Introduction to IC 4060 Pinout
The IC 4060, also known as the CD4060 or HCF4060, is a 14-stage ripple carry binary counter integrated circuit. It is a versatile chip that finds applications in various digital circuits, such as timers, frequency dividers, and oscillators. Understanding the pinout of the IC 4060 is essential for effectively utilizing its functions in circuit design.
IC 4060 Package and Pin Configuration
The IC 4060 is available in different package types, including DIP (Dual Inline Package), SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit), and TSSOP (Thin Shrink Small Outline Package). The most common package is the 16-pin DIP. The following table shows the pin configuration of the IC 4060 in a 16-pin DIP package:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Q13 | Counter output 13 |
| 2 | Q12 | Counter output 12 |
| 3 | Q11 | Counter output 11 |
| 4 | Q10 | Counter output 10 |
| 5 | Q9 | Counter output 9 |
| 6 | Q8 | Counter output 8 |
| 7 | Q7 | Counter output 7 |
| 8 | VSS | Ground |
| 9 | Q5 | Counter output 5 |
| 10 | Q4 | Counter output 4 |
| 11 | Q6 | Counter output 6 |
| 12 | RS | Reset input (active low) |
| 13 | CLK_IN | Clock input |
| 14 | VDD | Supply voltage |
| 15 | Q3 | Counter output 3 |
| 16 | Q14 | Counter output 14 |
IC 4060 Pin Functions
Let’s delve into the functions of each pin of the IC 4060:
Power Supply Pins (VDD and VSS)
- Pin 14 (VDD): This pin is the positive supply voltage input. It should be connected to the positive power supply, typically ranging from 3V to 15V, depending on the specific IC 4060 variant.
- Pin 8 (VSS): This pin is the ground or negative supply voltage input. It should be connected to the ground or negative power supply of the circuit.
Clock Input (CLK_IN)
- Pin 13 (CLK_IN): This pin is the clock input of the IC 4060. It accepts an external clock signal that triggers the counter to increment on each rising edge of the clock. The maximum clock frequency depends on the supply voltage and the specific IC variant.
Reset Input (RS)
- Pin 12 (RS): This pin is the active-low reset input. When this pin is pulled low (connected to ground), it resets the counter to its initial state (all outputs become low). When the reset pin is high (connected to VDD or left floating), the counter operates normally.
Counter Outputs (Q3 to Q14)
- Pins 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 15, 16 (Q3 to Q14): These pins are the counter outputs of the IC 4060. Each output represents a specific stage of the 14-stage ripple carry binary counter. The outputs are labeled from Q3 to Q14, with Q3 being the least significant bit (LSB) and Q14 being the most significant bit (MSB). The outputs toggle at different frequencies based on their position in the counter chain.
The following table shows the relationship between the counter outputs and their respective frequencies:
| Counter Output | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Q3 | CLK_IN ÷ 8 |
| Q4 | CLK_IN ÷ 16 |
| Q5 | CLK_IN ÷ 32 |
| Q6 | CLK_IN ÷ 64 |
| Q7 | CLK_IN ÷ 128 |
| Q8 | CLK_IN ÷ 256 |
| Q9 | CLK_IN ÷ 512 |
| Q10 | CLK_IN ÷ 1024 |
| Q11 | CLK_IN ÷ 2048 |
| Q12 | CLK_IN ÷ 4096 |
| Q13 | CLK_IN ÷ 8192 |
| Q14 | CLK_IN ÷ 16384 |

Applications of IC 4060
The IC 4060 finds various applications in digital circuits due to its versatility as a binary counter and frequency divider. Some common applications include:
Frequency Division
The IC 4060 can be used to divide an input clock frequency by powers of two, ranging from 8 to 16384. This is useful in circuits that require lower frequencies derived from a higher frequency clock source. By selecting the appropriate counter output, the desired frequency division can be achieved.
Timer Circuits
The IC 4060 can be used as a timer by connecting an RC network to the CLK_IN pin. The RC network determines the oscillation frequency, and the counter outputs can be used to generate precise time intervals. By selecting the appropriate counter output and RC values, various timing durations can be obtained.
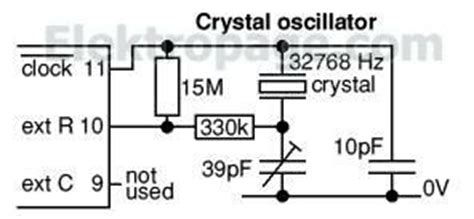
Oscillator Circuits
The IC 4060 can be configured as an oscillator by connecting an external crystal or ceramic resonator between the CLK_IN pin and ground. The counter outputs can then be used to provide clock signals at different frequencies for other parts of the circuit.
Sequencer and Control Circuits
The counter outputs of the IC 4060 can be used to generate sequences of pulses or to control the timing of events in a digital circuit. By combining the outputs using logic gates, specific sequences or patterns can be generated for various control applications.
Interfacing with IC 4060
When interfacing with the IC 4060, consider the following guidelines:
- Ensure proper power supply connections to the VDD and VSS pins, providing a stable and regulated voltage within the specified range.
- Connect the CLK_IN pin to the appropriate clock source, such as an oscillator, crystal, or external clock signal, depending on the desired frequency and application.
- Use the reset pin (RS) to initialize the counter to a known state when required. Pull the RS pin low to reset the counter, and keep it high or floating during normal operation.
- Select the appropriate counter output(s) based on the desired frequency division or timing requirements. Use the table provided earlier to determine the relationship between the counter outputs and their respective frequencies.
- Consider the loading effect of the connected circuitry on the counter outputs. Ensure that the output current and fanout limitations of the IC 4060 are not exceeded to maintain proper operation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the purpose of the IC 4060?
The IC 4060 is a 14-stage ripple carry binary counter that can be used for frequency division, timing, oscillation, and sequencing applications in digital circuits.
2. How does the reset pin (RS) work in the IC 4060?
The reset pin (RS) is an active-low input. When pulled low, it resets the counter to its initial state, where all outputs become low. When the reset pin is high or left floating, the counter operates normally.
3. Can the IC 4060 be used as an oscillator?
Yes, the IC 4060 can be configured as an oscillator by connecting an external crystal or ceramic resonator between the CLK_IN pin and ground. The counter outputs can then provide clock signals at different frequencies.
4. What is the maximum clock frequency that can be applied to the IC 4060?
The maximum clock frequency depends on the supply voltage and the specific IC variant. Refer to the datasheet of the specific IC 4060 variant for detailed information on the maximum clock frequency.
5. How can I select the desired frequency division using the IC 4060?
To select the desired frequency division, choose the appropriate counter output based on the relationship between the counter outputs and their respective frequencies. Refer to the table provided in the article to determine which output corresponds to the desired frequency division.
Conclusion
Understanding the pinout and functions of the IC 4060 is crucial for effectively utilizing this versatile binary counter in digital circuits. By properly connecting the power supply, clock input, reset pin, and selecting the appropriate counter outputs, designers can harness the capabilities of the IC 4060 for frequency division, timing, oscillation, and sequencing applications. With its wide range of frequency division options and ease of interfacing, the IC 4060 is a valuable component in many digital design projects.
Word count: 1292 words
No responses yet