9 Years of Experience Tell You That Big Trap of Cheap PCB
Introduction Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics. They are used in almost every electronic device, from smartphones to medical equipment. However,[…]
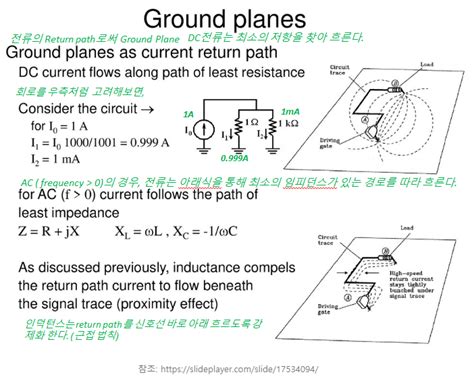
Return Current Topologies in PCB Design
Introduction to PCB Return Currents In the world of printed circuit board (PCB) design, understanding and managing return currents is crucial for ensuring the proper[…]
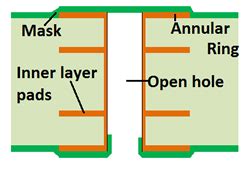
Plugged Vias: Is Plugging Your Vias Necessary?
What are Vias and Why are They Used in PCB Design? Vias are small holes drilled in a printed circuit board (PCB) that allow electrical[…]
94V 0 Circuit Board
Introduction to 94V 0 PCBs In the world of Electronic Manufacturing, the quality and reliability of printed circuit boards (PCBs) are of utmost importance. Among[…]
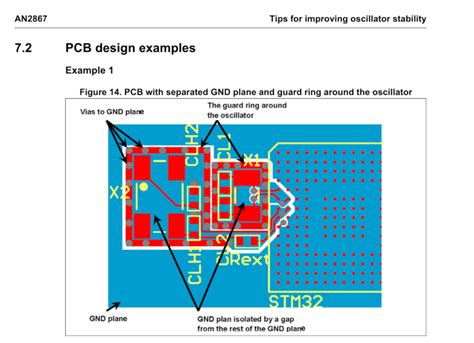
PCB Design Guidelines
Introduction to PCB Design Printed Circuit Board (PCB) design is a crucial aspect of electronic product development. A well-designed PCB ensures the proper functioning, reliability,[…]
How to do PCB Legend Print
What is a PCB Legend? A PCB (Printed Circuit Board) legend, also known as silkscreen or overlay, is the text and symbols printed on the[…]

Drilling printed circuit boards
Introduction to PCB Drilling Printed Circuit Board (PCB) drilling is a crucial step in the manufacturing process of PCBs. It involves creating holes in the[…]

Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
What is Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)? Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) is a non-contact, visual inspection method that uses cameras and image processing software to automatically[…]

Air Conditioner PCB Board: A Comprehensive Guide
What is an Air Conditioner PCB Board? An air conditioner PCB board is a complex electronic circuit that serves as the brain of the air[…]