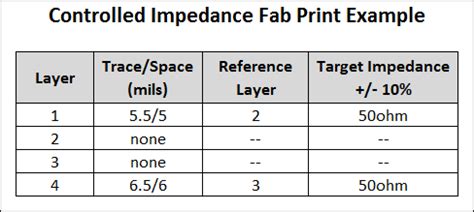
Controlled Impedance PCB: PCB Copper Traces with Minimal Signal Integrity Issues
Introduction to Controlled-Impedance PCBs In the world of high-speed electronic design, signal integrity is paramount. As digital systems continue to push the boundaries of speed[…]
PCB Terminology List in PCB Design-PCB Glossary
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) A PCB is a flat board made of insulating material, such as fiberglass or composite epoxy, with conductive pathways printed or[…]

Should You Use Star Grounding for Analog and Digital Ground Separation?
What is Star-Grounding? Star-grounding is a technique used in electrical and electronic systems to minimize noise and interference by creating a single, central grounding point[…]
Trace Impedance Calculator
What is Trace Impedance and Why Does it Matter? Trace impedance, also known as characteristic impedance, refers to the resistance to the flow of electrical[…]
Track Supply Chain Data And More Spectra Nexar
Introduction to Supply Chain Tracking In today’s globalized world, supply chains have become increasingly complex and interconnected. Companies face the challenge of managing and monitoring[…]
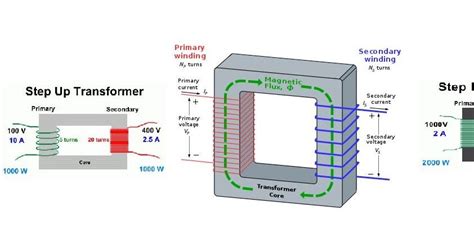
transformer theory made simple
Introduction to Transformers Simplified Transformers have revolutionized the field of natural language processing (NLP) and have become the backbone of many state-of-the-art models. In this[…]
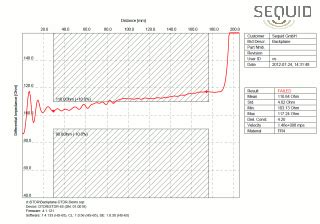
clearing trace impedance calculators and formulas
Understanding Trace Impedance Trace impedance is a critical factor in the design of high-speed printed circuit boards (PCBs). It refers to the opposition to the[…]
transmission line calculators pcb design
Introduction to PCB Transmission Line Calculators When designing high-speed printed circuit boards (PCBs), it’s crucial to consider the effects of transmission lines. Transmission lines are[…]
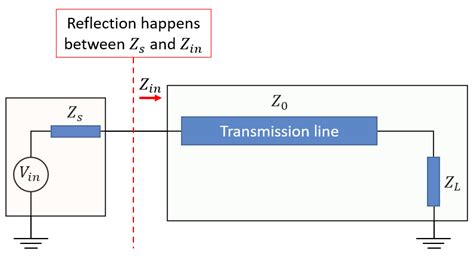
transmission line impedance six important values
Introduction to Transmission Line Impedance Transmission line impedance is a crucial concept in the field of electrical engineering, particularly when dealing with the design and[…]
transmission line pcb track
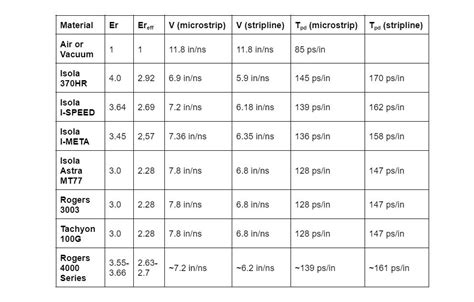
Introduction to PCB Transmission Lines Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics, providing a platform for interconnecting various components and enabling the[…]