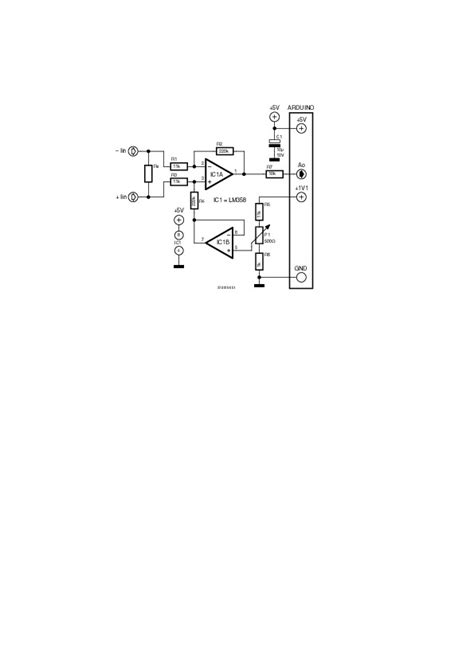
Digital Arduino Ammeter: How to Make Your Own Amp Meter At Home
Introduction An ammeter is an essential tool for measuring electrical current in various applications, from hobby electronics to industrial settings. While commercial ammeters are readily[…]
SPI I2C UART- Communication Protocols and Uses
Introduction to Communication Protocols In the world of electronics and embedded systems, communication protocols play a crucial role in enabling devices to exchange data and[…]
RoHS 2– How to Produce RoHS 2 Compliant PCB Products
Introduction to RoHS 2 and its Impact on PCB Manufacturing The Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive (RoHS) is a set of guidelines that aims to[…]
OpenWrt x86 – Installation, Advantages, and Projects You Can Try.
Introduction to OpenWrt x86 OpenWrt is an open-source, Linux-based operating system for embedded devices such as wireless routers. It provides a fully writable filesystem with[…]

PCB Board Price–Do You Need To Control It?
Understanding the Factors That Affect PCB Price Several key factors contribute to the overall cost of a PCB. By understanding these elements, you can make[…]
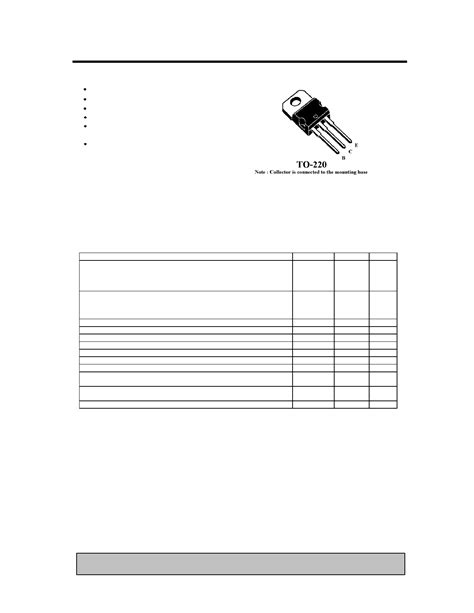
TIP31C Pinout; Technical Knowledge of the NPN transistor
What is the TIP31C? The TIP31C is a high-power NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) designed for general-purpose amplification and switching applications. It belongs to the[…]

PCB Manufacturers China-How To Choose Valuable Service
Introduction to PCB Manufacturing in China China has become a global hub for PCB manufacturing due to its vast resources, skilled workforce, and cost-effective production[…]
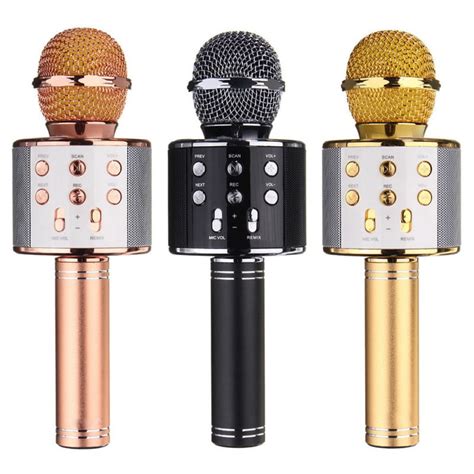

2.4 GHz Wireless Microphones: Can it Give you a Good Sound Quality?
Understanding 2.4 GHz Wireless Technology Before diving into the specifics of sound quality, let’s first understand what 2.4 GHz wireless technology entails. The 2.4 GHz[…]

11 Minefields to Get PCB Quotes Online
Introduction Getting PCB Quotes online can be a convenient and efficient way to compare prices and find the best deal for your project. However, navigating[…]
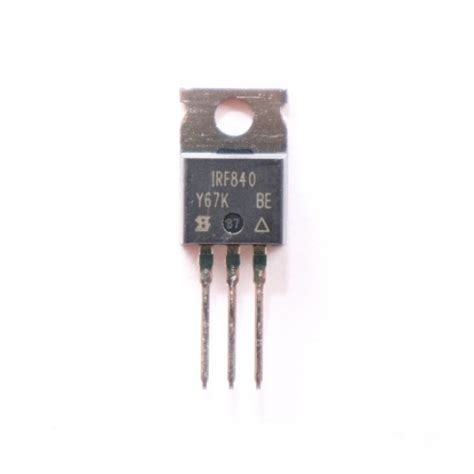
IRF840 Datasheet; A complete Introduction to IRF840 is an N-Channel MOSFET
What is an IRF840 MOSFET? The IRF840 is an N-Channel enhancement mode MOSFET designed for high-speed switching applications. It is part of the HEXFET® family[…]