What is a Rigid-flex PCB?
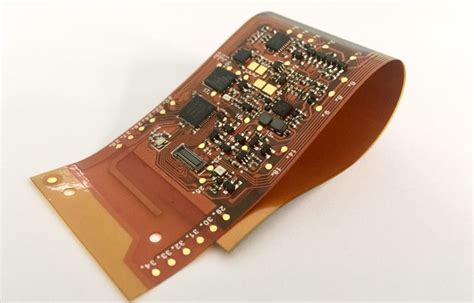
A Rigid-Flex PCB, also known as a flexible printed circuit board, is a unique type of PCB that combines the benefits of both rigid and flexible circuits. It consists of multiple layers of flexible and rigid PCB substrates laminated together into a single structure. This hybrid design allows for the creation of highly complex and compact electronic devices with enhanced reliability and durability.
Rigid-Flex PCBs are increasingly being used in various applications, such as:
- Aerospace and military equipment
- Medical devices
- Consumer electronics
- Automotive systems
- Industrial automation
The ability to bend and fold the flexible portions of the PCB enables designers to create three-dimensional configurations that can fit into tight spaces and withstand harsh environments.
Structure of a Rigid-Flex PCB
A Rigid-Flex PCB is composed of several layers, each serving a specific purpose. The typical structure of a Rigid-Flex PCB includes:
-
Rigid layers: These are the standard FR-4 PCB Layers that provide structural support and house the majority of the electronic components.
-
Flexible layers: Made from thin, flexible materials such as polyimide or polyester, these layers allow the PCB to bend and flex as needed.
-
Copper traces: Conductive copper traces are used to interconnect the electronic components on both the rigid and flexible layers.
-
Adhesive: A special adhesive is used to bond the rigid and flexible layers together, ensuring a strong and reliable connection.
-
Coverlay: A protective coverlay is applied to the outer surfaces of the flexible layers to provide insulation and protection against damage.
Here’s a table summarizing the key components of a Rigid-Flex PCB:
| Layer | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Rigid | FR-4 | Provides structural support and houses components |
| Flexible | Polyimide or polyester | Allows the PCB to bend and flex |
| Copper traces | Copper | Interconnects electronic components |
| Adhesive | Special bonding adhesive | Bonds rigid and flexible layers together |
| Coverlay | Insulating material | Protects and insulates the flexible layers |
Advantages of Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-Flex PCBs offer several advantages over traditional rigid PCBs:
-
Reduced size and weight: By eliminating the need for connectors and cables between rigid PCBs, Rigid-Flex PCBs enable more compact and lightweight designs.
-
Increased reliability: The elimination of connectors and cables also reduces the number of potential failure points, resulting in higher reliability.
-
Improved signal integrity: Shorter signal paths and reduced noise interference lead to better signal integrity in Rigid-Flex PCBs.
-
Enhanced durability: Rigid-Flex PCBs can withstand repeated bending and flexing, making them ideal for applications subject to vibration or motion.
-
Design flexibility: The ability to create three-dimensional configurations allows for greater design flexibility and the integration of multiple functionalities into a single PCB Assembly.

Manufacturing Process of Rigid-Flex PCBs
The manufacturing process of Rigid-Flex PCBs is more complex than that of standard rigid PCBs due to the integration of flexible layers. The main steps involved in the manufacturing process are:
-
Design and layout: The PCB design is created using specialized CAD software, taking into account the specific requirements of the Rigid-Flex construction.
-
Material selection: The appropriate materials for the rigid and flexible layers are chosen based on the application requirements.
-
Lamination: The rigid and flexible layers are laminated together using a special adhesive under high temperature and pressure.
-
Drilling and plating: Holes are drilled through the laminated layers, and the walls of the holes are plated with copper to create electrical connections between layers.
-
Etching: The unwanted copper is removed from the PCB using a chemical etching process, leaving only the desired copper traces.
-
Solder mask and silkscreen: A solder mask is applied to protect the copper traces, and a silkscreen layer is added for component identification and labeling.
-
Cutting and profiling: The PCB panel is cut and profiled to the desired shape, and the flexible regions are separated from the rigid areas.
-
Assembly: The electronic components are soldered onto the PCB using surface mount or through-hole techniques.
-
Testing and inspection: The assembled Rigid-Flex PCB undergoes thorough testing and inspection to ensure functionality and quality.
Costs Associated with Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-Flex PCBs are generally more expensive than traditional rigid PCBs due to the complexity of the manufacturing process and the specialized materials used. The cost of a Rigid-Flex PCB depends on several factors, such as:
- Size and complexity of the design
- Number of layers (both rigid and flexible)
- Material selection
- Quantity ordered
- Manufacturing turnaround time
Despite the higher initial costs, Rigid-Flex PCBs can offer long-term cost savings by:
- Reducing the number of components and assemblies required
- Improving reliability and reducing maintenance costs
- Enabling more compact and lightweight designs, which can lower shipping and handling costs
Choosing a Rigid-Flex PCB Manufacturer
When selecting a Rigid-Flex PCB manufacturer, consider the following factors:
-
Experience and expertise: Look for a manufacturer with a proven track record of producing high-quality Rigid-Flex PCBs.
-
Technical capabilities: Ensure that the manufacturer has the necessary equipment and expertise to handle your specific design requirements.
-
Quality control: Choose a manufacturer with strict quality control processes and industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 and IPC Standards.
-
Communication and support: Select a manufacturer that offers clear communication and responsive support throughout the design and manufacturing process.
-
Cost and lead time: Consider the manufacturer’s pricing and lead times to ensure they align with your budget and project schedule.
Some leading Rigid-Flex PCB manufacturers include:
- Epec Engineered Technologies
- Printed Circuits
- GS Swiss PCB AG
- Würth Elektronik
- Cirexx International Inc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the minimum bend radius for a Rigid-Flex PCB?
A: The minimum bend radius depends on the thickness and material properties of the flexible layers. Generally, the minimum bend radius is 6 to 10 times the thickness of the flexible material. -
Q: Can Rigid-Flex PCBs be repaired?
A: Repairing a Rigid-Flex PCB can be challenging due to the complex structure and specialized materials used. In most cases, it is more cost-effective to replace the entire PCB rather than attempting a repair. -
Q: Are Rigid-Flex PCBs suitable for high-temperature applications?
A: Yes, Rigid-Flex PCBs can be designed to withstand high temperatures by selecting appropriate materials and construction techniques. Polyimide, for example, is a common flexible material that can operate in temperatures up to 400°C. -
Q: How do I design a Rigid-Flex PCB?
A: Designing a Rigid-Flex PCB requires specialized knowledge and CAD software. It’s essential to work with experienced PCB designers and manufacturers who can guide you through the design process and ensure your PCB meets all necessary requirements. -
Q: What are the typical lead times for Rigid-Flex PCB manufacturing?
A: Lead times for Rigid-Flex PCBs can vary depending on the complexity of the design and the manufacturer’s workload. Typical lead times range from 3 to 6 weeks, but expedited services may be available for time-critical projects.
Conclusion
Rigid-Flex PCBs offer a unique combination of flexibility and durability, enabling the creation of compact, reliable, and high-performance electronic devices. By understanding the structure, manufacturing process, costs, and key considerations associated with Rigid-Flex PCBs, designers and engineers can leverage this technology to develop innovative solutions for a wide range of applications.
When embarking on a Rigid-Flex PCB project, it’s crucial to partner with an experienced and reputable manufacturer who can provide the necessary expertise and support throughout the design and production process. With the right approach and collaboration, Rigid-Flex PCBs can help drive the next generation of electronic devices and systems.
No responses yet