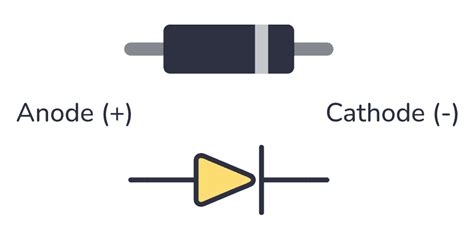
What is a 1N4002 Diode?
A 1N4002 diode is a general-purpose rectifier diode that belongs to the 1N400x series. It is designed to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by allowing current to flow in only one direction while blocking the current in the opposite direction. The 1N4002 diode has a maximum reverse voltage of 100V and a maximum forward current of 1A, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Key Specifications of the 1N4002 Diode
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Repetitive Peak Reverse Voltage (VRRM) | 100V |
| Maximum RMS Voltage (VRMS) | 70V |
| Maximum DC Blocking Voltage (VDC) | 100V |
| Maximum Average Forward Rectified Current (IF(AV)) | 1A |
| Peak Forward Surge Current (IFSM) | 30A |
| Maximum Instantaneous Forward Voltage Drop (VF) | 1.1V |
| Maximum Reverse Current (IR) | 5μA |
| Operating Junction Temperature Range (TJ) | -65°C to +175°C |
Reverse Voltage and Leakage Current
The 1N4002 diode has a maximum reverse voltage (VRRM) of 100V, which means it can withstand a reverse voltage of up to 100V without breaking down. When the reverse voltage exceeds this limit, the diode may experience reverse breakdown, leading to a high reverse current flow and potentially damaging the device.
The leakage current, or reverse current (IR), is the small amount of current that flows through the diode when it is reverse-biased. For the 1N4002 diode, the maximum reverse current is specified as 5μA at a reverse voltage of 100V and a temperature of 25°C.
Forward Voltage Drop and Current
When the 1N4002 diode is forward-biased, it allows current to flow through it. The forward voltage drop (VF) is the voltage across the diode when it is conducting. For the 1N4002, the maximum instantaneous forward voltage drop is 1.1V at a forward current of 1A and a temperature of 25°C.
The maximum average forward rectified current (IF(AV)) for the 1N4002 diode is 1A. This value represents the maximum current that the diode can continuously conduct without experiencing damage or a significant reduction in its lifespan.
Surge Current Capability
The peak forward surge current (IFSM) is the maximum current that the 1N4002 diode can handle for a short duration without suffering damage. This parameter is important when considering the diode’s ability to withstand transient current spikes. The 1N4002 has a peak forward surge current of 30A for a single half-cycle sine wave pulse of 60Hz with a duration of 8.3ms.
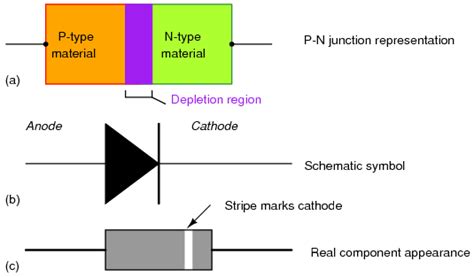
Applications of the 1N4002 Diode
The 1N4002 diode finds its use in various electronic applications, including:
-
Power Supply Rectification: The 1N4002 diode is commonly used in power supply circuits to convert AC to DC. It is often employed in bridge rectifier configurations to achieve full-wave rectification.
-
Reverse Polarity Protection: The diode can be used to protect sensitive electronic components from damage caused by accidental reverse polarity connections. By placing the 1N4002 diode in series with the power supply, it prevents current flow in the reverse direction.
-
Voltage Clamping: The 1N4002 diode can be used as a voltage clamp to limit the maximum voltage across a component or circuit. When the voltage exceeds the diode’s forward voltage drop, the diode conducts and clamps the voltage to a safe level.
-
surge protection: The 1N4002 diode’s high peak forward surge current capability makes it suitable for protecting circuits against voltage spikes and transient surges. It can be used in conjunction with other components, such as varistors or gas discharge tubes, to create robust surge protection systems.
-
Flyback Diodes: In inductive load switching applications, such as relay or solenoid control circuits, the 1N4002 diode can be used as a flyback diode. It is connected across the inductive load to provide a path for the current to dissipate when the switch is turned off, preventing voltage spikes that could damage the switching device.

Choosing the Right Diode for Your Application
When selecting a diode for your specific application, consider the following factors:
-
Voltage Rating: Ensure that the diode’s maximum reverse voltage (VRRM) is higher than the maximum voltage expected in your circuit to prevent reverse breakdown.
-
Current Rating: Choose a diode with a forward current rating (IF(AV)) that exceeds the maximum current expected in your application. Consider both continuous and surge current requirements.
-
Power Dissipation: Determine the maximum power dissipation of the diode based on its forward voltage drop and current. Ensure that the diode can handle the expected power dissipation without overheating.
-
Reverse Recovery Time: If your application involves high-frequency switching, consider the diode’s reverse recovery time. Faster diodes with shorter reverse recovery times are preferred for high-speed switching applications.
-
Package and Mounting: Select a diode package that is compatible with your circuit layout and mounting requirements. Common packages for the 1N4002 diode include DO-41, SMA, and SMB.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Can I use a 1N4002 diode for high-frequency rectification?
While the 1N4002 diode can be used for rectification, it may not be the best choice for high-frequency applications. Its reverse recovery time is relatively slow compared to fast-switching diodes like Schottky diodes. For high-frequency rectification, consider using diodes specifically designed for fast switching, such as the 1N5817 or 1N5819. -
Is the 1N4002 diode suitable for high-voltage applications?
The 1N4002 diode has a maximum reverse voltage rating of 100V. If your application involves voltages higher than 100V, you should consider using diodes with higher voltage ratings, such as the 1N4003 (200V), 1N4004 (400V), or 1N4007 (1000V), depending on your specific voltage requirements. -
Can I parallel multiple 1N4002 diodes to increase the current capacity?
While it is possible to parallel multiple 1N4002 diodes to increase the current handling capacity, it is not always recommended. Diodes have slightly different forward voltage drops, which can lead to uneven current sharing among the paralleled diodes. This can result in one diode conducting more current than the others, potentially leading to overheating and failure. If higher current capacity is required, it is advisable to use a single diode with a higher current rating. -
How do I protect the 1N4002 diode from voltage spikes?
To protect the 1N4002 diode from voltage spikes, you can use additional components such as varistors, gas discharge tubes, or transient voltage suppression (TVS) diodes. These components are designed to clamp voltage spikes to a safe level, preventing damage to the diode and other sensitive components in the circuit. -
Can I use the 1N4002 diode for temperature sensing applications?
While diodes can be used for temperature sensing due to their forward voltage drop’s temperature dependency, the 1N4002 diode is not specifically designed for this purpose. Its relatively high forward voltage drop and low sensitivity to temperature changes make it less suitable for precise temperature sensing. For temperature sensing applications, it is recommended to use dedicated Temperature Sensor diodes or thermistors that are optimized for accuracy and linearity.
Conclusion
The 1N4002 diode is a versatile and widely used rectifier diode that finds its place in numerous electronic applications. Its robust specifications, including a 100V reverse voltage rating and a 1A forward current rating, make it suitable for general-purpose rectification, reverse polarity protection, voltage clamping, surge protection, and flyback diode applications.
When selecting a diode for your project, consider factors such as voltage and current ratings, power dissipation, reverse recovery time, and package compatibility. By understanding the characteristics and limitations of the 1N4002 diode, you can effectively integrate it into your designs and ensure the proper functioning and reliability of your electronic circuits.
Remember to refer to the manufacturer’s datasheets for detailed specifications and application notes specific to the 1N4002 diode variant you are using. Additionally, always adhere to good design practices, such as providing adequate heat dissipation, using appropriate PCB layout techniques, and considering the impact of environmental factors on diode performance.
By leveraging the knowledge gained from this comprehensive guide, you can confidently employ the 1N4002 diode in your projects and harness its capabilities to achieve reliable and efficient electronic designs.
No responses yet