
Signal and Power Integrity Fundamentals on High Speed
Introduction to Signal and Power Integrity In the world of high-speed electronics, signal and power integrity (SPI) play a crucial role in ensuring the proper[…]

What About Underwriters Laboratory (UL)?
History of Underwriters Laboratory The story of Underwriters Laboratory begins in the late 19th century when electricity was becoming more widely used in homes and[…]

PCB Milling – How To Make(Helpful)
What is PCB Milling? PCB milling is a subtractive manufacturing process that involves using a computer-controlled milling machine to remove copper from a blank PCB[…]
Strategies on Designing PCB Layout
Understanding the Basics of PCB Layout Design Before diving into specific strategies, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of PCB layout design. A PCB, or[…]
The Benefits of The 4 Layer PCB Boards
Introduction to PCB Benefits Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics. They provide a reliable and efficient means of connecting electronic components[…]
The Definitive Guide to PCB Stencil: Everything You Need to Know
What is a PCB Stencil? A PCB (Printed Circuit Board) stencil is a thin sheet of metal, usually stainless steel, with laser-cut openings that correspond[…]
The Essential Guide to PCB Heatsink Design and Selection
Introduction to PCB Heatsinks In the world of electronics, heat management is a crucial aspect of designing reliable and efficient printed circuit boards (PCBs). As[…]
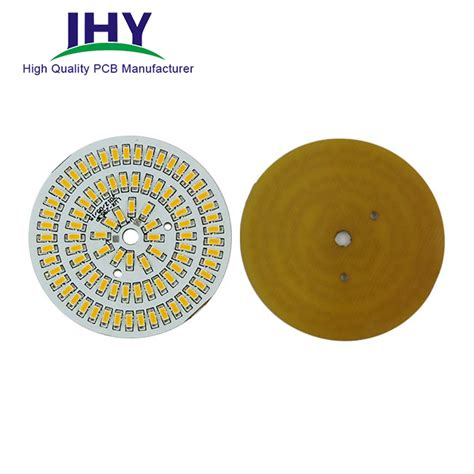

The Role of MCPCB (Metal Core PCB) In The Led Industry
What is MCPCB? MCPCB stands for Metal Core Printed Circuit Board. It is a special type of PCB that uses a metal core as the[…]
The Structure and Materials of Double Sided PCB
What is a Double Sided PCB? A double-sided PCB, also known as a two-layer PCB, is a printed circuit board that has conductive copper layers[…]

Drilled Holes in the PCB – all you need to know to avoid surprises.
Introduction to PCB Drilled Holes Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in electronic devices, serving as the foundation for mounting and interconnecting electronic components.[…]