Introduction to SMD LEDs
Surface-mount device light-emitting diodes (SMD LEDs) have become increasingly popular in recent years for use in printed circuit boards (PCBs) due to their small size, low power consumption, and high efficiency. SMD LEDs offer numerous advantages over traditional through-hole LEDs, making them an attractive choice for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to automotive lighting.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the world of SMD LEDs, discussing their benefits, types, applications, and how they can be effectively incorporated into your PCB designs and bill of materials (BOM).
Benefits of Using SMD LEDs
Space Savings
One of the primary advantages of SMD LEDs is their compact size. These miniature components are significantly smaller than their through-hole counterparts, allowing for more efficient use of PCB real estate. By opting for SMD LEDs, designers can create smaller, more compact devices or incorporate additional features within the same PCB dimensions.
Increased Efficiency
SMD LEDs are known for their high efficiency, meaning they can produce more light output per unit of power consumed compared to traditional LEDs. This efficiency translates to lower power consumption and extended battery life in portable devices, making SMD LEDs an eco-friendly and cost-effective choice.
Enhanced Durability
Due to their surface-mount nature, SMD LEDs are more resistant to vibration and shock compared to through-hole LEDs. The absence of long leads reduces the risk of mechanical stress and breakage, resulting in improved reliability and longer product lifespans.
Simplified Assembly
SMD LEDs are designed for automated assembly processes, such as pick-and-place machines and reflow soldering. This streamlined assembly approach reduces manual labor, improves production speed, and minimizes the risk of human error during the manufacturing process.

Types of SMD LEDs
SMD LEDs come in various packages and sizes to suit different applications and design requirements. Some of the most common types include:
| Package | Dimensions (mm) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 0402 | 1.0 x 0.5 | Ultra-compact devices, wearables |
| 0603 | 1.6 x 0.8 | Mobile devices, indicators |
| 0805 | 2.0 x 1.25 | General-purpose, backlighting |
| 1206 | 3.2 x 1.6 | High-power applications, automotive |
| 3528 | 3.5 x 2.8 | High-brightness, signage, decorative |
| 5050 | 5.0 x 5.0 | High-power RGB, general lighting |
Choosing the Right SMD LED
When selecting an SMD LED for your PCB design, consider the following factors:
- Brightness requirements
- Color and wavelength
- Viewing angle
- Forward voltage and current
- Size constraints
- Environmental conditions (temperature, humidity)
By carefully evaluating these factors and consulting the LED manufacturer’s datasheet, you can ensure that you choose the most suitable SMD LED for your specific application.

Incorporating SMD LEDs into Your PCB Design
Schematic Design Considerations
When incorporating SMD LEDs into your schematic design, pay attention to the following:
- Forward voltage and current: Ensure that the LED’s forward voltage and current are compatible with your circuit’s power supply and current-limiting resistors.
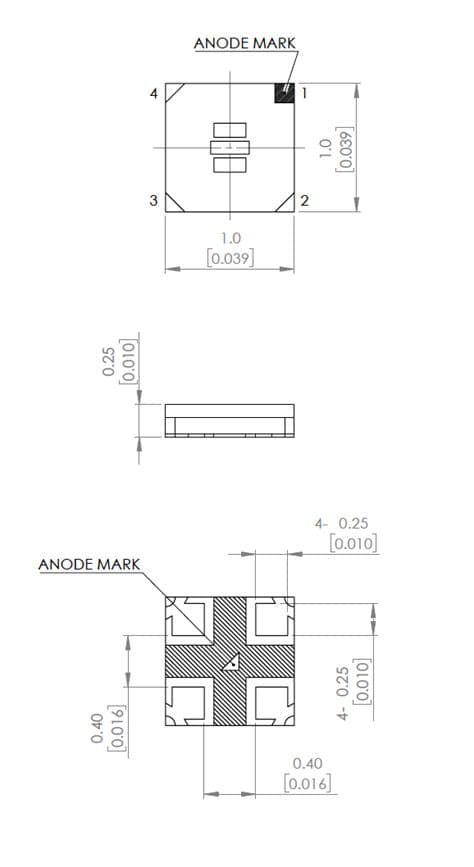
- Polarity: SMD LEDs are polarized components, so make sure to connect the anode (positive) and cathode (negative) terminals correctly.
- Current-limiting resistors: Include appropriate current-limiting resistors in series with each LED to prevent overcurrent and damage.
PCB Layout Considerations
When laying out your PCB with SMD LEDs, keep these tips in mind:
- Placement: Position the SMD LEDs in a way that optimizes light output and minimizes interference with other components.
- Thermal management: If using high-power SMD LEDs, consider incorporating thermal vias or heatsinks to dissipate heat effectively.
- Solder mask: Ensure that the solder mask aperture around the SMD LED pads is large enough to allow for proper soldering and light emission.
- Orientation: Pay attention to the orientation of polarized SMD LEDs, as incorrect placement can lead to non-functioning or damaged components.
SMD LEDs and Your Bill of Materials (BOM)
When creating a bill of materials (BOM) for your PCB that includes SMD LEDs, be sure to include the following information:
- Manufacturer and part number
- Quantity required
- Description (package size, color, brightness)
- Supplier and lead time
- Unit price and extended cost
Having a well-organized and detailed BOM helps ensure smooth procurement and production processes, minimizing the risk of errors or delays due to incorrect or missing components.
Applications of SMD LEDs
SMD LEDs find applications in a wide range of industries and products, including:
- Consumer electronics (smartphones, tablets, laptops)
- Automotive lighting (interior, exterior, instrument clusters)
- Industrial equipment (indicators, displays, control panels)
- Medical devices (diagnostic tools, surgical instruments)
- Lighting fixtures (bulbs, strips, panels)
- Wearable Technology (smartwatches, fitness trackers)
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices (sensors, smart home appliances)
As technology advances and new applications emerge, the demand for SMD LEDs continues to grow, driving innovation and improvements in efficiency, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
Future Trends in SMD LED Technology
The field of SMD LEDs is constantly evolving, with new advancements and trends shaping the future of this technology. Some notable developments include:
- Micro-LEDs: These ultra-small LEDs, typically less than 100 micrometers in size, offer higher brightness, lower power consumption, and improved contrast compared to traditional SMD LEDs.
- Chip-on-Board (COB) LEDs: COB technology involves mounting multiple LED chips directly onto a substrate, resulting in higher light output and better thermal management.
- Intelligent lighting: The integration of SMD LEDs with sensors, controllers, and communication protocols enables the development of smart lighting systems that can adapt to user preferences and environmental conditions.
- Sustainable materials: Manufacturers are exploring the use of eco-friendly, recyclable materials in the production of SMD LEDs to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainability.
As these trends continue to unfold, SMD LEDs are poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of lighting and electronics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between SMD LEDs and through-hole LEDs?
SMD LEDs are surface-mounted components that are soldered directly onto the PCB, while through-hole LEDs have long leads that are inserted through holes in the PCB and soldered on the opposite side. SMD LEDs are smaller, more efficient, and better suited for automated assembly compared to through-hole LEDs.
2. Can I replace a through-hole LED with an SMD LED in my existing design?
In most cases, replacing a through-hole LED with an SMD LED will require modifications to the PCB layout and schematic. The different package sizes, pad configurations, and electrical characteristics of SMD LEDs may necessitate changes to the circuit design and board layout to ensure proper functionality.
3. How do I calculate the current-limiting resistor value for an SMD LED?
To calculate the current-limiting resistor value, use the following formula: R = (Vs – Vf) / If, where R is the resistor value, Vs is the supply voltage, Vf is the LED’s forward voltage, and If is the desired forward current. Consult the LED’s datasheet for the specific forward voltage and current ratings.
4. Are SMD LEDs more expensive than through-hole LEDs?
In general, SMD LEDs are more cost-effective than through-hole LEDs due to their smaller size, higher efficiency, and compatibility with automated assembly processes. However, the actual cost comparison may vary depending on factors such as the specific LED type, quantity, and supplier.
5. How do I ensure proper thermal management for high-power SMD LEDs?
To ensure proper thermal management for high-power SMD LEDs, consider the following techniques:
– Use a PCB with a thick copper layer or a metal-core PCB to improve heat dissipation.
– Incorporate thermal vias to transfer heat from the LED to the opposite side of the PCB.
– Use a heatsink or other cooling solution to dissipate heat away from the LED and the PCB.
– Ensure adequate airflow around the LED and the PCB to promote convective cooling.
Conclusion
SMD LEDs have revolutionized the world of PCB design and have become an indispensable component in countless applications across various industries. By understanding the benefits, types, and design considerations associated with SMD LEDs, you can effectively incorporate these versatile components into your PCB designs and BOMs.
As technology continues to advance, staying informed about the latest trends and developments in SMD LED technology is crucial for staying competitive and delivering cutting-edge products. By embracing the power and potential of SMD LEDs, you can create innovative, efficient, and reliable electronic devices that meet the ever-evolving demands of the market.
No responses yet