What is an LM386 Amplifier?
The LM386 is a low-voltage audio power amplifier IC designed for use in low-power consumer applications. It is an 8-pin DIP (Dual Inline Package) or SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) package that requires minimal external components, making it easy to integrate into various audio projects. The IC can operate on a wide range of supply voltages, from 4V to 12V for the standard version (LM386N-1) and up to 18V for the high-voltage version (LM386N-3), allowing it to be used in battery-powered devices as well as AC-powered systems.
Key Features of the LM386 Amplifier
- Low quiescent current drain: 4mA
- Wide supply voltage range: 4V to 12V (LM386N-1) or 5V to 18V (LM386N-3)
- Low distortion: 0.2% at 1kHz, 0.5W
- Voltage gains from 20 to 200
- Input impedance: 50kΩ
- Output impedance: 1.2Ω (at 1kHz)
- Power output: up to 1.25W (at 8Ω load, 12V supply)
- Built-in thermal protection and short-circuit protection
Understanding the LM386 Pinout and Internal Schematic
To effectively use the LM386 in your projects, it’s essential to understand its pinout and internal schematic. The LM386 has 8 pins, each with a specific function:
| Pin | Function |
|---|---|
| 1 | Gain 1 |
| 2 | Inverting Input |
| 3 | Non-Inverting Input |
| 4 | Ground |
| 5 | Output |
| 6 | Vs (Positive Supply Voltage) |
| 7 | Bypass |
| 8 | Gain 2 |
The internal schematic of the LM386 consists of a differential amplifier input stage, followed by a voltage amplification stage and a class AB output stage. The gain of the amplifier is internally set to 20 (26dB) but can be increased up to 200 (46dB) by adding an external capacitor between pins 1 and 8.
Basic LM386 Amplifier Circuit
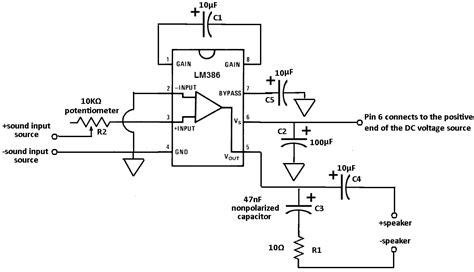
A basic LM386 amplifier circuit can be built using minimal external components. Here’s an example of a simple LM386 amplifier circuit:
[Insert basic LM386 amplifier circuit diagram]
Components:
– LM386 IC
– 10μF electrolytic capacitor (C1)
– 0.1μF ceramic capacitor (C2)
– 10Ω resistor (R1)
– 100μF electrolytic capacitor (C3)
– 220μF electrolytic capacitor (C4)
– 8Ω speaker
In this circuit, the input signal is coupled to the non-inverting input (pin 3) of the LM386 through the 0.1μF capacitor (C2). The 10μF capacitor (C1) serves as a power supply decoupling capacitor, while the 10Ω resistor (R1) and 100μF capacitor (C3) form a Zobel network to ensure amplifier stability and prevent oscillations. The output of the LM386 (pin 5) is connected to the 8Ω speaker through the 220μF capacitor (C4), which acts as a DC-blocking capacitor.

Advanced LM386 Amplifier Configurations
While the basic LM386 amplifier circuit is suitable for many applications, there are several advanced configurations that can enhance the amplifier’s performance, such as:
- Increasing the gain
- Adding bass boost
- Reducing noise and distortion
- Bridging two LM386 ICs for higher power output
Increasing the Gain
As mentioned earlier, the gain of the LM386 can be increased from 20 to 200 by adding a capacitor between pins 1 and 8. The value of the capacitor determines the gain, as shown in the table below:
| Capacitor Value | Gain |
|---|---|
| No capacitor | 20 |
| 10pF | 50 |
| 100pF | 100 |
| 1nF | 150 |
| 10nF | 200 |
To increase the gain, simply add the appropriate capacitor between pins 1 and 8 of the LM386.
Adding Bass Boost
To enhance the bass response of the LM386 amplifier, you can add a bass boost circuit by connecting a series RC network between pins 1 and 5. The values of the resistor and capacitor determine the frequency and magnitude of the bass boost. A typical bass boost circuit for the LM386 might use a 10kΩ resistor and a 0.1μF capacitor, which provides a 6dB boost at around 100Hz.
Reducing Noise and Distortion
To minimize noise and distortion in the LM386 amplifier, consider the following tips:
- Use a regulated power supply to minimize power supply noise.
- Keep the input signal level within the linear range of the amplifier to avoid clipping.
- Use a low-noise op-amp or preamp to buffer the input signal before feeding it to the LM386.
- Use high-quality, low-ESR capacitors for power supply decoupling and output coupling.
- Minimize the length of the leads between the LM386 and the speaker to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Bridging Two LM386 ICs for Higher Power Output
For applications that require higher power output, you can bridge two LM386 ICs to effectively double the output power. In a bridged configuration, one LM386 amplifies the input signal, while the other amplifies an inverted version of the input signal. The outputs of the two ICs are then connected to opposite ends of the speaker, resulting in a push-pull configuration that increases the available output power.
[Insert bridged LM386 amplifier circuit diagram]
LM386 Amplifier Applications
The versatility and simplicity of the LM386 make it suitable for a wide range of audio applications, such as:
- Portable audio devices (e.g., headphone amplifiers, portable speakers)
- Guitar and instrument amplifiers
- Intercoms and paging systems
- Alarm systems
- Automotive audio systems
- Toy and novelty sound effects
Troubleshooting Common LM386 Amplifier Issues
When working with LM386 amplifiers, you may encounter some common issues. Here are a few troubleshooting tips to help you resolve these problems:
- No sound output:
- Check the power supply voltage and polarity
- Verify that the input signal is present and connected correctly
- Ensure that the speaker is connected correctly and functioning properly
- Distorted sound:
- Reduce the input signal level to avoid clipping
- Check for loose or faulty connections
- Ensure that the power supply voltage is within the recommended range
- Excessive noise or hum:
- Use shielded cables for input signals
- Ensure proper grounding of the circuit
- Use a regulated power supply to minimize noise
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Can I use the LM386 with a single power supply?
A: Yes, the LM386 is designed to operate with a single power supply, making it suitable for battery-powered applications. -
Q: What is the maximum power output of the LM386?
A: The maximum power output of the LM386 depends on the supply voltage and load impedance. With a 12V supply and an 8Ω load, the LM386 can deliver up to 1.25W of power. -
Q: Can I use the LM386 for stereo applications?
A: Yes, you can use two LM386 ICs to build a stereo amplifier. Each IC will amplify one channel (left or right) of the stereo input signal. -
Q: How can I adjust the volume of the LM386 amplifier?
A: To adjust the volume, you can use a potentiometer to attenuate the input signal before it reaches the LM386. Connect the potentiometer between the input signal and the non-inverting input (pin 3) of the LM386. -
Q: Is the LM386 suitable for high-fidelity audio applications?
A: While the LM386 offers decent performance for its cost and simplicity, it may not be the best choice for high-fidelity audio applications that require extremely low noise and distortion levels. For such applications, consider using higher-end audio amplifier ICs or discrete component designs.
Conclusion
The LM386 is a versatile, low-cost, and easy-to-use audio power amplifier IC that has stood the test of time. Its simplicity and flexibility make it an excellent choice for a wide range of audio applications, from portable devices to instrument amplifiers and beyond. By understanding the LM386’s pinout, internal schematic, and various circuit configurations, you can harness its potential to create powerful and efficient audio amplifiers for your projects. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced electronics enthusiast, the LM386 is a valuable tool to have in your arsenal.
No responses yet