
Press Fit: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Press Fit? Press fit, also known as interference fit or friction fit, is a fastening method that relies on the friction between two[…]
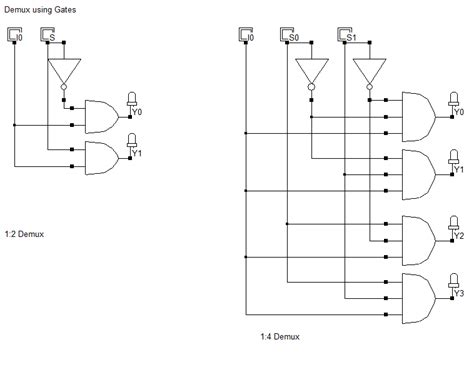
Multiplexer IC – A Complete Guide
Introduction to Multiplexers A multiplexer, often referred to as a “mux,” is a fundamental component in digital electronics that allows multiple input signals to be[…]
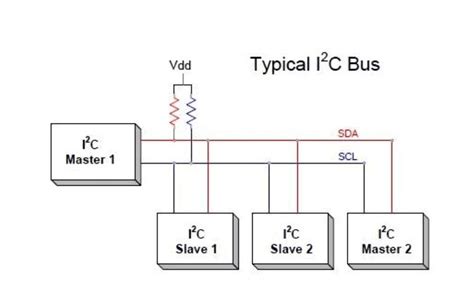
SPI vs. UART: Serial Communication Protocols for Microcontrollers and Embedded Systems
Introduction to Serial Communication Serial communication is a method of transmitting data between devices one bit at a time, as opposed to parallel communication, which[…]
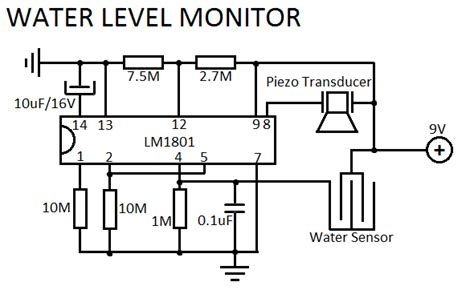
Water Level Sensors: Everything You Need To Know
What are Water Level Sensors? Water level sensors are devices that measure the height of water or other liquids in a container or a natural[…]

How to Test a Diode: The Best Ways to Find Faulty Diodes
What is a Diode and How Does it Work? A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance).[…]
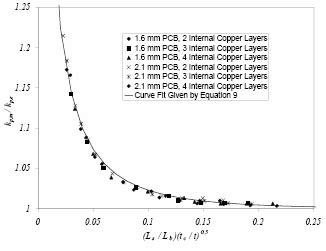
PCB Thermal Resistance: A Circuit Board’s Ability to Dissipate Heat
Introduction to PCB Thermal Resistance Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronic devices, providing a platform for components to be mounted and[…]
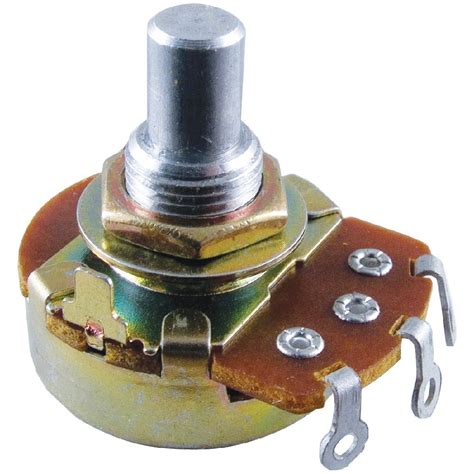

Potentiometer Wiring – Process Simplified
Introduction to Potentiometers A potentiometer, often referred to as a “pot,” is a three-terminal variable resistor commonly used in electronic circuits to control voltage, current,[…]
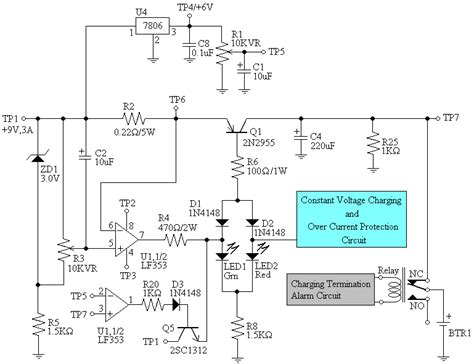
Constant Current Source – A Comprehensive Guide on Constructing Different Constant Current Circuit Designs
Introduction to Constant Current Circuits Constant current circuits are essential in many electronic applications where a stable and controlled current is required, regardless of variations[…]

ATMEGA8 Pinout: How to Get the Best Out of This Microcontroller
Introduction to ATMEGA8 The ATMEGA8 is an 8-bit RISC microcontroller with 8KB of in-system programmable flash memory, 1KB SRAM, and 512 bytes EEPROM. It operates[…]
Copper PCB – How Impacts PCB Board Manufacturing
Introduction to Copper in PCB Manufacturing Copper is an essential material in the production of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It plays a crucial role in[…]