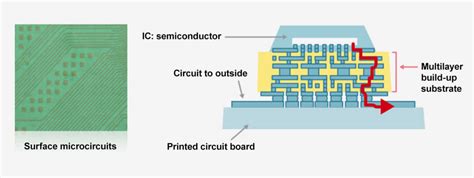
IC Substrate: Everything You Must Know About Integrated Circuit Substrates
Introduction to IC Substrates An Integrated Circuit (IC) substrate is a thin, flat material that serves as the foundation for the construction of an IC[…]
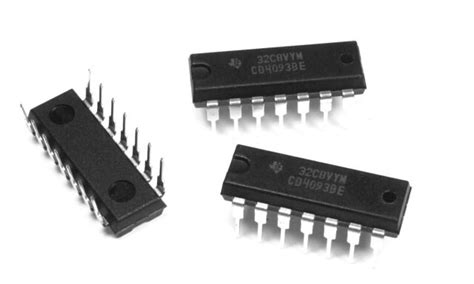
IC 4093- What is it, and How Does it Work?
Features of the IC 4093 The IC 4093 has several key features that make it a versatile and widely-used integrated circuit: Four independent 2-input NAND[…]

TTL vs. CMOS: Integrated Circuit Logic Families
Introduction to TTL and CMOS Logic Transistor-transistor logic (TTL) and complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) are two of the most widely used logic families in integrated circuits.[…]

changing pcb reference planes during routing multilayer boards
Introduction to Multilayer PCB routing Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics. They provide a platform for mounting and interconnecting electronic components[…]
Never Cross A Ground Plane Gap In High Speed Pcb Design
Why Avoiding Ground-Plane Gaps is Critical for Signal Integrity In high-speed printed circuit board (PCB) designs, one of the most important layout rules to follow[…]
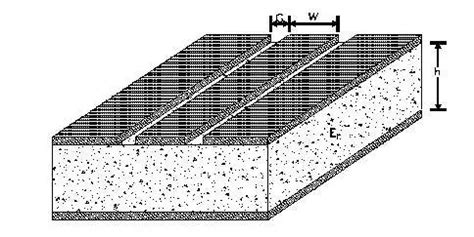
What Pcb Copper Thickness Should You Use
Understanding PCB Copper Thickness Units PCB copper thickness is typically measured in ounces per square foot (oz/ft²) or microns (µm). One ounce per square foot[…]
what pcb designers need know about conductive ink printing 3d printers
Introduction to PCB Conductive Ink Printing Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are essential components in modern electronics, providing the foundation for interconnecting electronic components. Traditional PCB[…]
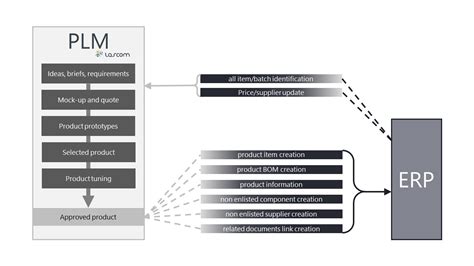
What Pcb Designers Need To Know About Plm Integration
The Importance of PCB-PLM Integration for Electronics Design and Manufacturing Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) solutions have become increasingly important for managing the complex process of[…]

Ten Common problems in PCB Design
PCB design Pitfalls to Avoid for Successful Manufacturing Printed circuit board (PCB) design is a complex process that requires careful planning and attention to detail.[…]
PCB Grounding Techniques
What is PCB Grounding and Why is it Important? PCB grounding refers to the techniques used to create a low-impedance path for electrical currents to[…]