Introduction to PCB CNC Machines
In the world of electronics manufacturing, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components that form the backbone of countless devices. To meet the growing demand for high-quality and precise PCBs, manufacturers rely on advanced technology like Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines. PCB CNC machines have revolutionized the PCB manufacturing process, offering unparalleled accuracy, speed, and consistency.
What are PCB CNC Machines?
PCB CNC machines are computer-controlled machines designed specifically for the manufacturing of printed circuit boards. These machines utilize CNC technology to automate and optimize various processes involved in PCB fabrication, such as drilling, routing, and milling. By combining high-precision mechanics with sophisticated software, PCB CNC machines enable manufacturers to produce complex PCB designs with tight tolerances and minimal human intervention.
Advantages of PCB CNC Machines
The use of PCB CNC machines offers several key advantages over traditional manual PCB fabrication methods:
-
Accuracy: CNC machines are capable of achieving extremely high levels of accuracy, with positioning precision in the range of microns. This ensures that PCBs are manufactured to exact specifications, minimizing the risk of errors and defects.
-
Consistency: With CNC technology, PCB manufacturing processes can be repeated with consistent results. Each PCB produced by a CNC machine will be identical to the previous one, ensuring uniformity and reliability across large production runs.
-
Speed: PCB CNC machines can operate at high speeds, significantly reducing the time required to manufacture PCBs compared to manual methods. This increased efficiency allows manufacturers to meet tight deadlines and handle high-volume orders.
-
Complexity: CNC machines can handle complex PCB designs with ease. They are capable of drilling tiny holes, routing intricate patterns, and milling fine details that would be challenging or impossible to achieve manually.
-
Cost-effectiveness: While the initial investment in PCB CNC machines may be higher than manual methods, the long-term cost savings are substantial. CNC machines reduce labor costs, minimize material waste, and improve overall production efficiency, resulting in lower costs per PCB.
Types of PCB CNC Machines
There are several types of PCB CNC machines available, each designed for specific tasks and applications. Some of the most common types include:
1. CNC Drilling Machines
CNC drilling machines are used to drill holes in PCBs with high precision. These machines can drill holes of various sizes and depths, accommodating different component requirements. They are equipped with multiple spindles, allowing for simultaneous drilling of multiple holes, which greatly enhances productivity.
2. CNC Routing Machines
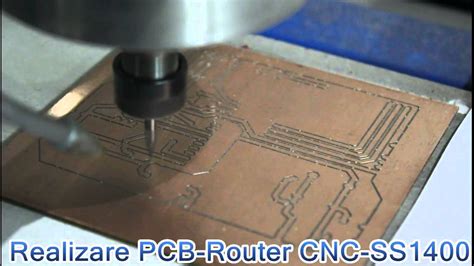
CNC routing machines are used to cut and shape the outline of PCBs. They employ high-speed spindles and specialised cutting tools to route the PCB substrate material accurately. CNC routers can create complex shapes, cut out openings, and trim the edges of PCBs with smooth finishes.
3. CNC Milling Machines
CNC milling machines are versatile tools used for various PCB fabrication processes. They can perform tasks such as creating cavities, pockets, and slots in PCBs, as well as removing excess material and creating surface finishes. CNC milling machines offer high precision and can handle a wide range of materials, including FR4, aluminum, and copper.
4. CNC Engraving Machines
CNC engraving machines are used to engrave text, logos, or other markings on PCBs. They employ high-speed spindles and diamond-tipped tools to create precise and permanent engravings on the PCB surface. Engraving machines are commonly used for labeling, branding, and adding traceability information to PCBs.
PCB CNC Machine Components
PCB CNC machines consist of several key components that work together to achieve precise and efficient PCB manufacturing. These components include:
1. Spindle
The spindle is the rotating axis of the CNC machine that holds and drives the cutting tool. It is responsible for providing the necessary speed and torque to perform drilling, routing, or milling operations. Spindles used in PCB CNC machines are typically high-speed, ranging from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of revolutions per minute (RPM).
2. Axis Motors and Drives
PCB CNC machines have multiple axes of motion, typically referred to as X, Y, and Z axes. Each axis is controlled by a dedicated motor and drive system. These motors, often stepper or servo motors, precisely position the spindle and cutting tool based on the CNC program instructions. The drives regulate the power and control signals to the motors, ensuring smooth and accurate motion.
3. CNC Controller
The CNC controller is the brain of the PCB CNC machine. It reads the CNC program, which contains the instructions for the desired PCB manufacturing operations, and translates it into machine commands. The controller sends signals to the axis motors and drives, controlling their movement and synchronizing their actions. It also monitors and regulates various machine parameters, such as spindle speed, feed rate, and tool changes.
4. Work Table and Fixture
The work table is the surface on which the PCB is placed during the manufacturing process. It is typically a flat, stable platform that provides a secure and precise foundation for the PCB. Fixtures, such as clamps or vacuum systems, are used to hold the PCB firmly in place, preventing any movement or vibration during the machining operations.
5. Cutting Tools
PCB CNC machines employ a variety of cutting tools, depending on the specific manufacturing process. For drilling, carbide-tipped drill bits are commonly used, available in different sizes to accommodate various hole diameters. Routing and milling operations utilize end mills, ball mills, and other specialized cutting tools designed for PCB materials. These tools are chosen based on factors such as material compatibility, desired cutting profile, and tool life.

PCB CNC Machine Software
To operate PCB CNC machines effectively, specialized software is used to design, program, and control the manufacturing process. Some of the essential software components include:
1. CAD/CAM Software
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software are used to create and prepare PCB designs for CNC Machining. CAD software allows designers to create detailed 2D or 3D models of the PCB, specifying the layout, dimensions, and component placement. CAM software takes the CAD model and generates the CNC program, which contains the machine instructions for drilling, routing, and milling operations.
2. Toolpath Generation Software
Toolpath generation software is a specialized CAM software that focuses on creating efficient and optimized toolpaths for PCB CNC machines. It considers factors such as tool geometry, cutting parameters, and material properties to generate toolpaths that minimize machining time, reduce tool wear, and ensure high-quality results. Toolpath generation software often includes simulation capabilities, allowing users to visualize and validate the machining process before actual production.
3. Machine Control Software
Machine control software is the interface between the CNC controller and the operator. It provides a user-friendly environment for setting up, monitoring, and controlling the PCB CNC machine. This software allows operators to load CNC programs, set machine parameters, initiate machining operations, and monitor the progress in real-time. It may also include features such as tool management, machine diagnostics, and data logging for process optimization and traceability.
PCB CNC Machine Maintenance and Calibration
To ensure consistent performance and longevity of PCB CNC machines, regular maintenance and calibration are essential. Some key aspects of machine maintenance and calibration include:
1. Lubrication
Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and durability of PCB CNC machines. Regularly lubricating the spindle bearings, linear guides, and other moving components helps reduce friction, prevent wear, and maintain precision. Manufacturers typically provide guidelines for the type and frequency of lubrication required for their machines.
2. Cleaning
PCB CNC machines generate dust, debris, and chips during the machining process. Regular cleaning of the machine, including the work table, spindle, and cutting tools, is necessary to prevent contamination and ensure accurate and consistent results. Compressed air, brushes, and vacuum systems are commonly used for cleaning PCB CNC machines.
3. Calibration
Calibration is the process of verifying and adjusting the accuracy of PCB CNC machines. Over time, mechanical components may experience wear or misalignment, affecting the machine’s precision. Regular calibration helps maintain the machine’s accuracy and ensures that PCBs are manufactured to the required specifications. Calibration procedures often involve using precision measurement tools, such as laser interferometers or dial gauges, to assess and correct any deviations.
4. Spindle Maintenance
The spindle is a critical component of PCB CNC machines and requires special attention. Regular inspection and maintenance of the spindle, including bearing replacement and balancing, are necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failure. Manufacturers typically provide guidelines for spindle maintenance intervals and procedures.
5. Software Updates
Keeping the PCB CNC machine software up to date is important for accessing new features, bug fixes, and performance improvements. Software updates may include enhancements to CAD/CAM functionality, toolpath generation algorithms, and machine control interfaces. Regularly checking for and installing software updates helps optimize the machine’s capabilities and ensures compatibility with the latest design and manufacturing standards.
Applications of PCB CNC Machines
PCB CNC machines find applications in various industries and sectors where precise and reliable PCB manufacturing is required. Some of the key applications include:
1. Electronics Manufacturing
PCB CNC machines are extensively used in the electronics manufacturing industry for producing PCBs for a wide range of products, such as consumer electronics, automotive systems, medical devices, and industrial equipment. They enable the fabrication of high-quality PCBs with intricate designs and tight tolerances, meeting the demands of modern electronic devices.
2. Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace and defense industries rely on PCB CNC machines for manufacturing PCBs used in critical systems, such as avionics, communication equipment, and military hardware. These industries require PCBs with exceptional reliability, durability, and performance, and PCB CNC machines help meet these stringent requirements.
3. Medical Devices
Medical devices often incorporate complex and miniaturized PCBs that demand high precision and reliability. PCB CNC machines are used to manufacture PCBs for various medical applications, including diagnostic equipment, monitoring systems, and implantable devices. The accuracy and consistency provided by CNC machines are essential for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical devices.
4. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry increasingly relies on electronic systems for vehicle control, entertainment, and safety features. PCB CNC machines are used to manufacture PCBs for automotive applications, such as engine control units, infotainment systems, and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). The high-volume production capabilities and reliability of PCB CNC machines are crucial for meeting the demands of the automotive industry.
5. Research and Development
PCB CNC machines are valuable tools for research and development (R&D) activities in various fields, including electronics, robotics, and IoT (Internet of Things). They allow researchers and engineers to quickly prototype and test PCB designs, enabling faster iteration and innovation cycles. The flexibility and precision of PCB CNC machines make them ideal for R&D environments where customization and experimentation are common.
| Application | Key Requirements |
|---|---|
| Electronics Manufacturing | High precision, complex designs, tight tolerances |
| Aerospace and Defense | Reliability, durability, performance |
| Medical Devices | Precision, reliability, miniaturization |
| Automotive Industry | High-volume production, reliability |
| Research and Development | Flexibility, customization, rapid prototyping |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between PCB CNC machines and traditional PCB manufacturing methods?
PCB CNC machines offer several advantages over traditional PCB manufacturing methods. They provide higher accuracy, consistency, and speed, enabling the production of complex PCB designs with tight tolerances. CNC machines also reduce labor costs, minimize material waste, and improve overall production efficiency.
2. What materials can PCB CNC machines work with?
PCB CNC machines can work with a variety of materials commonly used in PCB manufacturing, including FR4, aluminum, copper, and other substrate materials. The specific materials supported may vary depending on the machine’s capabilities and the cutting tools used.
3. How long does it take to manufacture a PCB using a CNC machine?
The manufacturing time for a PCB using a CNC machine depends on various factors, such as the complexity of the design, the size of the PCB, and the machine’s capabilities. However, CNC machines generally offer faster production times compared to manual methods. Simple PCBs can be manufactured in a matter of minutes, while more complex designs may take several hours.
4. What is the typical accuracy of PCB CNC machines?
PCB CNC machines are capable of achieving extremely high levels of accuracy, with positioning precision in the range of microns. The exact accuracy may vary depending on the specific machine and its configuration, but most modern PCB CNC machines can maintain tolerances well within industry standards.
5. How often should PCB CNC machines be calibrated?
The frequency of calibration for PCB CNC machines depends on factors such as the machine’s usage, environmental conditions, and manufacturer recommendations. As a general guideline, calibration should be performed at least once a year or whenever there are signs of decreased accuracy or precision. However, some high-precision applications may require more frequent calibration to ensure consistent performance.
Conclusion
PCB CNC machines have revolutionized the PCB manufacturing industry, offering unparalleled accuracy, speed, and consistency. These high-tech machines combine advanced mechanics, sophisticated software, and precision control to enable the fabrication of complex PCB designs with tight tolerances. By automating and optimizing various processes, such as drilling, routing, and milling, PCB CNC machines have become indispensable tools for electronics manufacturing, aerospace and defense, medical devices, automotive industry, and research and development.
The use of PCB CNC machines brings numerous advantages, including improved accuracy, consistent results, faster production times, and the ability to handle intricate designs. They also offer cost-effectiveness by reducing labor costs, minimizing material waste, and enhancing overall production efficiency.
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of PCB CNC machines, regular maintenance and calibration are crucial. This includes proper lubrication, cleaning, spindle maintenance, and software updates. By following manufacturer guidelines and best practices, manufacturers can keep their PCB CNC machines running smoothly and producing high-quality PCBs consistently.
As technology continues to advance, PCB CNC machines are expected to evolve further, offering even greater capabilities and performance. With their ability to meet the demanding requirements of various industries and applications, PCB CNC machines will remain essential tools in the world of electronics manufacturing, driving innovation and enabling the creation of cutting-edge products.
No responses yet