Introduction to PCB Cross-Section Analysis
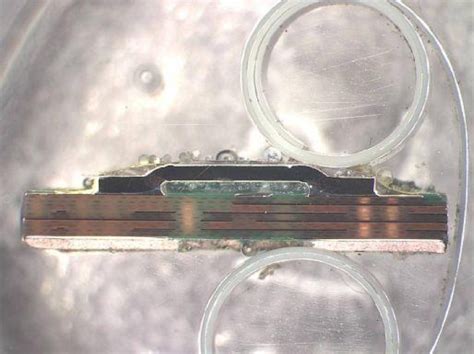
PCB cross-section analysis is a crucial technique used in the quality control and failure analysis of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This process involves cutting a small portion of the PCB and examining the internal structure, layers, and components under a microscope. By analyzing the cross-section, engineers and technicians can identify manufacturing defects, material anomalies, and potential reliability issues that may affect the performance and longevity of the PCB.
In this article, we will delve into the world of PCB cross-section analysis, exploring its importance, techniques, and applications. We will also discuss the equipment and tools used in this process and provide insights into interpreting the results.
Why Is PCB Cross-Section Analysis Important?
PCB cross-section analysis plays a vital role in ensuring the quality, reliability, and functionality of PCBs. Here are some key reasons why this technology is essential:
-
Quality Control: Cross-section analysis allows manufacturers to verify that the PCB fabrication process meets the specified design requirements and industry standards. By examining the internal structure, they can identify any manufacturing defects, such as voids, delamination, or improper plating, and take corrective actions to improve the production process.
-
Failure Analysis: When a PCB fails or malfunctions, cross-section analysis is often used to determine the root cause of the problem. By examining the cross-section, engineers can identify issues such as cracked solder joints, broken traces, or component defects that may have led to the failure. This information is crucial for implementing corrective measures and preventing similar failures in the future.
-
Material Characterization: Cross-section analysis enables engineers to study the properties and characteristics of the materials used in the PCB. They can evaluate the quality of the copper plating, the uniformity of the dielectric layers, and the adhesion between different materials. This information helps in selecting the appropriate materials and optimizing the PCB design for better performance and reliability.
-
Compliance with Industry Standards: Many industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, have stringent quality and reliability requirements for PCBs. Cross-section analysis is often used to demonstrate compliance with these standards and ensure that the PCBs meet the necessary specifications.
Techniques Used in PCB Cross-Section Analysis
Several techniques are employed in PCB cross-section analysis to obtain accurate and meaningful results. Let’s explore some of the most common methods:
1. Mechanical Sectioning
Mechanical sectioning involves cutting a small portion of the PCB using a precision saw or a grinding tool. The sample is then mounted in a resin or epoxy material to provide support and stability during the subsequent grinding and polishing processes. The mounted sample is gradually ground and polished using progressively finer abrasive materials until a smooth, mirror-like surface is achieved.
2. Ion Milling
Ion milling is a more advanced technique that uses a focused ion beam (FIB) to remove material from the PCB sample. This method allows for precise and localized sectioning, making it suitable for analyzing specific areas of interest or small features. Ion milling produces a clean and smooth cross-section surface without the need for extensive grinding and polishing.
3. Plasma Etching
Plasma etching is another technique used to prepare PCB cross-sections. In this method, the sample is exposed to a plasma containing reactive gases that selectively etch away the material. Plasma etching is particularly useful for revealing the internal structure of the PCB, such as the vias, traces, and dielectric layers, without causing mechanical damage or deformation.

Equipment and Tools Used in PCB Cross-Section Analysis
To perform PCB cross-section analysis effectively, several specialized equipment and tools are required. Here are some of the essential items:
-
Precision Saw or Grinding Tool: These tools are used for the initial cutting and grinding of the PCB sample. They should have high precision and the ability to produce clean and accurate cuts without causing excessive damage or deformation to the sample.
-
Mounting Press: A mounting press is used to embed the PCB sample in a resin or epoxy material. The press applies pressure and heat to ensure a secure and uniform mounting of the sample.
-
Grinding and Polishing Machine: This machine is used to gradually grind and polish the mounted sample until a smooth and mirror-like surface is achieved. It typically includes a series of abrasive pads with decreasing grit sizes to progressively refine the surface.
-
Microscope: A high-quality microscope is essential for examining the cross-section at various magnifications. Optical microscopes are commonly used for general inspection, while scanning electron microscopes (SEM) provide higher resolution and depth of field for detailed analysis.
-
Imaging and Measurement Software: Specialized software is used to capture, process, and analyze the microscope images. These tools allow for accurate measurements, feature dimensioning, and documentation of the cross-section analysis results.
Interpreting PCB Cross-Section Analysis Results
Interpreting the results of PCB cross-section analysis requires knowledge and experience in PCB manufacturing and materials science. Here are some key aspects to consider when analyzing the cross-section:
-
Layer Thickness and Uniformity: Examine the thickness and uniformity of the copper layers, dielectric layers, and solder mask. Ensure that they meet the specified design requirements and are consistent throughout the sample.
-
Plating Quality: Evaluate the quality of the copper plating in the vias and traces. Look for any voids, inclusions, or irregular plating that may affect the electrical conductivity and reliability of the PCB.
-
Solder Joint Integrity: Assess the quality of the solder joints between components and pads. Check for any cracks, voids, or insufficient solder coverage that may lead to mechanical or electrical failures.
-
Dielectric Material Integrity: Examine the dielectric materials for any signs of delamination, voids, or cracks. These defects can compromise the insulation properties and lead to short circuits or signal integrity issues.
-
Component Placement and Alignment: Verify the correct placement and alignment of components on the PCB. Ensure that the components are properly seated and make good contact with the pads.
Applications of PCB Cross-Section Analysis
PCB cross-section analysis finds applications in various industries and sectors where PCB reliability and performance are critical. Some notable applications include:
-
Aerospace and Defense: In these industries, PCBs are subjected to harsh environmental conditions and must meet stringent reliability requirements. Cross-section analysis is used to ensure that the PCBs can withstand the rigors of operation and maintain their functionality over extended periods.
-
Automotive Electronics: Modern vehicles rely heavily on electronic systems for safety, control, and entertainment functions. Cross-section analysis is employed to validate the quality and reliability of Automotive PCBs, ensuring they can operate reliably in challenging conditions such as temperature extremes, vibration, and moisture exposure.
-
Medical Devices: PCBs used in medical devices must meet strict quality and safety standards to ensure patient safety and accurate diagnosis or treatment. Cross-section analysis is used to verify the manufacturing quality and long-term reliability of these critical components.
-
Consumer Electronics: With the increasing complexity and miniaturization of consumer electronics, PCB reliability is paramount. Cross-section analysis is used to identify potential failure modes and optimize the PCB design for improved durability and performance.
-
Industrial Equipment: PCBs used in industrial equipment, such as control systems, sensors, and power electronics, must withstand harsh operating conditions and maintain reliable operation. Cross-section analysis helps in identifying design weaknesses and manufacturing defects that could lead to premature failures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the purpose of PCB cross-section analysis?
PCB cross-section analysis is performed to examine the internal structure, layers, and components of a PCB. It helps in identifying manufacturing defects, material anomalies, and potential reliability issues, ensuring the quality and functionality of the PCB. -
How is a PCB sample prepared for cross-section analysis?
A PCB sample is typically cut using a precision saw or grinding tool, mounted in a resin or epoxy material, and then gradually ground and polished until a smooth, mirror-like surface is achieved. Ion milling and plasma etching are also used for more advanced sample preparation. -
What equipment is needed for PCB cross-section analysis?
The essential equipment for PCB cross-section analysis includes a precision saw or grinding tool, mounting press, grinding and polishing machine, microscope, and imaging and measurement software. These tools enable accurate sample preparation, examination, and analysis. -
What are some common defects that can be identified through cross-section analysis?
Cross-section analysis can reveal defects such as voids, delamination, improper plating, cracked solder joints, broken traces, and component misalignment. These defects can affect the electrical performance, mechanical integrity, and reliability of the PCB. -
In which industries is PCB cross-section analysis commonly used?
PCB cross-section analysis is widely used in industries such as aerospace, defense, automotive, medical devices, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment. These industries have stringent quality and reliability requirements for PCBs, and cross-section analysis helps in ensuring compliance and optimizing PCB design and manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
PCB cross-section analysis is a powerful technology that enables manufacturers, engineers, and technicians to gain valuable insights into the internal structure and quality of PCBs. By examining the cross-section, they can identify manufacturing defects, material anomalies, and potential reliability issues, ensuring the production of high-quality and reliable PCBs.
This article has provided an overview of PCB cross-section analysis, covering its importance, techniques, equipment, and applications. We have also discussed the interpretation of cross-section analysis results and answered some frequently asked questions.
As PCB technology continues to advance and the demand for reliable electronic systems grows, PCB cross-section analysis will remain an essential tool for quality control, failure analysis, and product improvement. By leveraging this technology, manufacturers can enhance the performance, durability, and safety of their PCBs, ultimately benefiting various industries and end-users.
No responses yet