Introduction to PCB-Schematic-Sync
In the world of electronic design, ensuring that schematics and printed circuit boards (PCBs) remain synchronized is crucial for the success of any project. The synchronization process, often referred to as PCB-Schematic-Sync, involves maintaining consistency between the logical design represented in the schematic and the physical layout of the PCB. This article delves into the importance of PCB-Schematic-Sync, the challenges associated with it, and the best practices for achieving seamless synchronization.
The Importance of PCB-Schematic-Sync
Ensuring Design Integrity
One of the primary reasons for keeping schematics and PCBs synchronized is to ensure the integrity of the design. When the schematic and PCB are in sync, it means that the logical connections and components represented in the schematic are accurately reflected in the physical layout of the PCB. This is essential for the proper functioning of the electronic device.
Facilitating Collaboration
In many electronic design projects, multiple team members, such as designers, engineers, and manufacturers, collaborate on different aspects of the design. PCB-Schematic-Sync enables seamless collaboration by providing a common reference point for all stakeholders. When the schematic and PCB are synchronized, everyone involved in the project can work with the same updated information, reducing the risk of errors and miscommunications.
Streamlining Design Changes
Electronic designs often undergo iterations and modifications throughout the development process. PCB-Schematic-Sync simplifies the management of design changes. When a change is made to the schematic, it can be easily propagated to the PCB layout, ensuring that the physical implementation reflects the updated logical design. This streamlined approach saves time and effort, as manual updates to the PCB become unnecessary.
Improving Manufacturing Efficiency
A synchronized schematic and PCB are crucial for efficient manufacturing. When the PCB layout accurately represents the schematic, it reduces the likelihood of manufacturing errors and delays. The manufacturing team can rely on the synchronized data to produce the PCB correctly, minimizing the need for rework or modifications during the production process.
Challenges in PCB-Schematic-Sync
Design Complexity
As electronic designs become more complex, maintaining synchronization between schematics and PCBs becomes increasingly challenging. With a large number of components, hierarchical designs, and intricate connectivity, ensuring that every aspect of the schematic is accurately represented in the PCB layout can be a daunting task.
Manual Synchronization
In some cases, designers may resort to manual methods for synchronizing schematics and PCBs. This approach involves manually updating the PCB layout based on changes made to the schematic. Manual synchronization is time-consuming, error-prone, and becomes increasingly difficult as the design complexity grows.
Tool Limitations
While many electronic design automation (EDA) tools offer features for PCB-Schematic-Sync, they may have limitations. Some tools may not provide a seamless bidirectional synchronization, meaning that changes made in the PCB layout may not be automatically reflected in the schematic. Additionally, different tools may have varying levels of automation and efficiency in handling the synchronization process.
Design Rule Violations
During the PCB layout process, designers may encounter design rule violations, such as incorrect component placement or routing issues. These violations can arise due to the physical constraints of the PCB or the specific requirements of the manufacturing process. Resolving these violations while maintaining synchronization with the schematic can be challenging and may require manual intervention.

Best Practices for PCB-Schematic-Sync
Use Automated Synchronization Tools
To streamline the PCB-Schematic-Sync process, it is recommended to use automated synchronization tools provided by EDA software. These tools offer features such as real-time synchronization, bidirectional updates, and automatic change tracking. By leveraging these tools, designers can save time and reduce the risk of errors associated with manual synchronization.
Establish a Clear Workflow
Establishing a clear and well-defined workflow for PCB-Schematic-Sync is essential. This workflow should outline the steps involved in making changes to the schematic, propagating those changes to the PCB layout, and verifying the synchronization. By following a consistent workflow, team members can collaborate effectively and ensure that the design remains synchronized throughout the development process.
Regular Design Reviews
Conducting regular design reviews is crucial for maintaining PCB-Schematic-Sync. These reviews involve comparing the schematic and PCB layout to identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies. Design reviews should be performed at key milestones, such as before finalizing the schematic, after completing the initial PCB layout, and prior to manufacturing. By catching and addressing synchronization issues early, designers can avoid costly rework and delays.
Component and Library Management
Effective component and library management plays a significant role in PCB-Schematic-Sync. Designers should ensure that the component libraries used in the schematic and PCB layout are consistent and up to date. This includes using accurate component footprints, pin assignments, and metadata. By maintaining a centralized and well-organized component library, designers can minimize the risk of mismatches between the schematic and PCB.
Collaborate and Communicate
Collaboration and communication among team members are essential for successful PCB-Schematic-Sync. Designers, engineers, and manufacturers should maintain open lines of communication and share relevant information throughout the design process. This includes discussing design changes, addressing synchronization issues, and providing feedback on the PCB layout. Effective collaboration ensures that everyone is working towards the same goal and helps catch and resolve any discrepancies early on.
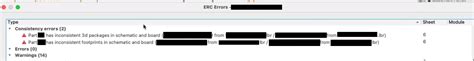
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is PCB-Schematic-Sync?
PCB-Schematic-Sync refers to the process of ensuring that the logical design represented in the schematic is accurately reflected in the physical layout of the printed circuit board (PCB). It involves maintaining consistency and synchronization between the schematic and PCB throughout the electronic design process.
2. Why is PCB-Schematic-Sync important?
PCB-Schematic-Sync is important for several reasons:
– It ensures the integrity of the design by guaranteeing that the PCB layout matches the intended logical connections and components.
– It facilitates collaboration among team members by providing a common reference point.
– It streamlines the management of design changes, allowing modifications made in the schematic to be easily propagated to the PCB layout.
– It improves manufacturing efficiency by reducing the likelihood of errors and delays during the production process.
3. What are some challenges associated with PCB-Schematic-Sync?
Some of the challenges in maintaining PCB-Schematic-Sync include:
– Dealing with complex designs that have a large number of components and intricate connectivity.
– Relying on manual synchronization methods, which can be time-consuming and error-prone.
– Facing limitations in electronic design automation (EDA) tools that may not provide seamless bidirectional synchronization.
– Resolving design rule violations that arise during the PCB layout process while maintaining synchronization with the schematic.
4. What are some best practices for achieving effective PCB-Schematic-Sync?
Best practices for PCB-Schematic-Sync include:
– Using automated synchronization tools provided by EDA software to streamline the process and reduce errors.
– Establishing a clear and well-defined workflow that outlines the steps involved in making changes and verifying synchronization.
– Conducting regular design reviews to identify and address any discrepancies between the schematic and PCB layout.
– Maintaining effective component and library management to ensure consistency between the schematic and PCB.
– Fostering collaboration and communication among team members to catch and resolve synchronization issues early.
5. How can I ensure that my component libraries are consistent for PCB-Schematic-Sync?
To ensure consistency in component libraries for PCB-Schematic-Sync:
– Use a centralized and well-organized component library system.
– Maintain accurate component footprints, pin assignments, and metadata.
– Regularly update and review the component libraries to ensure they are up to date.
– Collaborate with team members to establish standard naming conventions and library management practices.
– Utilize library management features provided by EDA tools to maintain consistency and synchronization between the schematic and PCB.
Conclusion
PCB-Schematic-Sync is a critical aspect of electronic design that ensures the integrity, collaboration, and efficiency of the development process. By keeping the schematic and PCB layout synchronized, designers can avoid errors, streamline design changes, and improve manufacturing outcomes. While challenges such as design complexity and tool limitations exist, adopting best practices such as using automated synchronization tools, establishing clear workflows, conducting regular design reviews, and fostering collaboration can greatly enhance the PCB-Schematic-Sync process. By prioritizing and effectively managing PCB-Schematic-Sync, electronic design teams can deliver high-quality products with confidence.
| PCB-Schematic-Sync Best Practices | Description |
|---|---|
| Automated Synchronization Tools | Use EDA software features for real-time synchronization and bidirectional updates |
| Clear Workflow | Establish a well-defined workflow for making changes and verifying synchronization |
| Regular Design Reviews | Conduct reviews at key milestones to identify and address discrepancies |
| Component and Library Management | Maintain consistent and up-to-date component libraries |
| Collaboration and Communication | Foster open communication among team members to catch and resolve issues early |
By implementing these best practices and addressing the challenges associated with PCB-Schematic-Sync, electronic design teams can streamline their design process, reduce errors, and ultimately deliver high-quality products to market.
No responses yet