Introduction to USB Pinout
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a widely used standard for connecting devices to computers and other electronic devices. Understanding the USB pinout is essential for anyone working with USB devices, whether you’re a hobbyist, an engineer, or a technician. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll dive into the details of USB pinouts, covering the different types of USB connectors, their pinouts, and their applications.
What is a USB Pinout?
A USB pinout refers to the arrangement and functionality of the pins in a USB connector. Each pin in a USB connector has a specific purpose, such as carrying power, data, or control signals. The pinout defines how these pins are arranged and what each pin is used for.
Types of USB Connectors
There are several types of USB connectors, each with its own pinout. The most common types of USB connectors include:
- USB Type-A
- USB Type-B
- USB Type-C
- USB Mini-A
- USB Mini-B
- USB Micro-A
- USB Micro-B
USB Type-A Pinout
USB Type-A is the most common type of USB connector, found on computers, laptops, and many other devices. It has a rectangular shape and typically serves as the host connector.
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBUS | +5V Power |
| 2 | D- | Data – |
| 3 | D+ | Data + |
| 4 | GND | Ground |
USB Type-B Pinout
USB Type-B connectors are commonly used on larger devices, such as printers and external hard drives. They have a square shape with slightly beveled corners.
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBUS | +5V Power |
| 2 | D- | Data – |
| 3 | D+ | Data + |
| 4 | GND | Ground |
USB Type-C Pinout
USB Type-C is a newer connector type that is reversible and capable of carrying higher power and data speeds. It is becoming increasingly popular on modern devices.
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | GND | Ground |
| A2 | SSTXp1 | SuperSpeed Transmit Data + |
| A3 | SSTXn1 | SuperSpeed Transmit Data – |
| A4 | VBUS | +5V Power |
| A5 | CC1 | Configuration Channel 1 |
| A6 | Dp1 | USB 2.0 Differential Pair + |
| A7 | Dn1 | USB 2.0 Differential Pair – |
| A8 | SBU1 | Sideband Use 1 |
| A9 | VBUS | +5V Power |
| A10 | SSRXn2 | SuperSpeed Receive Data – |
| A11 | SSRXp2 | SuperSpeed Receive Data + |
| A12 | GND | Ground |
| B1 | GND | Ground |
| B2 | SSTXp2 | SuperSpeed Transmit Data + |
| B3 | SSTXn2 | SuperSpeed Transmit Data – |
| B4 | VBUS | +5V Power |
| B5 | CC2 | Configuration Channel 2 |
| B6 | Dp2 | USB 2.0 Differential Pair + |
| B7 | Dn2 | USB 2.0 Differential Pair – |
| B8 | SBU2 | Sideband Use 2 |
| B9 | VBUS | +5V Power |
| B10 | SSRXn1 | SuperSpeed Receive Data – |
| B11 | SSRXp1 | SuperSpeed Receive Data + |
| B12 | GND | Ground |
USB Mini and Micro Pinouts
USB Mini and Micro connectors are smaller versions of USB connectors, commonly used on portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, and digital cameras.
USB Mini-A Pinout
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBUS | +5V Power |
| 2 | D- | Data – |
| 3 | D+ | Data + |
| 4 | ID | Identification |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
USB Mini-B Pinout
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBUS | +5V Power |
| 2 | D- | Data – |
| 3 | D+ | Data + |
| 4 | ID | Identification |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
USB Micro-A Pinout
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBUS | +5V Power |
| 2 | D- | Data – |
| 3 | D+ | Data + |
| 4 | ID | Identification |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
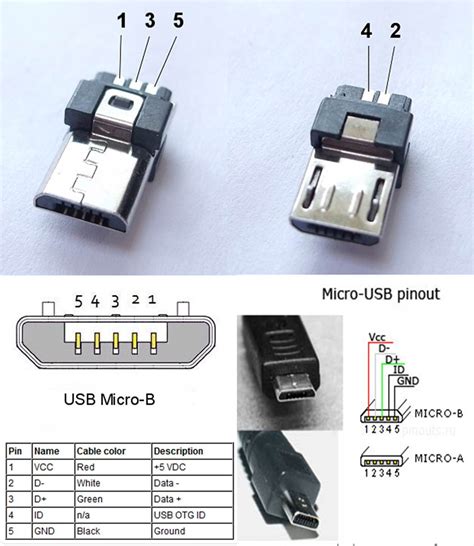
USB Micro-B Pinout
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBUS | +5V Power |
| 2 | D- | Data – |
| 3 | D+ | Data + |
| 4 | ID | Identification |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
USB Pinout Applications
Understanding USB pinouts is crucial for various applications, such as:
Designing USB Devices
When designing USB devices, engineers need to ensure that the pinout of the device’s USB connector matches the pinout of the host device. This involves selecting the appropriate USB connector type and assigning the correct functions to each pin.
Troubleshooting USB Devices
Knowledge of USB pinouts can be invaluable when troubleshooting USB devices. By understanding the purpose of each pin, technicians can identify issues such as short circuits, open circuits, or incorrect wiring.
Building Custom USB Cables
In some cases, you may need to build custom USB cables for specific applications. Understanding the USB pinout allows you to create cables with the correct wiring and ensure proper functionality.

USB Pinout Standards
The USB specification defines several standards for USB pinouts, including:
USB 1.1
USB 1.1 is an older standard that supports data transfer rates up to 12 Mbps. It uses a simplified pinout with four pins: VBUS, D-, D+, and GND.
USB 2.0
USB 2.0 is a widely used standard that supports data transfer rates up to 480 Mbps. It maintains the same basic pinout as USB 1.1 but introduces additional shielding and improved signal integrity.
USB 3.0 and Later
USB 3.0 and later versions (USB 3.1, USB 3.2) introduce higher data transfer rates and additional pins for enhanced functionality. These standards use the USB Type-A, Type-B, and Type-C connectors with expanded pinouts to support the increased speed and power delivery capabilities.
FAQ
-
Q: What is the difference between USB Type-A and Type-B connectors?
A: USB Type-A connectors are typically used on host devices, such as computers and laptops, while Type-B connectors are used on peripheral devices, such as printers and external hard drives. They have different shapes and pinouts to prevent incorrect connections. -
Q: Can I use a USB Type-C device with a USB Type-A port?
A: Yes, you can use a USB Type-C to Type-A adapter or cable to connect a USB Type-C device to a USB Type-A port. However, the connection will be limited to the capabilities of the USB Type-A port, such as lower power delivery and data transfer speeds. -
Q: Are USB Mini and Micro connectors still commonly used?
A: USB Mini and Micro connectors were widely used on portable devices in the past, but they are gradually being phased out in favor of USB Type-C connectors, which offer improved functionality and durability. -
Q: What happens if I connect a USB device with the wrong pinout?
A: Connecting a USB device with the wrong pinout can lead to various issues, such as the device not functioning correctly, damage to the device or host, or even short circuits. It’s essential to ensure that the pinout of the device matches the pinout of the host connector. -
Q: Can I use a USB 3.0 device with a USB 2.0 port?
A: Yes, USB 3.0 devices are backward compatible with USB 2.0 ports. However, the device will operate at the lower USB 2.0 speeds and will not take advantage of the enhanced features of USB 3.0.
Conclusion
Understanding USB pinouts is essential for anyone working with USB devices, whether you’re designing, troubleshooting, or building custom solutions. By familiarizing yourself with the different types of USB connectors, their pinouts, and the associated standards, you’ll be well-equipped to handle a wide range of USB-related tasks.
Remember to always refer to the official USB specifications and documentation when working with USB devices to ensure compatibility and correct functionality. With a solid understanding of USB pinouts, you’ll be able to tackle USB projects with confidence and efficiency.
No responses yet