion) | US PCB Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 60.2 | 12.5% |
| 2021 | 62.8 | 12.7% |
| 2022 | 65.5 | 12.9% |
| 2023 | 68.4 | 13.1% |
| 2024 | 71.4 | 13.3% |
| 2025 | 74.6 | 13.5% |
| 2026 | 77.9 | 13.7% |
| 2027 | 81.4 | 13.9% |
| 2028 | 85.1 | 14.1% |
Key Players in the US PCB Manufacturing Industry
The US PCB manufacturing industry is dominated by a mix of large, established companies and smaller, specialized manufacturers. Some of the key players include:
-
TTM Technologies: TTM is the largest PCB manufacturer in North America, with a focus on high-technology applications in the aerospace, defense, and medical industries.
-
Sanmina: Sanmina is a global electronics manufacturing services (EMS) provider with a significant presence in the US PCB market, serving customers in the communications, computing, medical, and automotive industries.
-
Benchmark Electronics: Benchmark is another EMS provider with a strong presence in the US PCB market, specializing in high-reliability applications for the aerospace, defense, and medical industries.
-
Sunstone Circuits: Sunstone is a smaller, specialized PCB manufacturer that focuses on quick-turn prototyping and low-volume production for a wide range of industries.
-
Advanced Circuits: Advanced Circuits is a leading supplier of quick-turn PCBs, offering a range of services from prototyping to medium-volume production.
Challenges and Opportunities
The US PCB manufacturing industry faces several challenges, including:
-
Competition from low-cost countries: The rise of low-cost manufacturing in countries like China and Taiwan has put pressure on US PCB manufacturers to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
-
Skilled labor shortage: The aging workforce and the lack of interest among younger generations in manufacturing careers have led to a shortage of skilled labor in the industry.
-
Supply chain disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains, leading to raw material shortages and increased lead times for PCB manufacturers.
Despite these challenges, the US PCB manufacturing industry also has several opportunities for growth and innovation:
-
Reshoring: The pandemic has accelerated the trend of reshoring, as companies seek to reduce their dependence on overseas suppliers and shorten supply chains. This presents an opportunity for US PCB manufacturers to capture a larger share of the domestic market.
-
Advanced technologies: The increasing demand for high-performance electronics in industries such as 5G, autonomous vehicles, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is driving the adoption of advanced PCB technologies, such as high-density interconnect (HDI), flexible, and Rigid-flex PCBs.
-
Automation and digitalization: Investments in automation and digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), can help US PCB manufacturers improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance quality control.
FAQ
-
What is the difference between through-hole and surface-mount technology (SMT) in PCB assembly?
Through-hole technology involves inserting component leads through drilled holes in the PCB and soldering them on the opposite side. SMT, on the other hand, involves placing components directly onto the surface of the PCB and soldering them in place. SMT allows for smaller components and higher component density, while through-hole technology is more robust and better suited for high-power applications. -
What are the advantages of using a US-based PCB manufacturer?
Using a US-based PCB manufacturer offers several advantages, including faster turnaround times, better communication, higher quality control standards, and easier intellectual property (IP) protection. Additionally, US-based manufacturers are more likely to comply with strict environmental and safety regulations, ensuring a more sustainable and ethical production process. -
How can I choose the right PCB manufacturer for my project?
When choosing a PCB manufacturer, consider factors such as their experience, capabilities, certifications (e.g., ISO, UL, IPC), and reputation. Look for manufacturers that specialize in your industry or application, and request quotes and samples from multiple suppliers to compare pricing and quality. Also, consider their customer support, lead times, and minimum order quantities (MOQs) to ensure they align with your project requirements. -
What are the main factors affecting the cost of PCB manufacturing?
The cost of PCB manufacturing depends on several factors, including the board size, layer count, material type, surface finish, component density, and order quantity. Generally, larger boards, higher layer counts, and more complex designs will increase the cost. Choosing the right material and surface finish for your application can also impact the cost. Finally, ordering in larger quantities can often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. -
What are the current trends in PCB manufacturing technology?
Some of the current trends in PCB manufacturing technology include the adoption of advanced materials, such as high-frequency laminates and thermal management solutions, the increasing use of HDI and embedded component technologies, and the growth of flexible and rigid-flex PCBs for wearable and IoT applications. Additionally, there is a growing focus on sustainability, with manufacturers exploring eco-friendly materials and processes to reduce their environmental impact.

Conclusion
PCB manufacturing is a critical industry that plays a vital role in the development and production of modern electronics. The US PCB manufacturing industry, despite facing challenges from globalization and low-cost competition, remains a significant player in the global market, with a focus on high-quality, high-reliability, and quick-turn production.
As the demand for advanced electronics continues to grow, driven by trends such as 5G, autonomous vehicles, and the IoT, US PCB manufacturers have the opportunity to innovate and adapt to meet the evolving needs of their customers. By investing in advanced technologies, automation, and digitalization, and by focusing on sustainability and ethical production practices, the US PCB manufacturing industry can remain competitive and continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of electronics.

No responses yet