Introduction to the Colpitts Oscillator
The Colpitts oscillator is a type of LC Oscillator that generates a sinusoidal output waveform using a combination of inductors and capacitors in its resonant tank circuit. It was invented in 1918 by American engineer Edwin H. Colpitts and has become one of the most widely used oscillator circuits due to its simplicity, stability, and low cost.
The basic principle behind the Colpitts oscillator is the use of capacitive voltage division in the feedback network to determine the oscillation frequency. The oscillator consists of an amplifier stage, typically a single transistor or op-amp, and a resonant tank circuit made up of an inductor and two capacitors in series. The capacitive voltage divider provides positive feedback to the amplifier, sustaining the oscillation.
Key Features of the Colpitts Oscillator
- Simple design with few components
- Stable frequency output
- Wide frequency range (from a few kHz to hundreds of MHz)
- Low harmonic distortion
- Suitable for various applications, including radio transmitters, receivers, and signal generators
Circuit Design and Operation
Basic Colpitts Oscillator Circuit
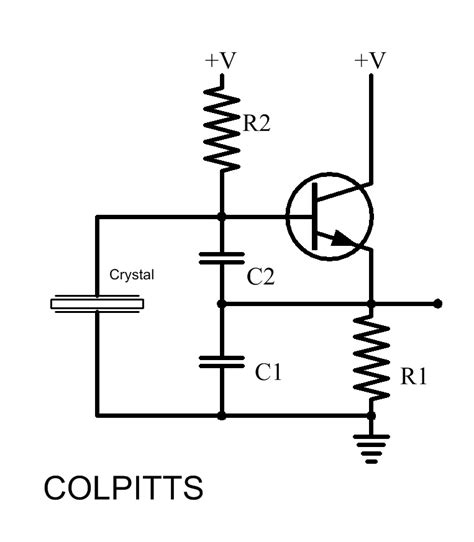
The basic Colpitts oscillator circuit consists of the following components:
- Amplifier stage (transistor or op-amp)
- Inductor (L)
- Two capacitors (C1 and C2)
- Biasing Resistors (R1 and R2)
- Emitter or source resistor (RE or RS)
Here is a simple Colpitts oscillator circuit using a bipolar junction transistor (BJT):
Circuit Operation
- The resonant tank circuit, formed by L, C1, and C2, determines the oscillation frequency.
- The capacitive voltage divider (C1 and C2) provides positive feedback to the amplifier stage.
- The amplifier stage (transistor) provides the necessary gain to sustain the oscillation.
- Biasing resistors (R1 and R2) set the operating point of the transistor.
- The emitter or source resistor (RE or RS) stabilizes the amplifier stage and limits the current.
Oscillation Frequency
The oscillation frequency of the Colpitts oscillator is determined by the values of the inductor (L) and capacitors (C1 and C2) in the resonant tank circuit. The formula for calculating the oscillation frequency is:
f = 1 / (2π√(LC))
where:
– f is the oscillation frequency in Hz
– L is the inductance in Henries
– C is the equivalent capacitance of C1 and C2 in parallel, given by:
C = (C1 × C2) / (C1 + C2)
Advantages of the Colpitts Oscillator
1. Simplicity and Low Cost
One of the main advantages of the Colpitts oscillator is its simplicity and low cost. The basic circuit requires only a few components, making it easy to design, build, and troubleshoot. This simplicity also translates to lower manufacturing costs, making the Colpitts oscillator an attractive choice for mass-produced electronic devices.
2. Frequency Stability
Colpitts oscillators are known for their excellent frequency stability, especially when compared to other types of oscillators, such as the Hartley oscillator. The frequency stability is attributed to the use of a capacitive voltage divider in the feedback network, which makes the oscillator less sensitive to changes in the amplifier stage’s characteristics.
Factors contributing to the frequency stability of Colpitts oscillators include:
- High Q-factor of the resonant tank circuit
- Low temperature coefficient of the inductor and capacitors
- Proper design of the amplifier stage to minimize the effect of temperature and supply voltage variations
3. Wide Frequency Range
Colpitts oscillators can be designed to operate over a wide range of frequencies, from a few kilohertz to hundreds of megahertz. This versatility makes them suitable for a variety of applications, such as:
- Low-frequency audio oscillators
- Intermediate-frequency (IF) oscillators in radio receivers
- High-frequency oscillators in radio transmitters
- Clock generators in digital systems
The oscillation frequency can be easily adjusted by changing the values of the inductor or capacitors in the resonant tank circuit. This allows for fine-tuning the frequency to meet specific application requirements.
4. Low Harmonic Distortion
Colpitts oscillators are capable of producing output waveforms with low harmonic distortion, especially when designed with a high Q-factor resonant tank circuit. Low harmonic distortion is essential in many applications, such as:
- Audio signal generation
- Telecommunications
- Precision measurement equipment
The low harmonic distortion characteristic of Colpitts oscillators is due to the filtering action of the resonant tank circuit, which attenuates the harmonics of the fundamental oscillation frequency.

Applications of the Colpitts Oscillator
1. Radio Transmitters and Receivers
Colpitts oscillators are widely used in radio transmitters and receivers for generating the carrier and local oscillator (LO) signals. In transmitters, the Colpitts oscillator generates the high-frequency carrier signal, which is then modulated with the information signal before being amplified and transmitted.
In receivers, Colpitts oscillators are used as local oscillators to down-convert the incoming radio frequency (RF) signal to an intermediate frequency (IF) signal for further processing. The stability and low noise characteristics of Colpitts oscillators make them ideal for these applications.
2. Signal Generators
Colpitts oscillators are often used in signal generators to produce sinusoidal waveforms with a wide range of frequencies. These signal generators are essential tools in electronic testing, calibration, and measurement. The simplicity and low cost of Colpitts oscillators make them an attractive choice for designing compact and portable signal generators.
3. Clock Generators in Digital Systems
Colpitts oscillators can be used as clock generators in digital systems, providing the timing reference for synchronizing the operation of various digital circuits. The frequency stability and low jitter characteristics of Colpitts oscillators are critical for ensuring the proper functioning of digital systems, especially in high-speed applications.
4. Audio Applications
Low-frequency Colpitts oscillators are used in various audio applications, such as:
- Electronic musical instruments
- Audio test equipment
- Sound synthesis
- Tone generators
The low harmonic distortion and frequency stability of Colpitts oscillators make them suitable for generating high-quality audio signals.
Comparison with Other Oscillator Types
Colpitts vs. Hartley Oscillator
The Hartley oscillator is another type of LC oscillator that uses a tapped inductor in its resonant tank circuit. While both Colpitts and Hartley oscillators are similar in their basic operating principle, there are some key differences:
| Feature | Colpitts Oscillator | Hartley Oscillator |
|---|---|---|
| Feedback network | Capacitive voltage divider | Tapped inductor |
| Frequency stability | Higher | Lower |
| Frequency range | Wide | Wide |
| Component count | Lower | Higher |
| Inductor design | Simple | Tapped |
The Colpitts oscillator’s higher frequency stability and simpler inductor design make it the preferred choice in many applications.
Colpitts vs. Crystal Oscillator
Crystal oscillators use a piezoelectric crystal as the frequency-determining element instead of an LC tank circuit. While crystal oscillators offer superior frequency stability and accuracy compared to Colpitts oscillators, they have some limitations:
| Feature | Colpitts Oscillator | Crystal Oscillator |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency stability | High | Very high |
| Frequency accuracy | Moderate | Very high |
| Frequency range | Wide | Narrow |
| Tunability | Easy | Limited |
| Cost | Low | Higher |
Colpitts oscillators are preferred when a wide frequency range, easy tunability, and low cost are required, while crystal oscillators are used in applications demanding the highest frequency stability and accuracy.
FAQ
-
What is a Colpitts oscillator?
A Colpitts oscillator is a type of LC oscillator that generates a sinusoidal output waveform using a resonant tank circuit consisting of an inductor and two capacitors. It uses capacitive voltage division in the feedback network to determine the oscillation frequency. -
What are the advantages of using a Colpitts oscillator?
The main advantages of Colpitts oscillators include: - Simplicity and low cost
- High frequency stability
- Wide frequency range
-
Low harmonic distortion
-
How does a Colpitts oscillator work?
A Colpitts oscillator works by using an amplifier stage (usually a transistor or op-amp) and a resonant tank circuit (an inductor and two capacitors) to generate a sinusoidal output waveform. The capacitive voltage divider in the feedback network provides positive feedback to the amplifier, sustaining the oscillation at the resonant frequency determined by the LC tank circuit. -
What determines the oscillation frequency of a Colpitts oscillator?
The oscillation frequency of a Colpitts oscillator is determined by the values of the inductor (L) and the two capacitors (C1 and C2) in the resonant tank circuit. The formula for calculating the oscillation frequency is:
f = 1 / (2π√(LC))
where L is the inductance and C is the equivalent capacitance of C1 and C2 in parallel. -
What are some common applications of Colpitts oscillators?
Colpitts oscillators are widely used in various applications, such as: - Radio transmitters and receivers
- Signal generators
- Clock generators in digital systems
- Audio applications (e.g., electronic musical instruments, test equipment)
Conclusion
The Colpitts oscillator is a versatile and widely used LC oscillator circuit, known for its simplicity, frequency stability, and low cost. Its ability to generate sinusoidal output waveforms over a wide range of frequencies makes it suitable for various applications, including radio transmitters and receivers, signal generators, clock generators, and audio equipment.
By understanding the basic principles, circuit design, and advantages of Colpitts oscillators, engineers and technicians can effectively utilize this oscillator topology in their projects and optimize its performance for specific requirements. As technology continues to advance, the Colpitts oscillator remains a reliable and essential building block in the world of electronic circuit design.
No responses yet