What is a 1N4002 Diode?
The 1N4002 is a widely used general-purpose rectifier diode. It is part of the 1N400x series of diodes, which are designed for low-voltage, high-current applications. The 1N4002 is capable of handling a maximum repetitive reverse voltage of 100 volts and an average rectified forward current of 1 amp.
Key Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Repetitive Reverse Voltage | 100 V |
| Maximum RMS Voltage | 70 V |
| Maximum DC Blocking Voltage | 100 V |
| Maximum Average Forward Rectified Current at TA = 75°C | 1.0 A |
| Peak Forward Surge Current 8.3ms Single Half Sine-Wave Superimposed on Rated Load | 30 A |
| Maximum Instantaneous Forward Voltage at 1.0 A | 1.0 V |
| Maximum DC Reverse Current at Rated DC Blocking Voltage TA = 25°C | 5.0 μA |
| Typical Junction Capacitance at 4V, 1MHz | 15 pF |
| Maximum Reverse Recovery Time | 30 ns |
| Operating and Storage Temperature Range | -65 to +175 °C |
How Does a 1N4002 Diode Work?
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction while blocking current in the opposite direction. The 1N4002 is a p-n junction diode, meaning it consists of a p-type semiconductor material and an n-type semiconductor material joined together to form a junction.
When the anode (p-type side) is positively biased relative to the cathode (n-type side), the diode is forward-biased, and current can flow through the device. When the cathode is positively biased relative to the anode, the diode is reverse-biased, and current flow is blocked.
Forward Bias Characteristics
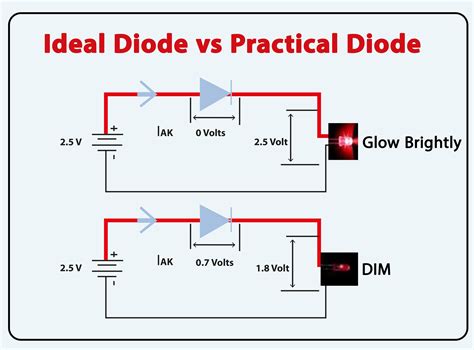
In the forward-biased condition, the diode exhibits a small forward voltage drop, typically around 0.7 volts for silicon diodes like the 1N4002. The forward voltage drop remains relatively constant over a wide range of forward currents.
Reverse Bias Characteristics
When reverse-biased, the 1N4002 can withstand a maximum reverse voltage of 100 volts before breaking down. In the reverse-biased state, a small leakage current, in the microampere range, may flow through the diode.
Applications of the 1N4002 Diode
The 1N4002 diode is used in various electronic circuits for rectification, voltage clamping, and reverse polarity protection.
Rectification
One of the most common applications of the 1N4002 is in rectifier circuits, which convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). In a full-wave rectifier, four 1N4002 diodes are arranged in a bridge configuration to rectify both the positive and negative halves of the AC waveform.
Voltage Clamping
The 1N4002 can be used as a voltage clamping device to limit the voltage across a component or circuit to a specific value. When the voltage exceeds the clamping level, the diode conducts and prevents the voltage from rising further.
Reverse Polarity Protection
In electronic circuits, the 1N4002 can be used to protect sensitive components from damage caused by reverse polarity connections. By placing the diode in series with the power supply, it will only allow current to flow in the correct direction, preventing damage to the connected components.

Choosing the Right Diode
When selecting a diode for a specific application, consider the following factors:
– Maximum reverse voltage: Ensure the diode can withstand the expected reverse voltage in the circuit.
– Forward current rating: Choose a diode with a forward current rating sufficient for the application.
– Recovery time: For high-frequency applications, select a diode with a fast recovery time to minimize losses.
– Package type: Consider the physical size and mounting requirements of the circuit when choosing the diode package (e.g., through-hole, surface-mount).
Proper Handling and Soldering
To ensure the longevity and proper functioning of the 1N4002 diode, follow these handling and soldering guidelines:
– Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection: Diodes are sensitive to ESD. Use appropriate ESD protection measures, such as grounded wrist straps and ESD-safe workstations, when handling the devices.
– Lead bending: When bending the leads of through-hole diodes, use tools designed for lead forming to avoid stressing the diode package.
– Soldering: Use a temperature-controlled soldering iron with a properly sized tip. Apply heat to the lead and pad simultaneously, ensuring the soldering process is completed quickly to avoid overheating the diode.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the difference between the 1N4001 and 1N4002 diodes?
The main difference between the 1N4001 and 1N4002 is their maximum repetitive reverse voltage rating. The 1N4001 is rated for 50 volts, while the 1N4002 is rated for 100 volts. They have the same forward current rating of 1 amp. -
Can I use a 1N4002 diode in place of a 1N4001?
Yes, the 1N4002 can be used as a substitute for the 1N4001 in most applications, as it has a higher reverse voltage rating. However, ensure that the 1N4002’s slightly higher forward voltage drop is acceptable for your circuit. -
Is the 1N4002 diode suitable for high-frequency applications?
The 1N4002 is a general-purpose rectifier diode and is not designed for high-frequency applications. For high-frequency use, choose a diode with a faster recovery time, such as a Schottky diode or a fast-recovery rectifier diode. -
Can I use the 1N4002 for reverse polarity protection in an automotive application?
Yes, the 1N4002 can be used for reverse polarity protection in automotive applications, provided the maximum reverse voltage and forward current ratings are not exceeded. However, for higher-voltage automotive systems, consider using a diode with a higher reverse voltage rating, such as the 1N5400 series. -
How do I test a 1N4002 diode?
To test a 1N4002 diode, use a multimeter in the diode test mode. Connect the positive lead to the anode and the negative lead to the cathode. A functioning diode should show a forward voltage drop of approximately 0.7 volts. When the leads are reversed, the multimeter should display an open circuit or a high resistance value, indicating that the diode is blocking current in the reverse direction.
In conclusion, the 1N4002 is a versatile and widely used general-purpose rectifier diode suitable for various low-voltage, high-current applications. By understanding its characteristics, applications, and proper handling techniques, you can effectively incorporate the 1N4002 into your electronic projects and designs.
No responses yet