thermal pad vs paste
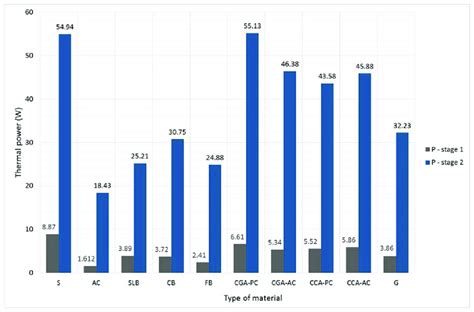
Introduction When it comes to ensuring optimal heat transfer between electronic components and heatsinks, two popular solutions emerge: thermal pads and thermal paste. Both materials[…]
circuit board thermal analysis
Introduction to PCB thermal management Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics, providing a platform for integrating and interconnecting various components. As[…]
thermal management in pcb today
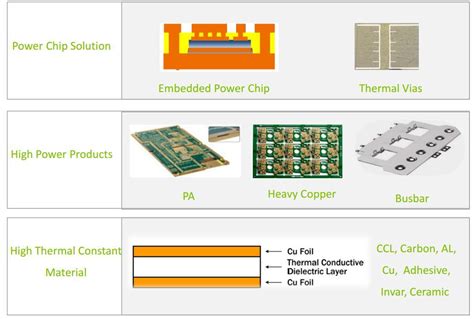
Introduction to PCB thermal management In the world of electronic devices, printed circuit boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in connecting and supporting various components.[…]

thermal shock testing
What is Thermal Shock? Thermal shock refers to the stress induced in a material due to sudden and significant changes in temperature. When a material[…]
thermal relief design
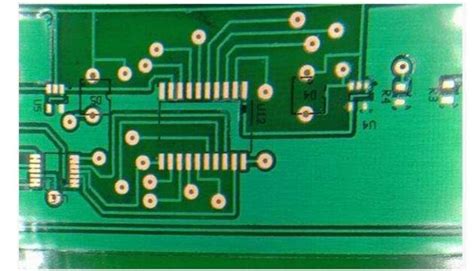
What is Thermal Relief? Thermal relief is a crucial aspect of printed circuit board (PCB) design that helps to prevent thermal stress and damage to[…]
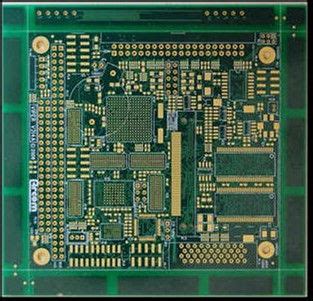
Immersion Silver and Other Lead Free PCB Surfaces
What is Immersion Silver? Immersion silver, also known as ImAg or IAg, is a lead-free surface finish that involves the deposition of a thin layer[…]

Selective soldering PCB Technical Details
Introduction to Selective soldering Selective soldering is a process used in printed circuit board (PCB) assembly where specific components are soldered onto the board without[…]
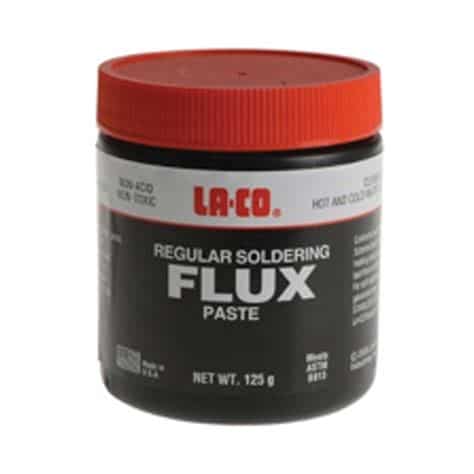

What Is Solder Flux And How Do You Use It
What is Solder Flux? Solder flux is a chemical cleaning agent used in the soldering process to remove oxidation, impurities, and other contaminants from the[…]

thoughtful systems based electronics design
Introduction to Thoughtful Electronics In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the concept of thoughtful electronics has gained significant traction. Thoughtful electronics refers to the design[…]
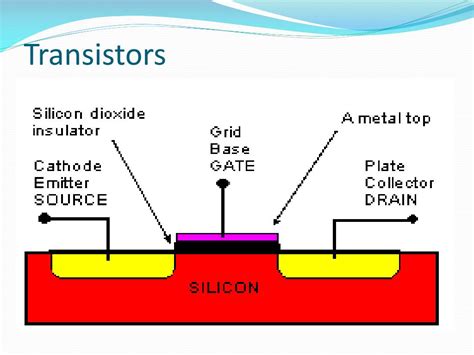
the transition of transistors
Introduction Transistors are the fundamental building blocks of modern electronics. These tiny devices control the flow of electricity in circuits and enable the creation of[…]