Understanding the Key Factors Influencing PCB Costs
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in electronic devices, connecting and supporting various electronic components. As businesses strive to remain competitive, optimizing PCB costs becomes crucial. This article explores the primary cost drivers in PCB manufacturing and provides strategies for designing cost-effective PCBs.
Material Selection
The choice of materials significantly impacts PCB costs. The most common PCB substrate is FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. However, specialized applications may require high-frequency materials like Rogers or Isola, which come at a higher cost. Carefully consider your application’s requirements and select materials accordingly.
| Material | Relative Cost | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | Low | Standard, versatile |
| Rogers | High | High-frequency, low-loss |
| Isola | Medium | High-performance, heat-resistant |
Board Complexity
PCB complexity directly affects manufacturing costs. Factors contributing to complexity include:
- Layer count
- Via types (through-hole, blind, buried)
- Trace width and spacing
- Component density
Simplifying the board design, whenever possible, can lead to significant cost savings. Consider the following strategies:
- Minimize the number of layers
- Use standard via types
- Adhere to recommended trace width and spacing guidelines
- Optimize component placement for manufacturing efficiency
Manufacturing Process
The choice of manufacturing process also influences PCB costs. Two common methods are:
- Through-hole technology (THT)
- Surface mount technology (SMT)
SMT is generally more cost-effective due to its higher automation and smaller component sizes. However, some components may only be available in through-hole packages, necessitating a mix of both technologies. Whenever feasible, opt for SMT to reduce manufacturing costs.
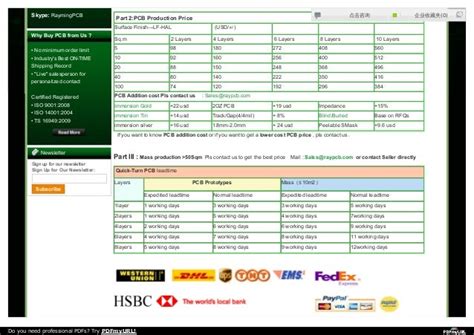
Order Quantity
PCB production involves fixed setup costs, which are distributed across the total number of boards ordered. As a result, ordering larger quantities can significantly reduce the per-unit cost. Consider your production volume and future requirements when placing orders to take advantage of economies of scale.
| Order Quantity | Relative Per-Unit Cost |
|---|---|
| 1-50 | High |
| 51-250 | Medium |
| 251-1000 | Low |
| 1000+ | Very Low |
Design Strategies for Cost Optimization
Standardization
Standardizing PCB designs across multiple products or projects can lead to cost savings. By reusing proven designs, you can reduce design time, minimize errors, and leverage existing manufacturing setups. Create a library of standard components, footprints, and layouts to streamline the design process and reduce costs.
Panelization
Panelization involves grouping multiple PCBs onto a single panel for manufacturing. This approach minimizes material waste and reduces handling time, resulting in lower production costs. When designing panels, consider the following:
- Optimize panel utilization by minimizing unused space
- Ensure adequate spacing between boards for depaneling
- Include fiducial marks for accurate placement and alignment
Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
Designing with manufacturing in mind can significantly reduce costs and improve production yields. Follow these DFM guidelines:
- Adhere to the manufacturer’s design rules and tolerances
- Avoid sharp corners and acute angles in traces
- Provide adequate clearances for components and vias
- Use standard component packages and footprints
Collaborating with your PCB manufacturer early in the design process can help identify potential issues and optimize the design for cost-effective production.
Component Selection
Component selection plays a crucial role in PCB cost optimization. Consider the following strategies:
- Use readily available, industry-standard components
- Minimize the variety of components used
- Select components with compatible packaging and footprints
- Opt for surface-mount devices (SMDs) whenever possible
By carefully selecting components, you can reduce sourcing costs, minimize inventory, and streamline the assembly process.
Cost-Saving Techniques in PCB Assembly
Automated Assembly
Automated PCB assembly, such as pick-and-place machines and reflow soldering, can significantly reduce labor costs and improve production efficiency. Invest in automation or partner with assembly providers that utilize automated processes to minimize manual intervention and reduce overall assembly costs.
Optimization of Solder Paste Stencils
Solder paste stencils are used to apply solder paste onto PCB pads during the SMT assembly process. Optimizing stencil design can minimize solder paste waste and improve the quality of solder joints. Consider the following:
- Use the appropriate stencil thickness for the component pitch
- Optimize aperture sizes and shapes for consistent paste deposition
- Include fiducial marks for accurate stencil alignment
Collaborating with your assembly partner to optimize solder paste stencils can lead to cost savings and improved assembly yields.
In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
In-Circuit Testing is an automated testing method that verifies the functionality of individual components and their interconnections on a PCB. Implementing ICT can help identify defects early in the production process, reducing rework costs and improving overall quality. Consider designing test points and incorporating ICT fixtures into your PCB design to facilitate efficient testing.

FAQ
1. What are the primary factors influencing PCB costs?
The primary factors influencing PCB costs include material selection, board complexity, manufacturing process, and order quantity. Material choice, such as FR-4 or high-frequency laminates, directly impacts costs. Board complexity, determined by factors like layer count and via types, also affects pricing. The manufacturing process (THT or SMT) and order quantity contribute to overall costs.
2. How can I reduce PCB costs through design optimization?
To reduce PCB costs through design optimization, consider the following strategies:
- Standardize designs across multiple products or projects
- Utilize panelization to minimize material waste
- Follow Design for Manufacturing (DFM) guidelines
- Select readily available, industry-standard components
- Minimize the variety of components used
Implementing these strategies can help streamline the design process, reduce manufacturing costs, and improve production efficiency.
3. What role does component selection play in PCB cost optimization?
Component selection significantly influences PCB costs. To optimize costs, consider using readily available, industry-standard components and minimizing the variety of components used. Select components with compatible packaging and footprints, and opt for surface-mount devices (SMDs) whenever possible. Careful component selection can reduce sourcing costs, minimize inventory, and streamline the assembly process.
4. How can automated assembly help reduce PCB costs?
Automated PCB assembly, such as pick-and-place machines and reflow soldering, can significantly reduce labor costs and improve production efficiency. By minimizing manual intervention, automated processes can lead to faster assembly times and reduced human error. Investing in automation or partnering with assembly providers that utilize automated processes can help lower overall assembly costs.
5. What is the importance of collaborating with PCB manufacturers and assembly partners?
Collaborating with PCB manufacturers and assembly partners early in the design process is crucial for cost optimization. Manufacturers can provide valuable insights into design rules, tolerances, and potential issues that may impact production costs. Assembly partners can offer guidance on optimizing solder paste stencils, component placement, and testing strategies. By working closely with these partners, you can identify cost-saving opportunities and ensure a smooth transition from design to manufacturing.
Conclusion
PCB cost optimization is a critical aspect of electronics manufacturing. By understanding the key cost drivers and implementing design strategies focused on cost reduction, businesses can significantly improve their bottom line. Material selection, board complexity, manufacturing process, and order quantity are among the primary factors influencing PCB costs.
To optimize costs, designers should consider standardizing designs, utilizing panelization, following DFM guidelines, and carefully selecting components. Automated assembly processes and collaboration with PCB manufacturers and assembly partners can further contribute to cost savings.
By adopting a holistic approach to PCB cost optimization, companies can streamline their design and manufacturing processes, reduce overall costs, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.

No responses yet