
How to Buy PCB Boards Meeting Demands and Cost-Effectively
Introduction Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in nearly all modern electronic devices. From smartphones and laptops to medical equipment and automotive systems, PCBs[…]
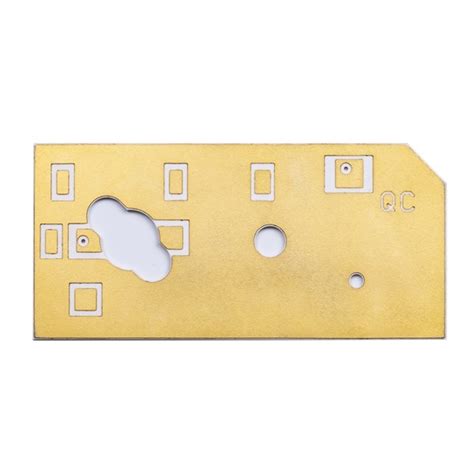

How to Make Ceramic PCBs: 7 Ceramic PCB Manufacturing Processes
What is Ceramic PCB Manufacturing? Ceramic printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing is a process that involves creating circuit boards using ceramic materials as the base[…]

On HF Circuit Board and Cov-19: Most Professional Post
Introduction to HF Circuit Boards and Cov-19 High-frequency (HF) circuit boards have become increasingly important in the era of COVID-19 (Cov-19). These specialized circuit boards[…]
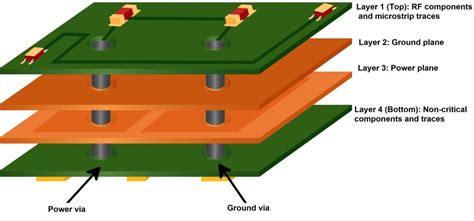
What is the inner layer of a PCB?
Understanding the Inner PCB Layer Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in modern electronic devices. They provide a platform for mounting and interconnecting various[…]

PCB & Assembly Services – STANDARD pool
Introduction to PCB Assembly Services Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assembly is the process of soldering or mounting electronic components onto a PCB. It is a[…]
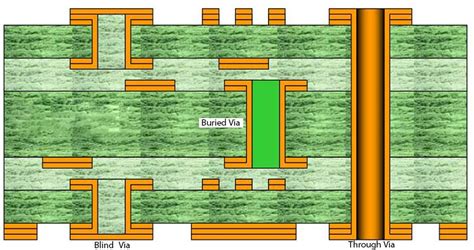
Blind and Buried Vias
Introduction to Blind Vias and Buried Vias In the world of printed circuit board (PCB) design, vias play a crucial role in connecting different layers[…]
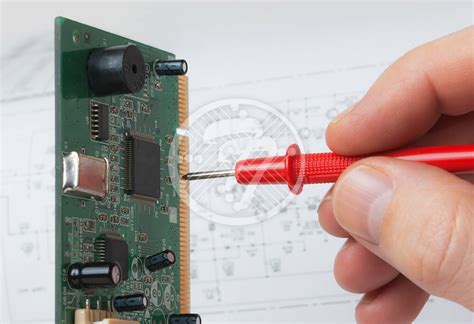
How to Clean PCBA in the Safest and Most Effective Ways?
Understanding PCBA Contamination Before diving into the cleaning methods, it is essential to understand the types of contamination that can affect PCBAs. Common contaminants include:[…]

How to Make RoHS Certified Electrics Products
What is RoHS Compliance? RoHS stands for “Restriction of Hazardous Substances”. It is a directive that originated in the European Union and restricts the use[…]

Innerlayer imaging for multilayer PCB
What is Innerlayer Imaging in PCB Manufacturing? Innerlayer imaging, also known as primary imaging, is a crucial step in the manufacturing process of multilayer printed[…]

How to Read and Understand SMD Capacitor Codes
Introduction to SMD Capacitor Codes Surface-mount device (SMD) capacitors are essential components in modern electronic circuits. These tiny components are marked with codes that provide[…]