Introduction to Circuit Components
Circuit boards are the backbone of modern electronics, consisting of various components that work together to perform specific functions. Understanding these components is essential for anyone interested in electronics, from hobbyists to professionals. In this comprehensive article, we will dive deep into the world of circuit board components, exploring their types, functions, and applications.
Types of Circuit Components
Circuit components can be broadly categorized into two main types:
-
Active Components: These components rely on a source of energy to perform their functions and can control the flow of current in a circuit. Examples include transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits.
-
Passive Components: These components do not require a power source to operate and do not have the ability to control current flow. They are used to store, filter, or resist electrical energy. Examples include resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
Active Components
Transistors
Transistors are semiconductor devices that can amplify or switch electronic signals and power. They are the building blocks of modern electronics and are used in a wide range of applications, from simple circuits to complex computer processors.
Types of Transistors
-
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs): These transistors have three terminals – emitter, base, and collector. They are used for amplification and switching applications.
-
Field-Effect Transistors (FETs): These transistors have three terminals – source, gate, and drain. They are used for switching and amplification applications and are known for their high input impedance.
Transistor Applications
Transistors are used in various applications, including:
- Amplifiers
- Switches
- Logic gates
- Voltage regulators
- Power control circuits
Diodes
Diodes are two-terminal semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in only one direction. They are used for rectification, protection, and voltage regulation.
Types of Diodes
-
Rectifier Diodes: These diodes are used to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
-
Zener Diodes: These diodes are used for voltage regulation and protection against overvoltage.
-
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs): These diodes emit light when current flows through them and are used for indication and lighting applications.
Diode Applications
Diodes are used in various applications, including:
- Power supplies
- Voltage regulators
- Overvoltage protection
- Rectification
- Indicator lights
Integrated Circuits
Integrated circuits (ICs) are miniaturized electronic circuits that consist of multiple components, such as transistors, diodes, and resistors, fabricated on a single semiconductor substrate. They are used to perform complex functions and are the backbone of modern electronics.
Types of Integrated Circuits
-
Analog ICs: These ICs process continuous signals and are used in applications such as amplifiers, regulators, and filters.
-
Digital ICs: These ICs process discrete signals and are used in applications such as logic gates, microprocessors, and memory devices.
-
Mixed-Signal ICs: These ICs combine both analog and digital circuitry on a single chip and are used in applications such as data converters and communication devices.
Integrated Circuit Applications
Integrated circuits are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Computers
- Smartphones
- Televisions
- Automobiles
- Industrial control systems
Passive Components
Resistors
Resistors are two-terminal components that oppose the flow of electric current in a circuit. They are used to control voltage, current, and power dissipation.
Types of Resistors
-
Fixed Resistors: These resistors have a fixed resistance value and are used in applications where a specific resistance is required.
-
Variable Resistors: These resistors have an adjustable resistance value and are used in applications such as volume controls and dimmer switches.
-
Thermistors: These resistors change their resistance value based on temperature and are used in temperature sensing applications.
Resistor Applications
Resistors are used in various applications, including:
- Voltage division
- Current limiting
- Load balancing
- Filtering
- Temperature sensing
Capacitors
Capacitors are two-terminal components that store electrical energy in an electric field. They are used for filtering, decoupling, and energy storage.
Types of Capacitors
-
Ceramic Capacitors: These capacitors are made from ceramic materials and are known for their high stability and low cost.
-
Electrolytic Capacitors: These capacitors use an electrolyte to achieve high capacitance values and are polarized, meaning they have a positive and negative terminal.
-
Tantalum Capacitors: These capacitors are made from tantalum and offer high capacitance values in a small package size.
Capacitor Applications
Capacitors are used in various applications, including:
- Power supply filtering
- Signal coupling and decoupling
- Timing circuits
- Energy storage
- Resonant circuits
Inductors
Inductors are two-terminal components that store electrical energy in a magnetic field. They are used for filtering, energy storage, and impedance matching.
Types of Inductors
-
Air Core Inductors: These inductors have no core material and are used in high-frequency applications.
-
Ferrite Core Inductors: These inductors use a ferrite core to increase their inductance value and are used in low-frequency applications.
-
Toroidal Inductors: These inductors have a donut-shaped core and offer high inductance values with low electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Inductor Applications
Inductors are used in various applications, including:
- Power supply filtering
- Impedance matching
- Resonant circuits
- Energy storage
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression

Circuit Component Selection
When designing a circuit, selecting the appropriate components is crucial for ensuring proper functionality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Factors to consider when choosing circuit components include:
- Electrical specifications (voltage, current, power, frequency)
- Environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, vibration)
- Size and packaging
- Cost and availability
- Reliability and lifetime
Designers should also consider the overall system requirements and any applicable industry standards when selecting components.
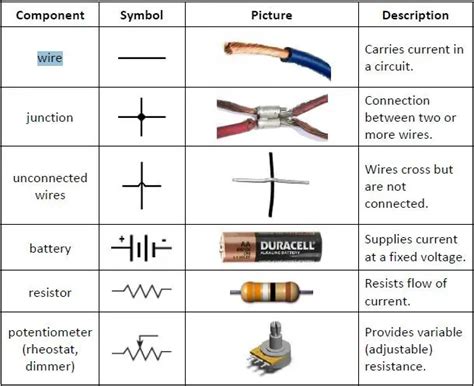
Circuit Component Symbols and Schematics
Understanding circuit component symbols and schematics is essential for reading and designing electronic circuits. The following table shows some common circuit component symbols:
| Component | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Resistor | |
| Capacitor | |
| Inductor | |
| Diode | |
| Transistor (BJT) |
Schematics use these symbols to represent the interconnections between components in a circuit. Learning to read and create schematics is a fundamental skill for anyone working with electronic circuits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the difference between active and passive components?
Active components require a power source to operate and can control the flow of current in a circuit, while passive components do not require power and cannot control current flow. -
How do I choose the right resistor for my circuit?
When selecting a resistor, consider the required resistance value, power rating, tolerance, and temperature coefficient. Also, ensure that the resistor can handle the expected voltage and current levels in your circuit. -
What is the purpose of a decoupling capacitor?
Decoupling capacitors are used to reduce noise and stabilize the power supply voltage in a circuit. They are placed close to the power pins of integrated circuits to provide a local reservoir of charge and minimize the effects of voltage fluctuations. -
How do I determine the power rating of a component?
The power rating of a component depends on its maximum voltage and current capabilities. For resistors, the power rating is calculated using the equation P = V² / R, where P is the power in watts, V is the voltage across the resistor, and R is the resistance value. For other components, consult the manufacturer’s datasheet for power rating information. -
What are the advantages of using integrated circuits?
Integrated circuits offer several advantages, including reduced size, increased reliability, lower power consumption, and improved performance compared to discrete components. They also simplify circuit design and manufacturing, as complex functions can be implemented on a single chip.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the world of circuit board components, covering active components like transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits, as well as passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors. We have also discussed the importance of component selection, circuit symbols, and schematics.
Understanding circuit components is essential for anyone involved in electronics, from hobbyists to professional engineers. By mastering the fundamentals of component types, functions, and applications, you can design, troubleshoot, and optimize electronic circuits with confidence.
As technology continues to advance, new and improved circuit components will emerge, offering even greater possibilities for innovation and problem-solving. By staying up-to-date with the latest developments in the field, you can remain at the forefront of the ever-evolving world of electronics.
No responses yet