Introduction to PCB standards
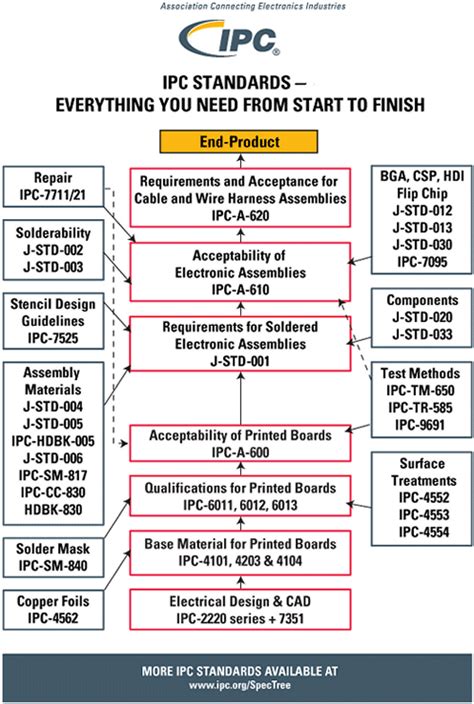
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in modern electronic devices, providing mechanical support and electrical connectivity for various components. To ensure the quality, reliability, and consistency of PCBs, the electronics industry relies on well-defined standards. Two of the most critical standards in PCB production are IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600. These standards provide guidelines for the qualification and performance of rigid printed boards and the acceptability of printed boards, respectively.
What is IPC?
IPC, formerly known as the Institute for Printed Circuits, is a global trade association that develops standards for the electronic interconnection industry. IPC Standards cover various aspects of PCB design, fabrication, assembly, and testing, ensuring that manufacturers follow best practices and deliver high-quality products.
IPC-6012: Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards
IPC-6012 is a standard that establishes the requirements for the qualification and performance of rigid printed boards. It covers a wide range of topics, including materials, fabrication processes, quality assurance, and testing.
Key Aspects of IPC-6012
-
Materials: IPC-6012 specifies the requirements for base materials, conductive materials, and solder mask materials used in PCB fabrication.
-
Fabrication Processes: The standard outlines the requirements for various fabrication processes, such as drilling, plating, etching, and solder mask application.
-
Quality Assurance: IPC-6012 defines the quality assurance requirements for PCB manufacturers, including inspection methods, sampling plans, and acceptance criteria.
-
Testing: The standard specifies the testing requirements for electrical, mechanical, and environmental performance of PCBs.
Benefits of Adhering to IPC-6012
Adhering to IPC-6012 offers several benefits for PCB manufacturers and end-users:
-
Consistency: By following the standard, manufacturers can ensure consistent quality across different production runs and facilities.
-
Reliability: IPC-6012 helps manufacturers produce PCBs that meet the required performance and reliability criteria, reducing the risk of failures in the field.
-
Customer Satisfaction: Adhering to IPC-6012 demonstrates a commitment to quality and can help manufacturers gain customer trust and loyalty.
IPC-A-600: Acceptability of Printed Boards
IPC-A-600 is a standard that provides visual acceptance criteria for printed boards. It helps manufacturers and customers determine whether a PCB meets the required quality standards by visually inspecting various aspects of the board.
Key Aspects of IPC-A-600
-
Visual Acceptance Criteria: IPC-A-600 defines the visual acceptance criteria for various aspects of PCBs, such as conductor width and spacing, solder mask coverage, and hole quality.
-
Defect Classification: The standard classifies defects into three categories: critical, major, and minor, based on their potential impact on the functionality and reliability of the PCB.
-
Inspection Methods: IPC-A-600 describes the inspection methods used to evaluate PCBs, including visual inspection, microscopic inspection, and automated optical inspection (AOI).
Benefits of Adhering to IPC-A-600
Adhering to IPC-A-600 offers several benefits for PCB manufacturers and end-users:
-
Quality Control: By following the visual acceptance criteria in IPC-A-600, manufacturers can identify and address quality issues early in the production process, reducing scrap and rework.
-
Customer Communication: IPC-A-600 provides a common language for communicating PCB Quality requirements between manufacturers and customers, helping to avoid misunderstandings and disputes.
-
Continuous Improvement: By tracking and analyzing defects according to IPC-A-600 classifications, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement in their processes and implement corrective actions.

The Relationship Between IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600
IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 are complementary standards that work together to ensure the quality and reliability of PCBs. While IPC-6012 focuses on the qualification and performance requirements for rigid printed boards, IPC-A-600 provides visual acceptance criteria for evaluating the quality of the finished product.
How IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 Work Together
-
Design and Fabrication: PCB manufacturers use IPC-6012 as a guide for designing and fabricating boards that meet the required performance and reliability criteria.
-
Quality Control: During the production process, manufacturers use IPC-A-600 to visually inspect the boards and identify any defects that may affect their functionality or reliability.
-
Customer Acceptance: When the finished PCBs are delivered to the customer, IPC-A-600 provides a common language for evaluating the quality of the boards and determining whether they meet the agreed-upon acceptance criteria.
The Impact of IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 on the Electronics Industry
The widespread adoption of IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 has had a significant impact on the electronics industry, driving improvements in PCB quality, reliability, and consistency.
Benefits for Manufacturers
-
Improved Processes: By adhering to IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600, manufacturers can optimize their processes, reduce defects, and increase efficiency.
-
Competitive Advantage: Manufacturers who consistently produce high-quality PCBs in accordance with these standards can gain a competitive advantage in the market.
-
Reduced Costs: By catching defects early and reducing scrap and rework, manufacturers can lower their production costs and improve profitability.
Benefits for End-Users
-
Reliable Products: PCBs produced in accordance with IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 are more likely to perform reliably in the field, reducing the risk of product failures and recalls.
-
Consistent Quality: End-users can expect consistent quality across different PCB Suppliers who adhere to these standards, simplifying the sourcing process.
-
Faster Time-to-Market: With a common language for PCB quality and acceptance criteria, end-users can streamline their communication with manufacturers, reducing delays and accelerating time-to-market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the difference between IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600?
IPC-6012 is a standard that establishes the requirements for the qualification and performance of rigid printed boards, while IPC-A-600 provides visual acceptance criteria for evaluating the quality of printed boards. -
Are IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 mandatory standards?
While IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 are not mandatory standards, they are widely adopted in the electronics industry and are often specified by customers as a requirement for PCB suppliers. -
How often are IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 updated?
IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 are periodically reviewed and updated by IPC committees to reflect changes in technology, materials, and industry best practices. The latest revisions of these standards are IPC-6012E and IPC-A-600K, respectively. -
Can manufacturers deviate from IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 requirements?
In some cases, manufacturers may deviate from IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 requirements if the customer approves the deviation and it does not compromise the functionality or reliability of the PCB. -
How can manufacturers demonstrate compliance with IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600?
Manufacturers can demonstrate compliance with IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 by maintaining proper documentation, such as process control plans, inspection records, and test reports. Some manufacturers may also seek third-party certification to these standards to provide additional assurance to their customers.
Conclusion
IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 are essential standards in PCB production that help ensure the quality, reliability, and consistency of rigid printed boards. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can optimize their processes, reduce defects, and gain a competitive advantage in the market. End-users also benefit from reliable products, consistent quality, and faster time-to-market. As technology continues to evolve, IPC-6012 and IPC-A-600 will remain critical tools for driving continuous improvement in the electronics industry.
No responses yet