Introduction to HDI Materials
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) materials are essential components in the manufacturing of advanced electronic devices. These materials enable the creation of compact, high-performance printed circuit boards (PCBs) that are crucial for modern electronics. In this article, we will explore 11 essential HDI materials that you need to know to understand the world of advanced PCB manufacturing.
1. Copper Foil
Copper foil is the foundation of HDI PCBs. It is a thin layer of copper that is laminated onto the surface of the dielectric material. The copper foil is then etched to create the desired circuit pattern. There are two main types of copper foil used in HDI PCBs:
Electrodeposited (ED) Copper Foil
ED copper foil is created by electroplating copper onto a rotating drum. This process results in a smooth, uniform surface that is ideal for fine-line etching. ED copper foil is available in various thicknesses, typically ranging from 9 to 70 microns.
Rolled Annealed (RA) Copper Foil
RA copper foil is produced by rolling and annealing copper sheets. This process creates a matte surface on one side and a shiny surface on the other. RA copper foil is generally thicker than ED copper foil, with thicknesses ranging from 35 to 400 microns.
| Copper Foil Type | Thickness Range | Surface Finish |
|---|---|---|
| ED Copper Foil | 9-70 microns | Smooth |
| RA Copper Foil | 35-400 microns | Matte/Shiny |
2. Dielectric Materials
Dielectric materials are the insulating layers that separate the conductive copper layers in an HDI PCB. They play a crucial role in determining the electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties of the PCB. Some common dielectric materials used in HDI PCBs include:
FR-4
FR-4 is a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate that is widely used in PCB manufacturing. It offers good electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and thermal stability. FR-4 is suitable for most HDI applications, but its relatively high dielectric constant (Dk) and dissipation factor (Df) can limit its use in high-frequency applications.
Polyimide
Polyimide is a high-performance polymer that offers excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. It has a lower Dk and Df compared to FR-4, making it suitable for high-frequency applications. However, polyimide is more expensive and challenging to process than FR-4.
PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer known for its low Dk, low Df, and high thermal stability. It is an ideal material for high-frequency and microwave applications. However, PTFE is expensive and difficult to process, limiting its use to specialized applications.
| Dielectric Material | Dielectric Constant (Dk) | Dissipation Factor (Df) | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | 4.2-4.6 | 0.02-0.03 | Good all-around performance |
| Polyimide | 3.2-3.6 | 0.002-0.008 | High thermal stability and low loss |
| PTFE | 2.0-2.3 | 0.0002-0.0009 | Lowest loss, suitable for high-frequency |

3. Solder Mask
Solder mask is a protective coating applied to the surface of the PCB to prevent solder bridging and protect the copper traces from oxidation and damage. In HDI PCBs, solder mask plays a critical role in ensuring the reliability and functionality of the board. There are two main types of solder mask used in HDI PCBs:
Liquid Photoimageable Solder Mask (LPISM)
LPISM is a photosensitive liquid solder mask that is applied to the PCB surface and then exposed and developed to create the desired pattern. LPISM offers high resolution, excellent adhesion, and good resistance to chemicals and heat.
Dry Film Solder Mask (DFSM)
DFSM is a solid photosensitive film that is laminated onto the PCB surface and then exposed and developed to create the desired pattern. DFSM offers good resolution, ease of processing, and excellent resistance to chemicals and heat.

4. Surface Finish
The surface finish is the final layer applied to the exposed copper traces and pads on the PCB. It serves to protect the copper from oxidation, enhance solderability, and improve the electrical and mechanical properties of the board. Some common surface finishes used in HDI PCBs include:
Immersion Gold (ENIG)
Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG) is a two-layer surface finish consisting of a thin layer of gold over a nickel barrier layer. ENIG offers excellent solderability, good shelf life, and compatibility with a wide range of soldering processes.
Immersion Silver (IAg)
Immersion Silver (IAg) is a single-layer surface finish that consists of a thin layer of silver deposited directly onto the copper surface. IAg offers good solderability, low cost, and compatibility with aluminum wire bonding.
Organic Solderability Preservative (OSP)
OSP is a thin, transparent organic coating applied to the copper surface to protect it from oxidation. OSP offers good solderability, low cost, and ease of processing. However, it has a limited shelf life and may not be suitable for all applications.
| Surface Finish | Composition | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| ENIG | Au/Ni | Excellent solderability, good shelf life |
| IAg | Ag | Good solderability, low cost, Al wire bonding |
| OSP | Organic coating | Good solderability, low cost, limited shelf life |
5. Bonding Materials
Bonding materials are used to join the various layers of an HDI PCB together. They play a critical role in ensuring the mechanical and thermal stability of the board. Some common bonding materials used in HDI PCBs include:
Prepreg
Prepreg is a partially cured glass-reinforced epoxy material that is used to bond the copper foil to the dielectric material. It is available in various thicknesses and glass styles to suit different applications.
Adhesive
Adhesive is a non-reinforced bonding material that is used to join the various layers of the PCB together. It is available in various formulations to suit different processing requirements and performance needs.
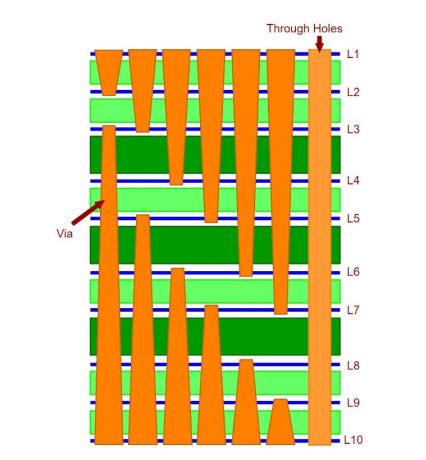
6. Via Fill Materials
Via fill materials are used to fill the plated through-holes (PTHs) and blind vias in an HDI PCB. They serve to improve the mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical performance of the board. Some common via fill materials used in HDI PCBs include:
Conductive Paste
Conductive paste is a metal-filled epoxy material that is used to fill the vias and provide electrical conductivity. It is available in various formulations to suit different processing requirements and performance needs.
Non-Conductive Paste
Non-conductive paste is an epoxy material that is used to fill the vias and provide mechanical support. It is available in various formulations to suit different processing requirements and performance needs.
7. Silk Screen
Silk screen is a printable ink that is used to add text, logos, and other markings to the surface of the PCB. It serves to identify components, provide assembly instructions, and improve the aesthetics of the board. Silk screen ink is available in various colors and formulations to suit different application requirements.
8. Flexible Circuit Materials
Flexible circuit materials are used to create flexible and bendable PCBs that can conform to various shapes and sizes. They are commonly used in wearable electronics, medical devices, and aerospace applications. Some common flexible circuit materials used in HDI PCBs include:
Polyimide Film
Polyimide film is a high-performance polymer film that is used as the base material for flexible circuits. It offers excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength.
Coverlay
Coverlay is a protective coating that is applied to the surface of the flexible circuit to protect the copper traces and provide electrical insulation. It is available in various thicknesses and materials to suit different application requirements.
9. Thermal Management Materials
Thermal management materials are used to dissipate heat generated by electronic components and ensure the reliable operation of the HDI PCB. They play a critical role in preventing thermal damage and improving the overall performance of the board. Some common thermal management materials used in HDI PCBs include:
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
TIMs are materials that are used to enhance the thermal conductivity between the electronic components and the heat sink. They are available in various forms, such as thermal pads, thermal pastes, and thermal adhesives.
Metal Core PCBs (MCPCBs)
MCPCBs are PCBs that have a metal core, typically aluminum, that serves as a heat spreader. They offer excellent thermal conductivity and can efficiently dissipate heat away from the electronic components.
10. Embedded Components
Embedded components are electronic components that are embedded within the layers of the HDI PCB. They offer several advantages, such as reduced board size, improved electrical performance, and enhanced reliability. Some common embedded components used in HDI PCBs include:
Embedded Capacitors
Embedded capacitors are thin, planar capacitors that are embedded within the layers of the PCB. They offer high capacitance density, low parasitic inductance, and excellent high-frequency performance.
Embedded Resistors
Embedded resistors are thin, planar resistors that are embedded within the layers of the PCB. They offer precise resistance values, low parasitic inductance, and excellent high-frequency performance.
11. 3D Printing Materials
3D printing materials are used to create three-dimensional structures and components on the surface of the HDI PCB. They offer several advantages, such as reduced board size, enhanced functionality, and improved design flexibility. Some common 3D printing materials used in HDI PCBs include:
Conductive Ink
Conductive ink is a metal-filled ink that is used to print conductive traces and components on the surface of the PCB. It offers good electrical conductivity, excellent adhesion, and compatibility with various printing processes.
Dielectric Ink
Dielectric ink is a non-conductive ink that is used to print insulating layers and structures on the surface of the PCB. It offers good electrical insulation, excellent adhesion, and compatibility with various printing processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the difference between ED and RA copper foil?
-
ED copper foil is created by electroplating copper onto a rotating drum, resulting in a smooth, uniform surface that is ideal for fine-line etching. RA copper foil is produced by rolling and annealing copper sheets, creating a matte surface on one side and a shiny surface on the other. ED copper foil is typically thinner than RA copper foil.
-
What are the advantages of using polyimide as a dielectric material?
-
Polyimide offers excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. It has a lower dielectric constant (Dk) and dissipation factor (Df) compared to FR-4, making it suitable for high-frequency applications.
-
What is the purpose of solder mask in HDI PCBs?
-
Solder mask is a protective coating applied to the surface of the PCB to prevent solder bridging and protect the copper traces from oxidation and damage. It plays a critical role in ensuring the reliability and functionality of the board.
-
What are the benefits of using embedded components in HDI PCBs?
-
Embedded components offer several advantages, such as reduced board size, improved electrical performance, and enhanced reliability. They can help to minimize parasitic inductance and improve high-frequency performance.
-
How can 3D printing materials be used in HDI PCBs?
- 3D printing materials can be used to create three-dimensional structures and components on the surface of the HDI PCB. Conductive ink can be used to print conductive traces and components, while dielectric ink can be used to print insulating layers and structures. 3D printing offers reduced board size, enhanced functionality, and improved design flexibility.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HDI materials play a crucial role in the manufacturing of advanced electronic devices. From copper foil and dielectric materials to solder mask and surface finishes, each material serves a specific purpose in ensuring the reliability, functionality, and performance of the HDI PCB. As technology continues to evolve, new materials and processes are being developed to meet the ever-increasing demands of the electronics industry. By understanding the properties and applications of these 11 essential HDI materials, designers and manufacturers can create innovative and high-performance electronic products that push the boundaries of what is possible.
No responses yet