The Importance of Product Lifecycle Management
In today’s highly competitive and globalized business environment, effective PLM is crucial for companies to remain competitive and successful. By implementing a robust PLM strategy, organizations can:
- Accelerate time-to-market
- Reduce product development costs
- Improve product quality and reliability
- Enhance collaboration and communication across teams and departments
- Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements
- Increase customer satisfaction and loyalty
The Stages of Product Lifecycle Management
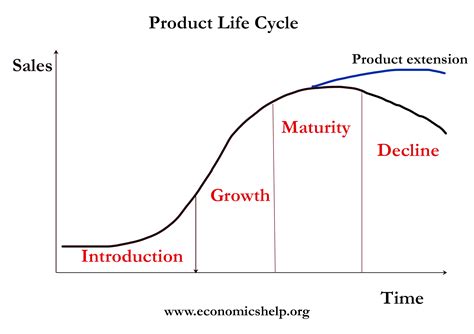
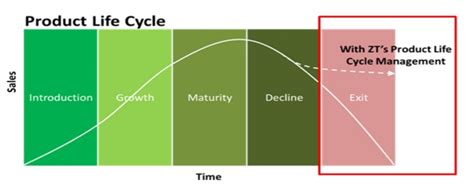
The product lifecycle typically consists of four main stages:
- Introduction
- Growth
- Maturity
- Decline
Each stage presents unique challenges and opportunities for companies, and effective PLM strategies must adapt to these changing circumstances.
Introduction Stage
In the introduction stage, a new product is launched into the market. This stage is characterized by low sales volumes, high marketing expenses, and limited competition. The main objectives during this stage are to create awareness, generate interest, and encourage early adopters to try the product.
Key activities in the introduction stage include:
- Market research and analysis
- Product development and testing
- Branding and packaging design
- Pricing and distribution strategy
- Promotional campaigns and product launches
Growth Stage
As the product gains traction in the market, it enters the growth stage. This stage is characterized by rapidly increasing sales, expanding market share, and the emergence of competitors. The main objectives during this stage are to maintain the product’s growth momentum, differentiate it from competitors, and establish a strong market position.
Key activities in the growth stage include:
- Expanding distribution channels
- Increasing production capacity
- Enhancing product features and benefits
- Engaging in competitive marketing and advertising
- Building customer loyalty and brand equity
Maturity Stage
In the maturity stage, the product has reached its peak sales and market share. This stage is characterized by intense competition, price pressure, and slowing growth rates. The main objectives during this stage are to defend the product’s market position, maintain profitability, and explore new growth opportunities.
Key activities in the maturity stage include:
- Cost optimization and process improvement
- Product line extensions and variations
- Targeted marketing and promotional campaigns
- Exploring new market segments and geographies
- Developing strategic partnerships and alliances
Decline Stage
As the product enters the decline stage, sales and profitability start to decrease. This stage is characterized by shrinking market demand, obsolescence, and the emergence of newer, more advanced products. The main objectives during this stage are to minimize losses, phase out the product, and transition resources to new initiatives.
Key activities in the decline stage include:
- Rationalization of product portfolio
- Cost reduction and resource optimization
- Selective marketing and promotional activities
- Planning for product discontinuation and replacement
- Evaluating lessons learned and best practices
Implementing a Product Lifecycle Management Strategy
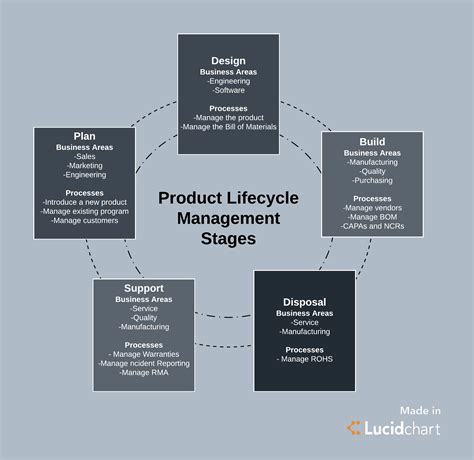
To successfully implement a PLM strategy, companies must follow a structured approach that encompasses people, processes, and technology. The key steps in implementing a PLM strategy include:
-
Defining PLM Objectives and Scope: Clearly articulate the goals and objectives of the PLM initiative, and define the scope of products, processes, and stakeholders to be included.
-
Assessing Current Capabilities: Evaluate the organization’s current PLM capabilities, including people, processes, and technology, to identify gaps and improvement opportunities.
-
Designing the PLM Solution: Develop a comprehensive PLM solution that addresses the identified gaps and aligns with the organization’s objectives and constraints. This includes selecting appropriate PLM software, defining processes and workflows, and establishing governance and control mechanisms.
-
Implementing the PLM Solution: Deploy the PLM solution across the organization, including data migration, system integration, and user training. Ensure adequate change management and communication to facilitate adoption and minimize disruption.
-
Measuring and Optimizing Performance: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of the PLM initiative, and continuously monitor and optimize performance based on data-driven insights and best practices.

PLM Software and Tools
PLM software and tools play a critical role in enabling organizations to effectively manage their product lifecycle. These solutions provide a centralized platform for managing product data, documents, and processes, enabling collaboration, version control, and traceability across the entire product lifecycle.
Key features and functionalities of PLM software include:
- Product data management (PDM)
- Bill of materials (BOM) management
- Engineering change management
- Document management and version control
- Workflow and process automation
- Collaboration and communication tools
- Integration with other enterprise systems (e.g., ERP, MES, CRM)
Some of the leading PLM software vendors include:
- Siemens PLM Software
- Dassault Systèmes
- PTC
- Oracle
- SAP
- Autodesk
When selecting a PLM software solution, organizations should consider factors such as functionality, scalability, ease of use, integration capabilities, and total cost of ownership.
PLM Best Practices
To maximize the benefits of PLM, organizations should adopt best practices that have been proven to drive success. Some of the key PLM best practices include:
-
Executive Sponsorship and Alignment: Ensure that PLM initiatives have strong executive sponsorship and are aligned with the organization’s strategic goals and objectives.
-
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration and communication across functions and departments, including engineering, manufacturing, sales, and marketing, to ensure a holistic approach to PLM.
-
Data Governance and Quality: Establish robust data governance and quality management processes to ensure the accuracy, consistency, and completeness of product data throughout the lifecycle.
-
Continuous Improvement and Innovation: Embrace a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, leveraging PLM tools and processes to drive product excellence and customer satisfaction.
-
Training and Change Management: Invest in comprehensive training and change management programs to ensure that employees have the skills and knowledge to effectively use PLM tools and processes.
The Future of Product Lifecycle Management
As technology continues to advance and customer expectations evolve, the future of PLM is likely to be shaped by several key trends and innovations, including:
-
Digital Transformation: The increasing digitization of products, processes, and services will require PLM solutions to support the management of digital twins, IoT data, and other digital assets.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML technologies will enable more intelligent and automated PLM processes, such as predictive maintenance, quality control, and design optimization.
-
Cloud and SaaS Deployment: The adoption of cloud-based and software-as-a-service (SaaS) PLM solutions will continue to grow, providing organizations with greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
-
Extended Reality (XR): The use of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies will enable more immersive and collaborative PLM experiences, such as Virtual Prototyping and remote assistance.
-
Circular Economy and Sustainability: PLM solutions will need to support the growing focus on circular economy and sustainability, enabling the design and management of products for reuse, recycling, and minimal environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the difference between PLM and ERP?
-
PLM focuses on managing the entire product lifecycle, from conception to disposal, while ERP focuses on managing the operational and financial aspects of a business, such as accounting, procurement, and supply chain management. PLM and ERP systems often integrate to provide a comprehensive solution for managing product and business data.
-
How does PLM benefit small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)?
-
PLM can help SMEs to streamline their product development processes, reduce time-to-market, improve product quality, and enhance collaboration with customers and suppliers. By leveraging cloud-based and SaaS PLM solutions, SMEs can access enterprise-grade capabilities at an affordable cost and scale.
-
What are the key challenges in implementing a PLM strategy?
-
Some of the key challenges in implementing a PLM strategy include resistance to change, data quality and integration issues, lack of executive sponsorship and alignment, and inadequate training and support. To overcome these challenges, organizations need to adopt a structured and holistic approach to PLM, with a focus on change management, data governance, and continuous improvement.
-
How does PLM support regulatory compliance?
-
PLM solutions provide a centralized platform for managing product data, documents, and processes, enabling organizations to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements such as product safety, environmental sustainability, and data privacy. PLM tools can also automate compliance workflows, generate audit trails, and provide real-time visibility into compliance status.
-
What is the ROI of PLM?
- The return on investment (ROI) of PLM can vary depending on the specific industry, company size, and implementation approach. However, studies have shown that PLM can deliver significant benefits, such as reduced product development costs, increased revenue from new products, improved product quality and customer satisfaction, and enhanced operational efficiency. To maximize the ROI of PLM, organizations need to establish clear objectives, measure performance, and continuously optimize their PLM processes and tools.
Conclusion
Product Lifecycle Management is a critical strategy for organizations seeking to drive innovation, efficiency, and competitiveness in today’s fast-paced and globalized business environment. By adopting a comprehensive and structured approach to PLM, encompassing people, processes, and technology, companies can effectively manage their products across the entire lifecycle, from conception to disposal.
As technology continues to advance and customer expectations evolve, the future of PLM is likely to be shaped by digital transformation, artificial intelligence, cloud and SaaS deployment, extended reality, and the circular economy. To stay ahead of the curve, organizations need to embrace these trends and innovations, while also adopting best practices in PLM implementation, such as executive sponsorship, cross-functional collaboration, data governance, continuous improvement, and training and change management.
By investing in PLM and making it a strategic priority, organizations can unlock significant benefits, such as accelerated time-to-market, reduced costs, improved product quality, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased profitability. As such, PLM should be a key consideration for any company looking to drive long-term success and competitiveness in the marketplace.
| PLM Stage | Objectives | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Create awareness, generate interest, encourage early adopters | Market research, product development, branding, pricing, promotion |
| Growth | Maintain growth, differentiate from competitors, establish market position | Expand distribution, increase production, enhance features, build loyalty |
| Maturity | Defend market position, maintain profitability, explore new opportunities | Cost optimization, product line extensions, targeted marketing, strategic partnerships |
| Decline | Minimize losses, phase out product, transition resources | Portfolio rationalization, cost reduction, selective marketing, product discontinuation |
Table 1: PLM Stages, Objectives, and Key Activities
| PLM Software Vendor | Key Products |
|---|---|
| Siemens PLM Software | Teamcenter, NX, Simcenter, Tecnomatix |
| Dassault Systèmes | CATIA, ENOVIA, DELMIA, SIMULIA, 3DEXCITE |
| PTC | Windchill, Creo, ThingWorx, Vuforia |
| Oracle | Oracle PLM Cloud, Agile PLM |
| SAP | SAP PLM, SAP Engineering Control Center |
| Autodesk | Fusion 360, Vault, PLM 360 |
Table 2: Leading PLM Software Vendors and Their Key Products
No responses yet