Introduction to V-cut Profiling
V-cut profiling, also known as V-grooving or V-scoring, is a popular technique used in various industries to create precise, angled cuts or grooves in materials such as paper, cardboard, plastic, and even metal. This method allows for easy folding, bending, or separation of the material along the scored line. V-cut profiling is widely used in packaging, printing, and manufacturing industries to create boxes, folders, displays, and other products that require clean, professional-looking folds.
What is a V-cut?
A V-cut is a type of scoring that involves cutting a V-shaped groove into a material, usually at a 90-degree angle. The depth of the cut determines the ease of folding or separating the material. A deeper cut will make it easier to fold or break along the line, while a shallower cut will result in a more subtle fold or bend.
Advantages of V-cut Profiling
V-cut profiling offers several advantages over other scoring methods:
- Clean, precise folds
- Reduced risk of tearing or damage to the material
- Versatility in creating various fold types and angles
- Increased efficiency in production processes
- Professional-looking finished products
Applications of V-cut Profiling
Packaging Industry
In the packaging industry, V-cut profiling is extensively used to create folding cartons, boxes, and displays. By strategically placing V-cuts, packaging designers can create boxes that are easy to assemble, fold, and store. Some common applications include:
- Product boxes (e.g., food, cosmetics, electronics)
- Gift boxes and specialty packaging
- Point-of-purchase displays
- Mailers and shipping boxes
Printing Industry
V-cut profiling is also widely used in the printing industry to create various printed materials, such as:
- Folders and presentation materials
- Greeting cards and invitations
- Brochures and pamphlets
- Book covers and dust jackets
Other Industries
Besides packaging and printing, V-cut profiling is used in other industries, such as:
- Manufacturing: Creating components for products, such as electronics enclosures or automotive parts
- Construction: Producing architectural elements, such as decorative panels or signage
- Textile: Scoring materials like leather or fabric for folding or shaping
V-cut Profiling Techniques
Manual V-cut Scoring
Manual V-cut scoring involves using hand tools, such as a scoring knife or a V-groove cutter, to create the V-shaped groove in the material. This method is suitable for small-scale projects or prototyping, as it allows for more control and flexibility in the scoring process. However, manual scoring can be time-consuming and may result in inconsistencies in the depth and angle of the cut.
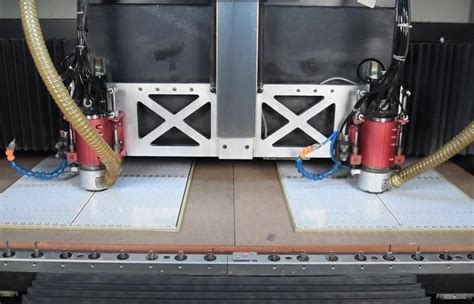
Machine V-cut Scoring
Machine V-cut scoring utilizes specialized equipment to automate the scoring process, ensuring consistent and precise V-cuts. There are several types of machines used for V-cut profiling:
-
Rotary V-cut Machines: These machines use a rotating cutting tool to create the V-groove as the material passes through the machine. They are suitable for high-volume production and can handle a wide range of materials.
-
Laser V-cut Machines: Laser scoring machines use a focused laser beam to create the V-groove in the material. This method is highly precise and can be used on delicate materials without causing damage.
-
Flatbed V-cut Machines: Flatbed machines are designed for scoring large, flat sheets of material. The cutting tool moves across the stationary material to create the V-groove.
Choosing the Right Technique
The choice between manual and machine V-cut scoring depends on several factors, such as:
- Project scale and production volume
- Material type and thickness
- Required precision and consistency
- Budget and available resources
For large-scale production or projects requiring high precision, machine V-cut scoring is often the preferred method. However, for smaller projects or custom work, manual scoring may be more suitable.

V-cut Profiling Tools and Equipment
Manual Scoring Tools
- V-groove Cutting Knife: A specialized knife with a V-shaped blade that allows for precise, angled cuts.
- Scoring Ruler: A metal or plastic ruler with a raised edge that guides the scoring knife and ensures straight, consistent cuts.
- Cutting Mat: A self-healing cutting surface that protects the work area and prolongs the life of the scoring tools.
Machine Scoring Equipment
- Rotary V-cut Machine: As mentioned earlier, this machine uses a rotating cutting tool to create V-grooves in the material.
- Laser V-cut Machine: This machine uses a focused laser beam to score the material, providing high precision and minimal damage.
- Flatbed V-cut Machine: A machine designed for scoring large, flat sheets of material, with the cutting tool moving across the stationary material.
Designing for V-cut Profiling
Factors to Consider
When designing products that will be scored using V-cut profiling, there are several factors to consider:
-
Material properties: The type, thickness, and grain direction of the material will affect the scoring process and the final result.
-
Fold type and placement: The desired fold type (e.g., single fold, double fold, or accordion fold) and the placement of the V-cuts will determine the layout and design of the product.
-
Scoring depth: The depth of the V-cut will affect the ease of folding and the overall appearance of the finished product.
-
Design elements: Any text, images, or other design elements should be placed in a way that accommodates the V-cuts and ensures a clean, professional look after folding.
Software for V-cut Design
There are various software options available for designing products that incorporate V-cut profiling. Some popular choices include:
- Adobe Illustrator: A vector graphics editor that allows for precise layout and design of packaging and print materials.
- ArtiosCAD: A specialized software for structural packaging design that includes tools for creating and visualizing V-cuts.
- AutoCAD: A computer-aided design (CAD) software that can be used for designing products with V-cuts, particularly in the manufacturing and construction industries.
When designing for V-cut profiling, it’s essential to work closely with the production team to ensure that the design is feasible and optimized for the specific scoring method and equipment being used.
Best Practices for V-cut Profiling
To achieve the best results when using V-cut profiling, consider the following best practices:
-
Choose the appropriate scoring method and equipment for your project, taking into account factors such as material type, production volume, and required precision.
-
Ensure proper maintenance and calibration of scoring tools and machines to maintain consistent quality and performance.
-
Test the scoring process on sample materials before starting full-scale production to identify any issues or necessary adjustments.
-
Follow recommended guidelines for scoring depth and placement to achieve the desired folding or bending properties without compromising the integrity of the material.
-
Incorporate V-cut profiling considerations early in the design process to optimize the layout and functionality of the final product.
-
Collaborate closely with production teams and suppliers to ensure smooth communication and efficient workflow throughout the V-cut profiling process.
Common Challenges and Solutions
While V-cut profiling offers many benefits, there are also some common challenges that may arise during the process. Here are a few examples, along with potential solutions:
-
Inconsistent scoring depth: Inconsistencies in scoring depth can result in uneven folding or weak points in the material. To address this issue, ensure that scoring tools and machines are properly calibrated and maintained, and consider using automated equipment for more consistent results.
-
Material tearing or damage: Some materials may be prone to tearing or damage during the scoring process, particularly if the scoring depth is too deep or the material is brittle. To minimize this risk, adjust the scoring depth as needed and consider using alternative scoring methods, such as laser scoring, for delicate materials.
-
Misaligned or shifted V-cuts: Misaligned or shifted V-cuts can result in poor folding or an unprofessional appearance in the finished product. To prevent this issue, use proper alignment guides and tools, such as scoring rulers or registration marks, to ensure precise placement of the V-cuts.
-
Limited design flexibility: V-cut profiling may impose some limitations on the design and layout of the product, particularly in terms of fold placement and orientation. To work around these limitations, consider alternative scoring methods or adjust the design to accommodate the V-cuts more effectively.
By anticipating and addressing these challenges proactively, you can minimize disruptions and ensure a smoother V-cut profiling process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What materials can be scored using V-cut profiling?
V-cut profiling can be used on a wide range of materials, including paper, cardboard, plastic, and even some thin metals. However, the specific scoring method and equipment may vary depending on the material type and thickness. -
How deep should a V-cut be?
The depth of a V-cut depends on the material being scored and the desired folding or bending properties. As a general rule, the scoring depth should be between one-third and one-half of the material thickness. However, it’s essential to test the scoring depth on sample materials to ensure the best results. -
Can V-cut profiling be used for creating perforated lines?
While V-cut profiling is primarily used for creating folding lines, it can also be used to create perforated lines that allow for easy separation of the material. To create a perforated line, a series of closely spaced V-cuts are made along the desired line, allowing the material to be torn or separated easily. -
What is the difference between V-cut profiling and other scoring methods?
V-cut profiling creates a V-shaped groove in the material, which allows for clean, precise folds at various angles. Other scoring methods, such as creasing or die-cutting, may create different types of folding lines or cut completely through the material. The choice of scoring method depends on the specific requirements of the project and the materials being used. -
How can I ensure consistent V-cut profiling results?
To ensure consistent V-cut profiling results, it’s important to use well-maintained and calibrated scoring equipment, follow recommended guidelines for scoring depth and placement, and test the scoring process on sample materials before starting full-scale production. Utilizing automated scoring equipment and collaborating closely with production teams can also help maintain consistency and quality throughout the process.
Conclusion
V-cut profiling is a valuable technique for creating precise, professional-looking folds and bends in a wide range of materials. By understanding the various methods, tools, and best practices associated with V-cut profiling, designers and production professionals can create high-quality products that meet the needs of their clients and customers. Whether you’re working in the packaging, printing, or manufacturing industry, incorporating V-cut profiling into your design and production processes can help elevate the functionality and aesthetics of your products while streamlining your workflow.
As with any production technique, V-cut profiling comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. However, by staying informed about the latest tools, techniques, and best practices, and by collaborating closely with your team and suppliers, you can overcome these challenges and achieve outstanding results. With the right approach and expertise, V-cut profiling can be a powerful tool for bringing your creative vision to life and delivering products that stand out in the market.
No responses yet