What is Wire Ampacity?
Wire ampacity refers to the maximum current-carrying capacity of an electrical wire or cable before it sustains damage or becomes unsafe. It is a critical factor in determining the appropriate wire size for a specific application, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. The ampacity of a wire depends on several factors, including the wire’s material, gauge (thickness), insulation type, ambient temperature, and the number of conductors in a cable.
Factors Affecting Wire Ampacity
-
Wire Material: The most common materials used for electrical wires are copper and aluminum. Copper has a higher electrical conductivity than aluminum, allowing for higher ampacity ratings for the same wire gauge.
-
Wire Gauge: Wire gauge refers to the thickness of the wire, with smaller gauge numbers indicating thicker wires. Thicker wires can carry more current, thus having higher ampacity ratings.
-
Insulation Type: The insulation material surrounding the wire affects its ampacity rating. Some common insulation types include PVC, THHN, XHHW, and USE. Each insulation type has different thermal properties and temperature ratings, which influence the wire’s ampacity.
-
Ambient Temperature: The surrounding temperature affects a wire’s ampacity rating. As the ambient temperature increases, the wire’s ability to dissipate heat decreases, resulting in a lower ampacity rating. Conversely, lower ambient temperatures allow for higher ampacity ratings.
-
Number of Conductors: When multiple wires are bundled together in a cable, their ampacity ratings are lower compared to single wires. This is because the wires in a cable have less exposure to air, which reduces their ability to dissipate heat.
How to Use a Wire Ampacity Calculator
A wire ampacity calculator is a tool that helps determine the maximum current-carrying capacity of a wire based on various factors. Follow these steps to use a wire ampacity calculator effectively:
Step 1: Gather the Required Information
Before using the calculator, collect the following information about your wire or cable:
- Wire material (copper or aluminum)
- Wire gauge (AWG or kcmil)
- Insulation type (e.g., PVC, THHN, XHHW, USE)
- Ambient temperature (°C or °F)
- Number of conductors in the cable (if applicable)
Step 2: Select the Wire Material
Choose the appropriate wire material from the options provided in the calculator. Most calculators offer a choice between copper and aluminum.
Step 3: Enter the Wire Gauge
Input the wire gauge into the calculator. The gauge is typically represented by AWG (American Wire Gauge) for smaller wires or kcmil (thousand circular mils) for larger wires.
Step 4: Select the Insulation Type
Choose the insulation type that matches your wire or cable. Common options include PVC, THHN, XHHW, and USE.
Step 5: Input the Ambient Temperature
Enter the expected ambient temperature in which the wire or cable will be operating. This temperature is usually provided in either degrees Celsius (°C) or degrees Fahrenheit (°F).
Step 6: Specify the Number of Conductors (if applicable)
If you are working with a cable containing multiple wires, input the number of conductors in the cable. This step may not be necessary for single wires.
Step 7: Calculate the Ampacity
After entering all the required information, the calculator will display the ampacity rating for your wire or cable. This value represents the maximum current the wire can safely carry under the specified conditions.
Interpreting Wire Ampacity Calculator Results
The wire ampacity calculator provides the maximum current-carrying capacity for the specified wire or cable. It is essential to understand that this value is a theoretical maximum and should be used as a guideline when selecting wires for your electrical applications.
When designing an electrical system, it is crucial to consider additional factors such as voltage drop, circuit breaker ratings, and local electrical codes. Always consult with a qualified electrician or engineer to ensure your electrical system is safe, efficient, and compliant with relevant regulations.

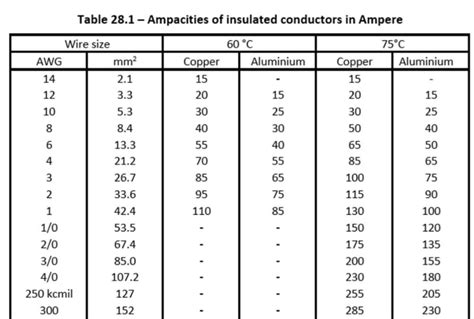
Wire Ampacity Tables
In addition to wire ampacity calculators, you can also refer to wire ampacity tables provided by various organizations, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) or the Insulated Cable Engineers Association (ICEA). These tables offer a quick reference for determining the ampacity of wires based on their gauge, insulation type, and ambient temperature.
Here is an example of a wire ampacity table for copper wires with THHN insulation at 30°C (86°F) ambient temperature:
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Ampacity (A) |
|---|---|
| 14 | 20 |
| 12 | 25 |
| 10 | 35 |
| 8 | 50 |
| 6 | 65 |
| 4 | 85 |
| 2 | 115 |
| 1 | 130 |
| 1/0 | 150 |
| 2/0 | 175 |
| 3/0 | 200 |
| 4/0 | 230 |
Note that these values are for reference only and may vary depending on the specific application and local electrical codes.
FAQ
-
What is the difference between wire gauge and ampacity?
Wire gauge refers to the physical size (thickness) of the wire, while ampacity is the maximum current-carrying capacity of the wire. Thicker wires (lower gauge numbers) generally have higher ampacity ratings. -
Can I use a wire with a lower ampacity rating than the calculated value?
No, it is not recommended to use a wire with a lower ampacity rating than the calculated value. Doing so may lead to overheating, insulation damage, and potential fire hazards. Always choose a wire with an ampacity rating equal to or greater than the required current. -
How does ambient temperature affect wire ampacity?
Higher ambient temperatures reduce a wire’s ability to dissipate heat, thus lowering its ampacity rating. Conversely, lower ambient temperatures allow for higher ampacity ratings. It is essential to consider the expected ambient temperature when selecting wires for your electrical application. -
Can I use aluminum wires instead of copper wires?
Yes, aluminum wires can be used in certain applications. However, copper wires have higher electrical conductivity and are more commonly used in residential and commercial wiring. Aluminum wires require special considerations, such as larger wire gauges and compatible connectors, to ensure safe and reliable performance. -
What should I do if my calculated ampacity exceeds the rating of standard wires?
If your calculated ampacity exceeds the rating of standard wires, you may need to use parallel conductors or larger wire gauges. Parallel conductors involve running multiple wires of the same gauge to increase the overall current-carrying capacity. Alternatively, you can use larger wire gauges (e.g., kcmil) to accommodate higher amperages. Consult with a qualified electrician or engineer to determine the best solution for your specific application.
Conclusion
Understanding wire ampacity is crucial for designing safe and efficient electrical systems. A wire ampacity calculator is a valuable tool that helps determine the maximum current-carrying capacity of wires based on factors such as wire material, gauge, insulation type, ambient temperature, and the number of conductors.
By gathering the required information and inputting it into the calculator, you can easily determine the appropriate wire size for your application. However, it is essential to use the calculated ampacity as a guideline and consider additional factors such as voltage drop, circuit breaker ratings, and local electrical codes.
Always consult with a qualified electrician or engineer to ensure your electrical system is properly designed, installed, and maintained. By following best practices and adhering to relevant regulations, you can create a safe and reliable electrical infrastructure for your home, business, or industrial facility.
No responses yet